
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
I only need help with d and e, i'm confused how it works
 for further exploration of the implications or [**Previous**](#) to review prior financial data.](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/b227e11a-bbc7-42b9-aba2-7e353597c2c3/7eb034d5-0b75-443b-9568-4f25aa986ef2/wspu03b_thumbnail.jpeg)
Transcribed Image Text:**Martin's Controlling Interest in Rowen: Financial Overview and Tax Implications**
*Financial Data Accumulated at Year-End:*
| Company | Separate Operating Income | Dividends Paid |
|---------|----------------------------|----------------|
| **Martin** | $645,000 (includes a $115,000 net gross profit in intra-entity ending inventory) | $110,000 |
| **Rowen** | $380,000 | $85,000 |
Martin uses the initial value method to account for the investment in Rowen. The separate operating income figures presented above include neither dividend nor other investment income. The effective tax rate for both companies is 21%.
### Tax Implication Scenarios:
**a. 100% Ownership and Consolidated Tax Return:**
Assume that Martin owns 100 percent of Rowen's voting stock and is filing a consolidated tax return. Calculate the income tax amount this affiliated group will pay for the current period.
**b. 92% Ownership and Consolidated Tax Return:**
Assume that Martin owns 92 percent of Rowen's voting stock and is filing a consolidated tax return. Determine the income tax amount this affiliated group will pay for the current period.
**c. 65% Ownership and Separate Tax Returns:**
Assume that Martin owns 65 percent of Rowen's voting stock, with the companies electing to file separate tax returns. What is the total amount of income taxes that these two companies will pay for the current period?
**d. 70% Ownership and Separate Tax Returns:**
Assume that Martin owns 70 percent of Rowen's voting stock, necessitating separate tax returns. Compute the total amount of income tax expense to be recognized in the consolidated income statement for the current period. *(Round your intermediate calculations and final answer to the nearest whole dollar amount.)*
**e. 70% Ownership and Separate Tax Returns Calculation:**
With Martin owning 70 percent of Rowen's voting stock and thereby triggering separate tax returns, calculate the amount of income taxes Martin must pay for the current year.
------
Navigate to [**Next**](#) for further exploration of the implications or [**Previous**](#) to review prior financial data.
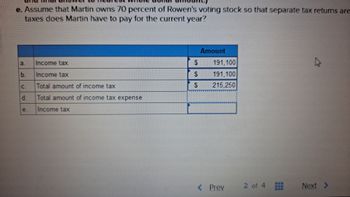
Transcribed Image Text:### Tax Considerations for Martin Owning 70% of Rowen's Voting Stock
In calculating the taxes owed by Martin, who owns 70 percent of Rowen's voting stock, we analyze the data presented for the current year. The following table outlines the specified amounts and categories of income tax:
| | | Amount |
|:-|---|--------|
| a. | Income Tax | $191,100 |
| b. | Income Tax | $191,100 |
| c. | Total Amount of Income Tax | $215,250 |
| d. | Total Amount of Income Tax Expense | |
| e. | Income Tax | |
#### Explanation of the Table:
- **Income Tax Entries (a, b, e)**: These entries indicate the assessed income tax amounts of $191,100.
- **Total Amount of Income Tax (c)**: This entry consolidates the total income tax amount, recorded as $215,250.
- **Total Amount of Income Tax Expense (d)**: This entry appears to be pending or not filled out.
This information is crucial for understanding the financial responsibilities related to ownership and taxation in a scenario where shares are predominantly held by one entity.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Is there a different format for Maufacturing account? I am not familliar with this lay outarrow_forwardit is not correct, some calculations are wrong, can you try againarrow_forwardHi, my name is Jennifer. I am having trouble with this same problem. But the sub-parts I need help with are C, D, and E. But more specifically, really just sub-parts D and E. The only parts I see being answered are sub-parts A, B, and C only in the 8 solutions posted. May I please receive help for the top sub-parts of C, D, and E ONLY, please? It would be much appreciated. Thank you. :) -- Jennifer Suttonarrow_forward
- Im having an issue with this problem. Thank you!arrow_forwardPlease do not rely too much on chatgpt, because its answer may be wrong. Please consider it carefully and give your own answer. You can borrow ideas from gpt, but please do not believe its answer.Very very grateful!Please do not rely too much on chatgpt, because its answer may be wrong. Please consider it carefully and give your own answer. You can borrow ideas from gpt, but please do not believe its answer.Very very grateful!arrow_forwardPlease do not rely too much on chatgpt, because its answer may be wrong. Please consider it carefully and give your own answer. You can borrow ideas from gpt, but please do not believe its answer.Very very grateful!Please do not rely too much on chatgpt, because its answer may be wrong. Please consider it carefully and give your own answer. You can borrow ideas from gpt, but please do not believe its answer.Very very grateful!arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education