
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Molal boiling-point-elevation constant (Kp) for pure water is
0.51°C/ m. A dilute solution of a nonvolatile solute (does not
dissociate) in water was found to boil at 105.1 °C. The
concentration of the nonvolatile solute in the solution is
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
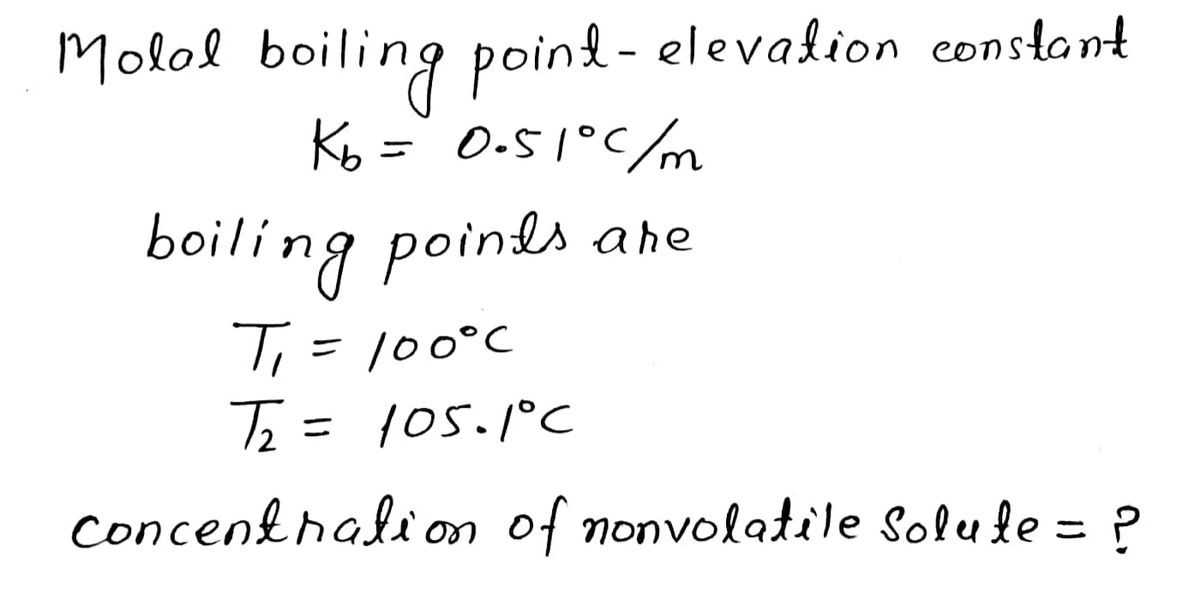
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Sulfuric acid in water dissociates completely into H+ and HSO4 - ions. The HSO4 - ion dissociates to a limited extent into H+ and SO4 2 - . The freezing point of a 0.1000 m solution of sulfuric acid in water is 272.76 K. Calculate the molality of SO4 2 - in the solution, assuming ideal solution behavior.arrow_forwardCalculate the freezing point of 1.25 m sucrose dissolved in formic acid. The Kf of formic acid is 2.76 °C m-1 and its freezing point is 8.40 °C.arrow_forwardThe solubility of Ne in water at 25 °C is 2.1 × 10⁻⁴ M when the partial pressure of Ne is 0.20 atm. What is the value of the Henry's law constant for Ne?arrow_forward
- 8.71ml of a 4.00M HIO3(aq) solution is added to an ice-water mixture, and the freezing points were collected before and after addition of HIO3(aq). Once the temperature was stable after addition, the ice was separated from the solution and the mass of the beaker with solution was measured. The data below was recorded. Calculate the van't Hoff factor for HIO3. The freezing point depression constant for water is 1.86°C/m. Mass of beaker (g)l|Mass of beaker + solution (g T°f (°C)||Tf (°C) 87.438 176.179 0.305 ||-0.796arrow_forwardThe normal boiling point of a certain liquid X is 121.00 °C, but when 0.12 kg of benzamide (C,H,NO) are dissolved in 800. g of X the solution boils at 122.9 °C instead. Use this information to calculate the molal boiling point elevation constant K, of X. Be sure your answer is rounded to the correct number of significiant digits. °C· kg x10 K, = || molarrow_forwardWhen 4.59 g of a certain molecular compound X are dissolved in 35. g of dibenzyl ether ((C%H,CH,),°). the freezing point of the solution is measured to be 0.9 °C. Calculate the molar mass of X. If you need any additional information on dibenzyl ether, use only what you find in the ALEKS Data resource. Also, be sure your answer has a unit symbol, and is rounded to 1 significant digit. 0 00 0.0 X x10arrow_forward
- When 1.38 g of a certain molecular compound X are dissolved in 90.0 g of cyclohexane (C,H,,), the freezing point of the solution is measured to be 6.3 °C. Calculate the molar mass of X. If you need any additional information on cyclohexane, use only what you find in the ALEKS Data resource. Also, be sure your answer has a unit symbol, and is rounded to the correct number of significant digits. x10arrow_forwardThe molal boiling point elevation constant K = 1.15 °C-kg-mol for a certain substance X. When 14.4 g of urea the solution boils at 145.4 °C. Calculate the boiling point of pure X. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. °C X a ((NH,), CO) S are dissolved in 150. g of X,arrow_forwardThe organic compounds chloroform and dichloromethane form ideal solutions when mixed together; at 25 �C the total vapor pressure from a mixture of these two compounds was 345.322 torr. What is the mole fraction of chloroform? Given that the vapor pressure of pure chloroform and pure dichloromethane are 205 torr and 415 torr, respectively, at 25�C. 0.6682 0.4430 0.3318 0.5570arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY