
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Mead Incorporated began operations in Year 1. Following is a series of transactions and events involving its long-term debt investments in available-for-sale securities.
Year 1
| January 20 | Purchased Johnson & Johnson bonds for $28,500. |
|---|---|
| February 9 | Purchased Sony notes for $62,640. |
| June 12 | Purchased Mattel bonds for $48,500. |
| December 31 | Fair values for debt in the portfolio are Johnson & Johnson, $31,100; Sony, $53,150; and Mattel, $56,950. |
Year 2
| April 15 | Sold all of the Johnson & Johnson bonds for $31,500. |
|---|---|
| July 5 | Sold all of the Mattel bonds for $41,450. |
| July 22 | Purchased Sara Lee notes for $19,900. |
| August 19 | Purchased Kodak bonds for $20,900. |
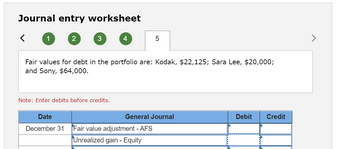
| December 31 | Fair values for debt in the portfolio are Kodak, $22,125; Sara Lee, $20,000; and Sony, $64,000. |
Year 3
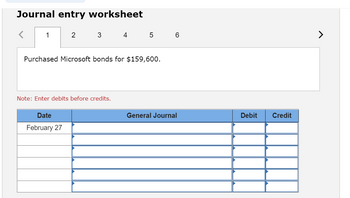
| February 27 | Purchased Microsoft bonds for $159,600. |
|---|---|
| June 21 | Sold all of the Sony notes for $64,000. |
| June 30 | Purchased Black & Decker bonds for $58,400. |
| August 3 | Sold all of the Sara Lee notes for $16,950. |
| November 1 | Sold all of the Kodak bonds for $25,675. |
| December 31 | Fair values for debt in the portfolio are Black & Decker, $59,400; and Microsoft, $160,200. |
Problem 15-2A (Algo) Part 1
Required:
1. Prepare
Transcribed Image Text:**Journal Entry Worksheet**
**Fair values for debt in the portfolio are:**
- Kodak: $22,125
- Sara Lee: $20,000
- Sony: $64,000
**Note:** Enter debits before credits.
| Date | General Journal | Debit | Credit |
|----------------|------------------------------|-------|--------|
| December 31 | Fair value adjustment - AFS | | |
| | Unrealized gain - Equity | | |
This worksheet provides a structure for calculating and recording adjustments in fair value for available-for-sale (AFS) securities in a portfolio. It includes fields indicating the fair value of securities and guidelines for entering debits and credits to reflect unrealized gains in equity.
Transcribed Image Text:**Journal Entry Worksheet**
_Tab 1 of 6_
**Entry Prompt:**
Purchased Microsoft bonds for $159,600.
*Note: Enter debits before credits.*
**Table Structure:**
- **Date:** February 27
- **General Journal:** (Rows for multiple entries)
- **Debit:** (Corresponding debit values)
- **Credit:** (Corresponding credit values)
_Explanation:_
This worksheet allows users to record journal entries for financial transactions. In this case, the transaction involves the purchase of Microsoft bonds. The table is structured to record the date of the transaction, the accounts affected (entered in the General Journal section), and the respective debit and credit amounts. The note emphasizes the importance of entering debits before credits to maintain proper accounting standards.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 6 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
Year 2 and 3 for Fair Value at the end of the year are still incorrect and I do not understand why?
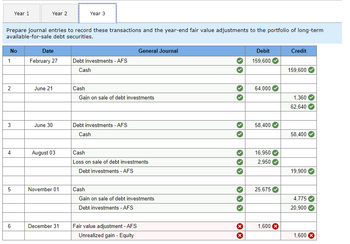
Transcribed Image Text:No
1
Prepare journal entries to record these transactions and the year-end fair value adjustments to the portfolio of long-term
available-for-sale debt securities.
2
3
4
Year 1
5
6
Year 2
Date
February 27
June 21
June 30
August 03
November 01
Year 3
December 31
Debt investments - AFS
Cash
Cash
Gain on sale of debt investments
Debt investments - AFS
Cash
General Journal
Cash
Loss on sale of debt investments
Debt investments - AFS
Cash
Gain on sale of debt investments
Debt investments - AFS
Fair value adjustment - AFS
Unrealized gain - Equity
X
Debit
159,600
64,000
58,400
16,950
2,950
25,675
1,600
Credit
159,600
1,360
62,640
58,400
19,900
4,775
20,900
1,600 X
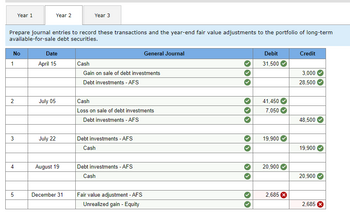
Transcribed Image Text:No
1
Prepare journal entries to record these transactions and the year-end fair value adjustments to the portfolio of long-term
available-for-sale debt securities.
2
3
Year 1
4
5
Year 2
Date
April 15
July 05
July 22
August 19
Year 3
December 31
Cash
Gain on sale of debt investments
Debt investments - AFS
Cash
Loss on sale of debt investments
Debt investments - AFS
Debt investments - AFS
Cash
General Journal
Debt investments - AFS
Cash
Fair value adjustment - AFS
Unrealized gain - Equity
Debit
31,500
41,450
7,050
19,900
20,900
2,685
Credit
3,000
28,500
48,500
19,900
20,900
2,685
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
Year 2 and 3 for Fair Value at the end of the year are still incorrect and I do not understand why?

Transcribed Image Text:No
1
Prepare journal entries to record these transactions and the year-end fair value adjustments to the portfolio of long-term
available-for-sale debt securities.
2
3
4
Year 1
5
6
Year 2
Date
February 27
June 21
June 30
August 03
November 01
Year 3
December 31
Debt investments - AFS
Cash
Cash
Gain on sale of debt investments
Debt investments - AFS
Cash
General Journal
Cash
Loss on sale of debt investments
Debt investments - AFS
Cash
Gain on sale of debt investments
Debt investments - AFS
Fair value adjustment - AFS
Unrealized gain - Equity
X
Debit
159,600
64,000
58,400
16,950
2,950
25,675
1,600
Credit
159,600
1,360
62,640
58,400
19,900
4,775
20,900
1,600 X

Transcribed Image Text:No
1
Prepare journal entries to record these transactions and the year-end fair value adjustments to the portfolio of long-term
available-for-sale debt securities.
2
3
Year 1
4
5
Year 2
Date
April 15
July 05
July 22
August 19
Year 3
December 31
Cash
Gain on sale of debt investments
Debt investments - AFS
Cash
Loss on sale of debt investments
Debt investments - AFS
Debt investments - AFS
Cash
General Journal
Debt investments - AFS
Cash
Fair value adjustment - AFS
Unrealized gain - Equity
Debit
31,500
41,450
7,050
19,900
20,900
2,685
Credit
3,000
28,500
48,500
19,900
20,900
2,685
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Prepare Natura Company's journal entries to record the following transactions involving its short-term investments in held-to-maturity debt securities, all of which occurred during the current year. a. On June 15, paid $180,000 cash to purchase Remed's 90-day short-term debt securities ($180,000 principal), dated June 15, that pay 7% interest. b. On September 16, received a check from Remed in payment of the principal and 90 days' interest on the debt securities purchased in transaction a. Note: Use 360 days in a year. Do not round your intermediate calculations. View transaction list Journal entry worksheet < 1 2 On June 15, paid $180,000 cash to purchase Remed's 90-day short-term debt securities ($180,000 principal), dated June 15, that pay 7% interest. Note: Enter debits before credits. Transaction a. Record entry General Journal Clear entry Debit Credit View general journalarrow_forwardOn January 1, Year 1, Hanover Corporation issued bonds with a $39,000 face value, a stated rate of interest of 8%, and a 5-year term to maturity. The bonds were issued at 97. Hanover uses the straight-line method to amortize bond discounts and premiums. Interest is payable in cash on December 31 each year. How much interest expense will Hanover report on its income statement on December 31, Year 1? Multiple Choice O O O O $234 $1,170 $3.354 $3,120arrow_forwardDoyle Company issued $362,000 of 10-year, 5 percent bonds on January 1, Year 1. The bonds were issued at face value. Interest is payable in cash on December 31 of each year. Doyle immediately invested the proceeds from the bond issue in land. The land was leased for an annual $52, 500 of cash revenue, which was collected on December 31 of each year, beginning December 31, Year 1. Journal entry worksheet Note: Enter debits before credits. 4 Date Dec 31 5 ü 6 Record the interest expense for bonds payable for Year 2. General Journal C 7 8 Debit Credit >arrow_forward
- 1.Prepare Hertog Company’s journal entries to record the following transactions for the current year. May 7 Purchases Kraft bonds as a short-term investment in trading securities at a cost of $10,830. June 6 Sells its entire investment in Kraft bonds for $11,330 casharrow_forwardThe Melon Company issues $519,000 of 8%, 10-year bonds at 103 on March 31, Year 1. The bonds pay interest on March 31 and September 30. Assume that the company uses the straight- line method for amortization. Calculate the net balance that will be reported for the bonds on the September 30, Year 1 balance sheet. (Round your intermediate answers to the nearest dollar.) Group of answer choices $533, 791 $535, 349 $519,000 $534, 570arrow_forwardOn January 1, Jim Shorts Corporation issued bonds for $580 million. This bond issue was originally issued at premium. During the same year, $1,500,000 of the bond premium was amortized. On a statement of cash flows prepared using the indirect method, Jim Shorts Corporation should report: O that $1.5 million to be added to net income O An investing activity of $580 million. O A financing activity of $300 million. O that $1.5 million to be deducted from net incomearrow_forward
- Selected debt investment transactions for Easy A Inc., a retail business, are listed below. Easy A Inc. has a fiscal year ending on December 31. Year 1: Feb. 1 May 1 Jun. 1 Sept. 1 Oct. 1 Dec. 1 Dec. 31 Year 2: Mar. 1 Jun. 1 Sept. 1 Bought $35,000 of 6%, XYZ Co. 12-year bonds at their face amount plus accrued interest of $700. The bonds pay interest semiannually on June 1 and December 1. Bought $200,000 of Simple Tree 5%, 20-year bonds at their face amount plus accrued interest of $2,500. The bonds pay interest semiannually on March 1 and September 1. Received semiannual interest on the XYZ Co. bonds. Received semiannual interest on the Simple Tree bonds. Sold $15,000 of Simple Tree bonds at 102% plus accrued interest of $63. Received semiannual interest on the XYZ Co. bonds. Accrued $3,135 interest on the Simple Tree bonds. Accrued $175 interest on the XYZ Co. bonds. Received semiannual interest on the Simple Tree bonds. Received semiannual interest on the XYZ Co. bonds. Received…arrow_forwardOn September 1, Year 1, Parsons Company purchased $84, 000 of 10-year, 7% government bonds at 100 plus accrued interest. The semiannual interest payment dates are June 30 and December 31. Interest computations are done by the month. Required: a. Joumalize the entry for the bond purchase. b. Joumalize the receipt of interest on December 31 of the first year. c. Journalize the sale of the bonds on February 1 of the second year for 582, 000 plus accrued interest. If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank. a. Year 1 Sept. 1 b. Year 1 Dec. 31 c. Year 2 Feb. 1arrow_forwardPrepare journal entries to record the following transactions involving short-term debt investments.arrow_forward
- On January 1 of the current year, the Queen Corporation issued 12% bonds with a face value of $83,000. The bonds are sold for $80,510. The bonds pay interest semiannually on June 30 and December 31 and the maturity date is December 31, five years from now. Queen records straight-line amortization of the bond discount. Determine the bond interest expense for the year ended December 31. Select the correct answer. a-$830 b-$10,458 c-$2,490 d-$9,960arrow_forwardWildhorse Corporation issued $410,000 of 10-year bonds at a discount. Prior to maturity, when the carrying value of the bonds was $379,250, the company redeemed the bonds at 94. Prepare the entry to record the redemption of the bonds. (Credit account titles are automatically indented when amount is entered. Do not indent manually.) Account Titles and Explanation Debit Creditarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education