
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
The figure below shows a bar of mass m = 0.220 kg that can slide without friction on a pair of rails separated by a distance ℓ = 1.20 m and located on an inclined plane that makes an angle θ = 32.0° with respect to the ground. The resistance of the resistor is R = 2.70 Ω and a uniform magnetic field of magnitude B = 0.500 T is directed downward, perpendicular to the ground, over the entire region through which the bar moves. With what constant speed v does the bar slide along the rails?
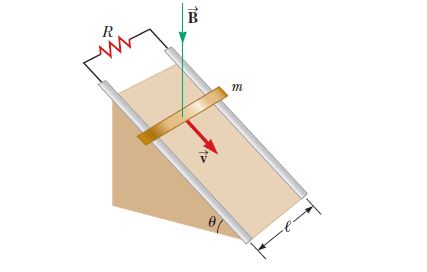
Transcribed Image Text:m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 7 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The figure below shows a bar of mass m = 0.270 kg that can slide without friction on a pair of rails separated by a distance ℓ = 1.20 m and located on an inclined plane that makes an angle ? = 29.5° with respect to the ground. The resistance of the resistor is R = 3.30 Ω, and a uniform magnetic field of magnitude B = 0.500 T is directed downward, perpendicular to the ground, over the entire region through which the bar moves. With what constant speed v does the bar slide along the rails? m/sarrow_forwardThe figure shows a bar of mass 0.2kg that can slide without friction on a pair of rails separated by a distance l=1.20m and located on an inclined plane that makes an angle of 25° with respect to the ground. The resistance of the resistor is 1 ohm and a uniform magnetic field of magnitude H=0.5T is directed downward, perpendicular to the ground,over the entire region through which the bar moves. Find the speed at which the bar slides along the rails.arrow_forwardThe loop in the figure has a resistance of 2.5 2 and is being pulled to the right at 1.0 m/s. X X X||X × X 2.0 T X||X 1.0 T 2.0 m X X X ||× × X X X X X • 2.0 m 2.0 m (a) Find the total magnetic flux through the loop, directed into the page, at the time instant shown. b)In the above problem, find the total magnetic flux through the loop, directed into the page, 2.0 s later. (c) In the above problem, find the magnitude of the induced current in the loop during this 2.0 s interval.arrow_forward
- A rod of length L = 10.0 cm that is forced to move at constant speed v = 5.00 m/s along horizontal rails. The rod, rails, and connecting strip at the right form a conducting loop. The rod has resistance 0.400 Ω; the rest of the loop has negligible resistance. A current i = 100 A through the long straight wire at distance a = 10.0 mm from the loop sets up a (nonuniform) magnetic field through the loop. Find the (a) emf and (b) current induced in the loop. (c) At what rate is thermal energy generated in the rod? (d) What is the magnitude of the force that must be applied to the rod to make it move at constant speed? (e) At what rate does this force do work on the rod?arrow_forwardL R = 5.00 Q X Xix x 1 |X X X X R P = FexV =8.50 J/s Fext W X xx x X X X X X X X X A rectangular wire loop of length L, width w, is pulled out of a constant, uniform magnetic field with constant velocity v. The loop has a resistance R. The magnetic field of magnitude B, points into the plane of the paper, and is confined to the rectangular region shown above. Work must be done on the loop at the rate of P, to move it through the magnetic field at constant velocity. Find the magnitude of the emf, & and the current I for the loop.arrow_forwardA solenoid in your car is 36 cm long and has a diameter of 7.9 cm. It is made of copper wire with a radius of 0.50 mm. The turns are closely packed and form a single layer. Assume the resistivity of copper is 1.68 ✕ 10−8 Ω · m. (a) When the solenoid is connected to your battery with E = 11.6 V, what is the magnetic field inside the solenoid? (Enter the magnitude.) Tarrow_forward
- Find the flux of the Earth's magnetic field of magnitude 5.00 ✕ 10-5 T, through a square loop of area 30.0 cm2 for the following. (a) when the field is perpendicular to the plane of the loop T·m2(b) when the field makes a 30.0° angle with the normal to the plane of the loop T·m2(c) when the field makes a 90.0° angle with the normal to the plane T·m2arrow_forwardAsaparrow_forwardA square wire loop (side length 1.5 m) is oriented so that it is perpendicular to an external magnetic field B, with half the area of the loop embedded in the field, as shown below. The loop contains a battery with a constant emf Eb = 7.2 V and a resistor R = 3.2 Ω. The external magnetic field is B(t) = [0.027 T − (0.56 T/s) t] î where î is out of the page. (a) Findtheemfproducedbyinductionintheloop. (b) Findthenetcurrentintheloopfromboththeinducedemfandthebattery. (c) What direction is the current in? (a) Findtheemfproducedbyinductionintheloop. (b) Findthenetcurrentintheloopfromboththeinducedemfandthebattery. (c) What direction is the current in? (a) Find the emf produced by induction in the loop. (b) Find the net current in the loop from both the induced emf and the battery. (c) What direction is the current in?arrow_forward
- A time-dependent uniform magnetic field of magnitude B (t) is confined in a cylindrical region of radius R. A conducting rod of length 2D is placed in the region, as shown. Show that the magnitude of the emf between the ends of the rod is given by dB ε = D√R²-D² dt P₁1 B(t) 2D Rarrow_forwardA loop of wire with radius r=0.025m is placed in a region of uniform magnetic field with magnitude B. As shown in the figure, the field direction is perpendicular to the plane of the loop. The magnitude of the magnetic field changes at a constant rate from B1=0.65T to B2=6.5T in time Δt=3.5s. The resistance of the wire is R=15Ω. Part (a) Calculate, in Tesla squared meters, the magnitude of the change in the magnetic flux. Part (b) Calculate, in volts, the average EMF induced in the loop. Part (c) Calculate, in amperes, current induced in the loop.arrow_forwardThe figure below shows a bar of mass m = 0.240 kg that can slide without friction on a pair of rails separated by a distance { = 1.20 m and located on an inclined plane that makes an angle e = 35.0° with respect to the ground. The resistance of the resistor is R = 1.50 N and a uniform magnetic field of magnitude B = 0.500 T is directed downward, perpendicular to the ground, over the entire region through which the bar moves. With what constant speed v does the bar slide along the rails? m/sarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON