
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
A square coil of wire, with side l = 5.00 cm and total resistance of 100Ω, contains 100 turns and is placed perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field of 1.20 T, as shown in the figure. It is quickly pulled out of the field with constant speed (moving perpendicular to B) into a region where B drops abruptly to zero. At t = 0, the right edge of the coil is at the edge of the field. For the entire coil to reach the free field region, 0.100 s elapse. Find a) the rate of change in flux through the coil, b) the induced emf, and c) the induced current.
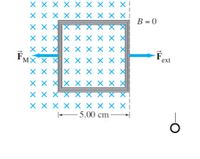
Transcribed Image Text:X X X X X X X X X!
X X X X X X X X X!
×× ×区XxX
XX X X
X X XX X x X
FMX X Xx × x x
B = 0
ext
X X XX X X
X X XX X x X X
X X XX X X X X X
X X X X X X x X Xi
-5.00 cm-
× ×区× x x x ×× ×
XX X X X X Xx x
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.70 T is directed perpendicular to the plane of a rectangular loop having dimensions 7.8 cm by 11 cm. Find the magnetic flux through the loop.arrow_forwardA loop of a wire has the shape shown in the drawing. The top part of the wire is bent into a semicircle of radius r = 0.19 m. The normal to the plane of the loop is parallel to a constant magnetic field of magnitude 0.74 T. What is the magnitude of the change in the magnetic flux that passes through the loop when, starting with the position shown in the drawing, the semicircle is rotated through a quarter of a revolution? (Look at the image for more clarification )arrow_forwardIn the figure, a metal rod is forced to move with constant velocity along two parallel metal rails, connected with a strip of metal at one end. A magnetic field of magnitude B = 0.402 T points out of the page. (a) If the rails are separated by 28.9 cm and the speed of the rod is 70.7 cm/s, what is the magnitude of the emf generated in volts? (b) If the rod has a resistance of 21.9 Ω and the rails and connector have negligible resistance, what is the current in amperes in the rod? (c) At what rate is energy being transferred to thermal energy?arrow_forward
- A conducting loop is in the shape of a square of side ℓ. Current I flows clockwise through the loop. A conducting loop in the shape of a square of edge length ℓ = 480m carries a current I = 10.4 A as in the figure above. Calculate the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field at the center of the square. If this conductor is reshaped to form a circular loop and carries the same current, what is the value (magnitude and direction) of the magnetic field at the center?arrow_forwardA metal rod is forced to move with constant velocity = 75.0 cm/s along two parallel metal rails, connected with a strip of metal at one end, as shown in the figure. A magnetic field B = 0.35 T points out of the page. The rails are seperated by 35.0 cm. a)What emf is generated? b)If the rod has a resistance of 17.0 Ω and the rails and connectors have negligible resistance, what is the current in the rod? c)At what rate is energy being tranferred to thermal energy?arrow_forwardA circular coil enclosing an area of 160 cm² is arranged horizontally. The coil has 210 turns of copper wire. The wire making up the coil has resistance of 3.00 2, and the ends of the wire are connected to form a closed circuit. Initially, a 2.00-mT uniform magnetic field points perpendicularly upward through the plane of the coil. The direction of the field then reverses so that the final magnetic field has a magnitude of 3.10-mT and points downward through the coil. If the time required for the field to reverse directions is 0.750 s, determine the magnitude of the average current in the coil during that time. Bi Initial Bf ↓↓↓↓ Finalarrow_forward
- A loop of wire has the shape shown in the drawing. The top part of the wire is bent into a semicircle of radius r = 0.19 m. The normal to the plane of the loop is parallel to a constant magnetic field (p = 0°) of magnitude 0.60 T. What is the change AO in the magnetic flux that passes through the loop when, starting with the position shown in the drawing, the semicircle is rotated through half a revolution? B (into paper) ΔΦ = i x X میرا www Iarrow_forwardA coil consisting of 88 windings of insulated wire is circular in shape with a radius r = 9.5 cm. The magnetic field is uniform throughout the coil and perpendicular to the coil's area, but it is changing with time. The magnitude of the magnetic field is initially 0.45 T and then changes at a constant rate until it has the same magnitude in the opposite direction. This change occurs over a time interval At =0.20 s. What is the magnitude of average emf induced in the coil during this time interval? E = V If instead the magnetic field in the same coil remains constant at B = 0.45 T (in the same direction perpendicular to the coil's area, initially) and the coil itself is then rotated at a constant rate until it has inverted (gone through a rotation of 180°) during a time interval At = 0.10 s, what is the magnitude of the average emf induced in the coil during this time interval?arrow_forwardAt a certain place, Earth's magnetic field has magnitude B =0.806 gauss and is inclined downward at an angle of 71.1° to the horizontal. A flat horizontal circular coil of wire with a radius of 13.1 cm has 939 turns and a total resistance of 73.9 Q. It is connected to a meter with 130 Q resistance. The coil is flipped through a half-revolution about a diameter, so that it is again horizontal. How much charge flows in coulombs through the meter during the flip? Number Unitsarrow_forward
- A loop of wire has the shape shown in the drawing. The top part of the wire is bent into a semicircle of radius r = 0.16 m. The normal to the plane of the loop is parallel to a constant magnetic field (p=0") of magnitude 0.74 T. What is the change AO in the magnetic flux that passes through the loop when, starting with the position shown in the drawing, the semicircle is rotated through half a revolution? B (into paper) AD= Y i 0.0296 Wb Varrow_forwardA flexible conducting loop of diameter d0 and resistance R lies perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field B⃗ . At time t=0 the loop begins to expand, with its diameter given by d(t)=d0+bt, where b is a constant. The loop's resistance doesn't change as it expands.arrow_forwardIn the given figure, a square metal loop of side 4.00 cm and resistance 5.00 2 moves to the right (+x-direction) into, through, and out of a 6.00-cm-wide region of uniform magnetic field perpendicular to the plane of the loop. The magnetic field in the region is 0.250 T. At t= 0, the loop just begins to enter the region of magnetic field. The loop moves at a constant 1.00 cm/s. Which of the following correctly plots the graph of the external force applied to the loop (to keep it moving at constant velocity) as a function of time? х х 1 XI X ix R d х х Multiple Choice Applied force to loop 300 200 100 time 2 6 10 12arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON