
Practical Management Science
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337406659
Author: WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
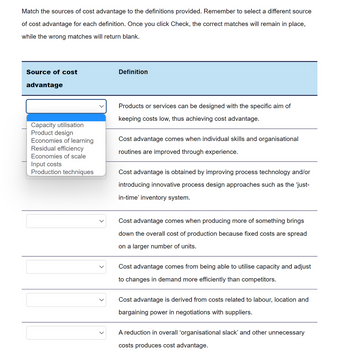
Transcribed Image Text:Match the sources of cost advantage to the definitions provided. Remember to select a different source
of cost advantage for each definition. Once you click Check, the correct matches will remain in place,
while the wrong matches will return blank.
Source of cost
advantage
Capacity utilisation
Product design
Economies of learning
Residual efficiency
Economies of scale
Input costs
Production techniques
Definition
Products or services can be designed with the specific aim of
keeping costs low, thus achieving cost advantage.
Cost advantage comes when individual skills and organisational
routines are improved through experience.
Cost advantage is obtained by improving process technology and/or
introducing innovative process design approaches such as the 'just-
in-time' inventory system.
Cost advantage comes when producing more of something brings
down the overall cost of production because fixed costs are spread
on a larger number of units.
Cost advantage comes from being able to utilise capacity and adjust
to changes in demand more efficiently than competitors.
Cost advantage is derived from costs related to labour, location and
bargaining power in negotiations with suppliers.
A reduction in overall 'organisational slack' and other unnecessary
costs produces cost advantage.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
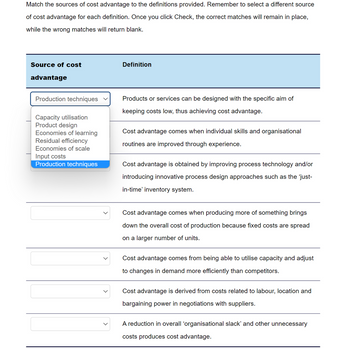
Transcribed Image Text:Match the sources of cost advantage to the definitions provided. Remember to select a different source
of cost advantage for each definition. Once you click Check, the correct matches will remain in place,
while the wrong matches will return blank.
Source of cost
advantage
Production techniques
Capacity utilisation
Product design
Economies of learning
Residual efficiency
Economies of scale
Input costs
Production techniques
Definition
Products or services can be designed with the specific aim of
keeping costs low, thus achieving cost advantage.
Cost advantage comes when individual skills and organisational
routines are improved through experience.
Cost advantage is obtained by improving process technology and/or
introducing innovative process design approaches such as the 'just-
in-time' inventory system.
Cost advantage comes when producing more of something brings
down the overall cost of production because fixed costs are spread
on a larger number of units.
Cost advantage comes from being able to utilise capacity and adjust
to changes in demand more efficiently than competitors.
Cost advantage is derived from costs related to labour, location and
bargaining power in negotiations with suppliers.
A reduction in overall 'organisational slack' and other unnecessary
costs produces cost advantage.
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question

Transcribed Image Text:Match the sources of cost advantage to the definitions provided. Remember to select a different source
of cost advantage for each definition. Once you click Check, the correct matches will remain in place,
while the wrong matches will return blank.
Source of cost
advantage
Production techniques
Capacity utilisation
Product design
Economies of learning
Residual efficiency
Economies of scale
Input costs
Production techniques
Definition
Products or services can be designed with the specific aim of
keeping costs low, thus achieving cost advantage.
Cost advantage comes when individual skills and organisational
routines are improved through experience.
Cost advantage is obtained by improving process technology and/or
introducing innovative process design approaches such as the 'just-
in-time' inventory system.
Cost advantage comes when producing more of something brings
down the overall cost of production because fixed costs are spread
on a larger number of units.
Cost advantage comes from being able to utilise capacity and adjust
to changes in demand more efficiently than competitors.
Cost advantage is derived from costs related to labour, location and
bargaining power in negotiations with suppliers.
A reduction in overall 'organisational slack' and other unnecessary
costs produces cost advantage.
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- For this queestion, findd the correct match for each item in the first column labeled 'Concept' to the corrrect item in the second column labeled 'Example'. The items in the concept colummn referr to the terminology used in the product-process matrix. Concept Example Job Shop Batch Processing Continuous Assembly Line Options: Automobile manufacturing, Sugar Production, Baking bagels in bakeryy, Making custom furntiurearrow_forwardFigures derived from a ratio analysis of a firm need to be evaluated against the past performance of the firm to understand its current health. True or Falsearrow_forwardStrategies for proactive demand management would not include O a. offering products or services with countercyclical demand patterns. O b. using subcontracting to meet unexpected high demand levels. O c. O d. shifting demand into other time periods. partnering with suppliers to reduce information distortion along the supply chain.arrow_forward
- The product life cycle is described as ______. ____ the financial commitment a firm makes in a product from development to its disposal. ____ the evolution a product goes through in the marketplace, from introduction to decline. ____ the movement of a product from the point of manufacture to the point of purchase. ____ the process by which a product is given new features and benefits to improve it.arrow_forwardIs this statement true or false? Can you please explain in detail. A performance dashboard of an online retailer which follows the customer intimacy value discipline will include delivery time as most important KPIarrow_forwardFind the missing information for different companies Output (units) Fixed Costs Variable Costs Total Costs Cost per unit Company A 4000 70000 50000 ? ? Company B 5000 80000 ? 140000 ? Company C 8000 30000 130000 ? ? Company D ? ? 80000 100000 20arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage, Operations ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781259667473Author:William J StevensonPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Operations ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781259667473Author:William J StevensonPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781259666100Author:F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B ChasePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781259666100Author:F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B ChasePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781478623069Author:Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon OlsenPublisher:Waveland Press, Inc.
Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781478623069Author:Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon OlsenPublisher:Waveland Press, Inc.

Practical Management Science
Operations Management
ISBN:9781337406659
Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:Cengage,

Operations Management
Operations Management
ISBN:9781259667473
Author:William J Stevenson
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi...
Operations Management
ISBN:9781259666100
Author:F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B Chase
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Purchasing and Supply Chain Management
Operations Management
ISBN:9781285869681
Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. Patterson
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi...
Operations Management
ISBN:9781478623069
Author:Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon Olsen
Publisher:Waveland Press, Inc.