
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
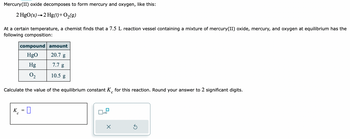
Transcribed Image Text:Mercury(II) oxide decomposes to form mercury and oxygen, like this:
2 HgO(s) 2 Hg(1) + O₂(g)
At a certain temperature, a chemist finds that a 7.5 L reaction vessel containing a mixture of mercury(II) oxide, mercury, and oxygen at equilibrium has the
following composition:
K
compound amount
HgO
20.7 g
7.7 g
10.5 g
Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant K for this reaction. Round your answer to 2 significant digits.
с
с
Hg
0₂
0
x10
X
S
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Iron(III) oxide and hydrogen react to form iron and water, like this: Fe,O3(s)+3 H2(9)–→2 Fe(s)+3 H,O(g) At a certain temperature, a chemist finds that a 4.5 L reaction vessel containing a mixture of iron(III) oxide, hydrogen, iron, and water at equilibrium has the following composition: compound amount Fe,O3 3.54 g H2 3.20 g Fe 4.49 g H,O 1.06 g Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant K_ for this reaction. Round your answer to 2 significant digits.arrow_forwardMercury(II) oxide decomposes to form mercury and oxygen, like this: 2 HgO(s)→2 Hg(1)+O2(g) At a certain temperature, a chemist finds that a 3.3 L reaction vessel containing a mixture of mercury(II) oxide, mercury, and oxygen at equilibrium has the following composition: compound amount HgO 19.5 g Hg 14.6 g O2 0, 17.4 g Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant K, for this reaction. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. K_ = 0 x10arrow_forwardOne of the steps in the production of sulfuric acid involves the catalytic oxidation of sulfur dioxide. 2 SO2 (g) + O2 (g) → 2 SO3 (g) What is the equilibrium expression?arrow_forward
- Write the equilibrium constant expression. Solid carbon and carbon dioxide gas react and form carbon monoxide: C(s) + CO₂(g) = 2CO(g)arrow_forwardIron and water react to form iron(III) oxide and hydrogen, like this: 2 Fe(s)+3 H,0(g)→ Fe,O3(s)+3 H,(g) At a certain temperature, a chemist finds that a 9.2 L reaction vessel containing a mixture of iron, water, iron(III) oxide, and hydrogen at equilibrium has the following composition: compound amount ol. Fe 4.85 g Ar H,O 1.44 g Fe,O3 2.98 g H2 2.51 g Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant K, for this reaction. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. K_ = 0 Ox10 Explanation Check © 2022 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibilityarrow_forward4 Titanium(IV) chloride decomposes to form titanium and chlorine, like this: Ticl,()-Ti(s)+2 Cl,(9) At a certain temperature, a chemist finds that a 7.7 L reaction vessel containing a mixture of titanium(IV) chloride, titanium, and chlorine at equilibrium has the following composition: compound amount TiCl, 4.90 g Ti 1.24 g Cl, 2.16 g Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant K, for this reaction. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. K = 0 Submit Assignment Continue O 2022 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center Accessibility Finder F12 F11 F9 F10 F8 F7 F5 F6 .arrow_forward
- Mercury and oxygen react to form mercury(II) oxide, like this: 2 Hg(1)+O2(g)–→2 HgO(s) At a certain temperature, a chemist finds that a 6.3 L reaction vessel containing a mixture of mercury, oxygen, and mercury(II) oxide at equilibrium has the following composition: compound amount Hg 5.8 g O2 22.5 g HgO 18.9 g Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant K, for this reaction. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. K_ = 0arrow_forwardMercury and oxygen react to form mercury(II) oxide, like this: 2 Hg(1)+O2(g)→2 HgO(5) At a certain temperature, a chemist finds that a 3.6 L reaction vessel containing a mixture of mercury, oxygen, and mercury(II) oxide at equilibrium has the following composition: compound amount Hg 9.7 g O2 21.8 g HgO 10.2 g Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant K̟ for this reaction. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. K_ = 0arrow_forwardCarbon disulfide and chlorine react according to the following equation: CS2(g) + 3Ch(g) =S,Cl½(g) + CC1,(g) When 1.14 mol of CS, and 4.80 mol of Clh are placed in a 2.00-L container and allowed to come to equilibrium, the mixture is found to contain 0.650 mol of CC14. How many moles of Cl are present at on equilibrium? Select one: O a. 0.490 mol O b. 2.85 mol O c. 3.50 mol O d. 0.650 mol O e. 1.43 mol e to search F3 F4 F5 F6 FZ FB F9 F10 F11 F12 Prise %24 E R T G H K B N M 立arrow_forward
- Mercury and oxygen react to form mercury(II) oxide, like this: 2 Hg(1)+O2(9)→2 HgO(s) At a certain temperature, a chemist finds that a 10. L reaction vessel containing a mixture of mercury, oxygen, and mercury(II) oxide at equilibrium has the following composition: compound amount Hg 12.7 g O2 13.4 g HgO 15.5 g Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant K for this reaction. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. K = | Submit Assignm Continue O 2022 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center| Access 43.203 FEB 19 MacBook Airarrow_forwardplease see attached imagearrow_forwardIron and water react to form iron(III) oxide and hydrogen, like this: 2 Fe(s) + 3 H₂O(g) → Fe₂O3(s)+ 3 H₂(g) At a certain temperature, a chemist finds that a 2.5 L reaction vessel containing a mixture of iron, water, iron(III) oxide, and hydrogen at equilibrium has the following composition: compound Fe H₂O Fe₂O3 H₂ amount 4.04 g 2.87 g 3.49 g 2.08 g Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant K for this reaction. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. C K = 0 C Dx1 x10 X Śarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY