
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Problem Set 04
3
00
Assignment Score:
Question 5 of 6 >
80
F3
Macmillan Learning
$
4
Velocity (m/s)
38.9%
n
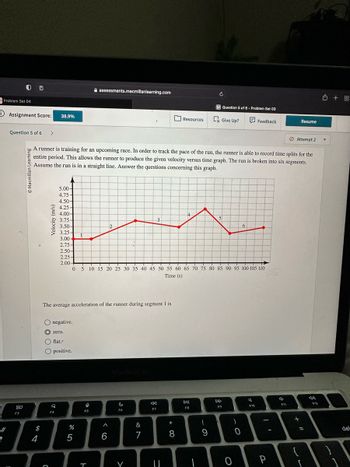
A runner is training for an upcoming race. In order to track the pace of the run, the runner is able to record time splits for the
entire period. This allows the runner to produce the given velocity versus time graph. The run is broken into six segments.
Assume the run is in a straight line. Answer the questions concerning this graph.
5.00-
4.75-
4.50-
4.25-
4.00-
3.75-
3.50-
3.50-
3.25-
3.25-
3.00-
2.75-
2.50-
2.25-
2.00-
O negative.
zero.
flat..
O positive.
Q
The average acceleration of the runner during segment 1 is
FA
%
assessments.macmillanlearning.com
5
F5
T
2
^
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100 105 110
Time (s)
6
c
F6
V
&
7
3
18
F7
Resources
*
8
4
DII
F8
7
U
-
Ć
(
M Question 5 of 6- Problem Set 03
C Give Up?
Feedback
9
5
DD
F9
O
)
-O
6
0
7
F10
-
P
F11
Attempt 2
Resume
+
+ 11
=
r
F12
+88
del
Transcribed Image Text:Problem Set 04
Assignment Score:
Question 5 of 6 >
80
F3
Learning
O
$
4
O negative.
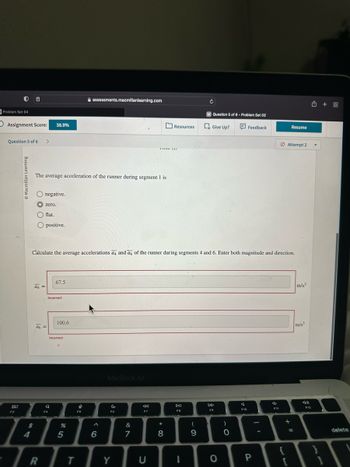
The average acceleration of the runner during segment 1 is
flat.
O positive.
a4=
38.9%
zero.
a6 =
R
F4
Q
67.5
Incorrect
Calculate the average accelerations a4 and a6 of the runner during segments 4 and 6. Enter both magnitude and direction.
100.6
Incorrect
%
5
T
assessments.macmillanlearning.com
e
FS
6
MacBook Air
C
F6
Y
&
7
8:
F7
AM (0)
C
Resources
* 00
8
DII
F8
I
C
(
9
M Question 5 of 6- Problem Set 03
Give Up?
DD
F9
O
)
0
A
Feedback
F10
P
4
F11
Resume
Attempt 2
+ 11
=
m/s²
m/s2
F12
✩ +88
delete
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Can i get help step by step with this problem?arrow_forwardPlease answer all parts or leaves for someone else.arrow_forwardWhat are the similarities and differences in average speed and velocity and how are these related to instantaneous speed and velocity. Also include graphical interpretations.arrow_forward
- Figure below is a velocity-versus-time graph for a moving object. The object starts at position x = 0. What is the acceleration at t= 1.0 s, in m/s2? Your answer needs to have 3 significant figures, including the negative sign in your answer if needed. Do not include the positive sign if the answer is positive. No unit is needed in your answer, it is already given in the question statement. time in secondsarrow_forward5. Draw a distance vs. time graph for Melinda’s journey. Her home is located at 0 meters.Melinda is riding her bike over to her friend Sara’s house to complete an assignment. Her friend lives 5 km away. She accelerates away from her home for250 m in the next 2.5 minutes. She then rides at a constant speed of 300 m/min for 15 minutes. Melinda sees Sara’s house approaching so she slows downuntil she reaches her destination in the next 2.5 minutes. She stays at Sara’s house for 30 minutes while they work on the assignment. It is time to go home,Melinda rides home at a steady speed of 250 m/min for 10 minutes. Melinda is getting tired so she slows down for 250 m during the next 5 minutes thenstops for 2.5 minutes to have a drink. Realizing it’s getting late, she had to speed up 1 km in the next 5 minutes then rides at a constant speed of 300 m/minfor 2.5 minutes. Almost home, she decelerates for the next 10 minutes until she reaches her house.arrow_forwardHelp me pleasearrow_forward
- *- cer pua page dn page up delete Name 8 6. Date Block Score Graphing Motion Lab Coar. The goal of this lab is to draw conclusions about motion graphs and practice graphing motion. mtroduction: Motion graphs are important to understand how objects are moving. In this lab activity, we will create motion graphs from motion diagrams and from description situations. O8 ) = 1 s こ=} as 9 =1 8. Feet 4. 12 FIGURE 1-9 Motion diagram of a skateboarder, showing position and time. Part 1: Motion Diagrams Basics Instead of graphing from a data table, we will be graphing from a motion diagram. The diagram below shows Harold running from 0m to 100m on the track. He is moving along the positions, shown on the number line and his time at each position is tracked above him. Using these values, first create a data table. Then graph the motion (using time on the x and position on the y). Lor on Ceu 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 0 10 S0arrow_forwardfigure 1 shows a velocity-versus-time graph for the bicycle trips of two friends with respect to the parking lot where they started. Xena's position at time zero is 0 and Gabriele's position is 60 m. Determine the displacement of Xena in 40 s. Determine the displacement of Gabriele in 30 s. What time interval is needed for Xena to catch Gabriele?arrow_forwardan object falls from rest on a high tower and takes 5.0s to hit the ground. calculate the objects position from the top of the tower at 1.0s intervals. Please make a position- time graph for the objects motion. Please make sure to include the equation that you used, a table of data, and the graph.arrow_forward
- A roly-poly bug moves on the x axis. The bug has a variable velocity which is denoted by 2 v = t² - 2.50t.t is time in seconds and v is meters per second. The origin of the roly-poly bug is at t=0. Your job is to figure out the following after 3s have passed. Be sure to use the correct amount of sig figs! a) Velocity of the bug b) The bugs acceleration c) The bugs position THIS IS How I ROLLarrow_forwardThe motion of a person as seen by another person is described by the equation v=-3.0m/s+0.5m/s^2t. Draw a motion diagram. draw a motion potion vs time graph draw a motion velocity versus time graph draw a acceleration vs time graph say everything you can about this motion and what happens to the person when his speed becomes zero.arrow_forwardWhich of the following statements are true regarding velocity-time graphs?I. The slope of a velocity-time graph is acceleration. II. The graph has a slope of zero if the object is at rest. III. A line with negative slope indicates that the object is slowing down.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON