
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Please answer questions 3-6 in the first image based off the picture of the second.
Transcribed Image Text:u will get ready for the lab by completing these warm-up exercises and making a prediction. Complete the steps
ow in your lab notebook or on paper and upload a PDF file containing photos and/or text which address all the
pects listed here. You can merge multiple images by inserting them in a Google document or other word processo
d then exporting the result as a PDF.
Jarm up
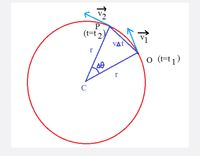
. Make a drawing of the path of an object in circular motion at constant speed. On that path, use a dot to represen
the object's position at time t1. Label this point as O, and draw a vector at O to represent the magnitude and
direction of the object's velocity at time t1. Draw another dot to represent the object's position at a later time t2,
shortly after t1, and label this point P. Draw a vector at P to show the magnitude and direction of the object's
velocity at time t2.
2. Redraw the velocity vectors with the tail of one vector (point P) at the tail of the other vector (point O). Keep the
same size and direction as in the previous drawing. To find the acceleration of the object, you are interested in the
change in velocity (Av). The change Av is the increment that must be added to the velocity at time t so that the
resultant velocity has the new direction after the elapsed time At = t – t2. Add the change in velocity Av to your
drawing of the velocity vectors; it should be a straight line connecting the heads of the vectors.
3. On your drawing from question 1, label the distance r from the center of the circle to points O and P. In the limit
that the time interval is very small, the arc length distance traveled by the object can be approximated as a straight
line. Use this approximation to label the distance traveled by the object along the circle from point O to P in terms
of the object's velocity and the elapsed time.
4. The triangle drawn in question 2 (with v and Av) is similar to the triangle drawn in question 3 (with r and the straight
line distance traveled by the object) because they have the same apex angle. Use the relationship of similar triangles
to write an equation that connects the sides and the bases of the two triangles.
5. Solve your equation for Av/At to get an expression for the acceleration in terms of the object's uniform velocity and
the distancer.
6. From your equation, is the acceleration of an object in circular motion ever zero? Does the magnitude of the
acceleration change with time?
Prediction
Does an object moving in a circle accelerate? If so, does the magnitude of the acceleration change with time? Explain
your reasoning. Use the acceleration equation you derived in the Warm-up to support your claim.
立
Transcribed Image Text:V2
P
(t=t 2)
Vat
o (t=t¡)
40
r
C
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A convex lens produces an image with a magnification of +5. Describe the locatior size, and orientation of the image produced. Circle one from each pair of answers Same side as object/ opposite side as object Upright/Inverted Real /Virtual Enlarged /Reducedarrow_forwardH G F A E D In the image above, a light ray moves from a material with an index of refraction n2 = 1.46 into an material with an index of refraction n1 = 3. angle A + B = 90 degrees. %3D andgle B+C = 90 degrees. %3D angle C = 2 Calculate the angle of refraction, F. Give your answer with one decimal place.arrow_forwardWhere can I add only one more force vector to this object to make it have 0 net force? Please explain step-by-step and draw on the attached image.arrow_forward
- Calculate the image distance when an object is placed 6 cm in front of a mirror with focal length -10 cm.(Give your answer in centimeters but don't include units in your answer.)arrow_forwardA concave mirror of focal length 17.5 cm forms a real image 24.8 cm from the mirror. What is the magnification? (Mind your minus signs.) (Unit = cm)arrow_forwardConsider the compound optical system shown in the diagram, where two thin lenses of focal lengths 7.5 cm (left lens) and 35 cm (right lens) are separated by a distance 25 cm. If a 2.9 cm tall object is placed as indicated in part (a), and the image formed is 0.74 cm tall, what is the magnification of the first lens? M1 = b. Using the information from part (a), calculate the image distance, in centimeters, from the first lens. di1 =arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON