The image with the diagram serves as a reference for the second image with the actual question. Please answer the question on the image without the diagram.
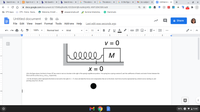
Given
In the figure above, the block of mass M has come to rest at a location to the right of the spring's equilibrium position. The spring has a spring constant k, and the coefficients of kinetic and static friction between the block and the surface area, and respectively.
(i) On the dot below, which represents the block at rest and to the right of z=0 draw and label the forces (not components) that act on the block. Each force must be represented by a distinct arrow starting on, and pointing away from the dot.
(ii) Derive an expression for the maximum displacement possible for the block that will allow the block to still remain at rest. Express your answer in terms of M. and physical constants, as appropriate, as following below.
(i)
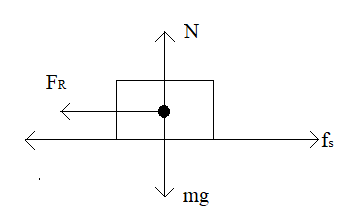
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

- Please answer question #2. Please open the image to see #2. Thank you.arrow_forwardIf you move the convex lens away from the object. What happen to the image as you move to a distance > 1m. How far was the object (approximately) from the convex lens when the image changed its orientation?arrow_forwardYou are imaging a pencil through a thin, converging lens as shown in the image below. If p (the distance from the object to the center of the thin lens) is 10m and the focal length of the thin lens is 1.26m, how far away (in meters) from the center of the thin lens is the real image located (the real image will be on the right side of the lens in this particular example illustrated below)?arrow_forward
- An object is placed 12 cm in front of a concave mirror of radius 40 cm. Find the position and magnification of the image. State whether the image is real or virtual, and draw a light ray diagram to show the image.arrow_forwardThe upper part of the figure (drawn to scale) shows how a light beam travels through a traditional converging lens. How would the light beam shown in the lower part of the figure travel after leaving the lens? (Copy the figure onto the working paper. You have to explain briefly how you have found the beam.)arrow_forwardAn object is placed in front of a concave mirror with a 20-cm focal length. What is the position of the resulting image (in cm) if the image is inverted and three times larger than the object? Where is the position of object?arrow_forward
- Please complete the drawings, if necessary, based on the name/type of diagrams named on top and then determine the focal length for each. This is the complete question.arrow_forwardMy answer is correct, but please write find my wrong in my explanation(process detail). Also, watch the professor's comment. I attach the image and write my process of explanation and the professor's process and comment.arrow_forwardAn air bubble inside a plastic ball with a diameter of 20.0 cm is 7.0 cm from the surface. When you look at the ball in the configuration in the figure below (observer, center of the ball, and bubble are on the same straight line), at what distance from the center of the ball will the image form? Consider nₚₗₐₛₜ=1.6 and nₐᵣ = 1 a)5.85 cm to the right of the center of the ball b)5.85 cm left of center of ball c)4.85 cm right from center of ball d)4.85 cm left from center of ball e)3.85 cm right from center of ball f)3.85 cm left from center of ball g)6.85 cm right from center of ball h)6.85 cm left from center of ball i)7.85 cm right from center of ball j)7.85 cm left from center of ballarrow_forward