Question
A wedge with mass M rests on a frictionless, horizontal
tabletop. A block with mass m is placed on the wedge, and a horizontal
force F S is applied to the wedge (Fig.). What must the magnitude
of F S be if the block is to remain at a constant height above the
tabletop?
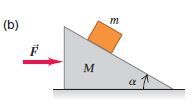
Transcribed Image Text:m
(b)
M
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Force T pulls at angle a up from the horizontal on a section of pipe of weight W as shown, but the pipe remains motionless. The coefficient of static friction between pipe and floor is µ. We know that the magnitude of the total frictional force on the pipe by the floor is: 1(c T. A) 27 cos a B) µ(W +T sin a) C) µW +T cos a D) T cosa W A Barrow_forward1) A force of magnitude 31 N pushes from the left on a horizontally stacked set of blocks made of the same material on a rough surface with masses from left to right m1 = 1kg, m2 = 2.0kg, and m3 = 3.0kg. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the blocks and the surface is μk = 0.17 (a) What is the acceleration of the stack? (b) What is the force exerted by m1 on m2? (c) What is the force exerted by m2 on m3?arrow_forwardThe diagram shows a block of mass m = 3.50 kg resting on a plane inclined at an angle of 0 = 40° to the horizontal. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the plane is μstatic = 0.30, and the block is stationary but just on the point of sliding down the slope. Ff F₁ 3 mg N 0 The diagram shows the four forces acting on the block: an applied force F₁ acting perpendicular to the slope (in the -y direction), the block's weight mg, the normal reaction force N and the force of static friction, Ff. In this case, the force of static friction acts up the slope, opposing the tendency of the block to move down the slope. Find the the minimum magnitude of the applied force F₁ that can be exerted if the block is to remain stationary. Specify your answer by entering a number into the empty box below.arrow_forward
- A block of mass mį = 4.00 kg is put on top of a block of mass mp = 7.00 kg. To cause the top block to slip on the bottom one while the bottom one is held fixed, a horizontal force of at least 15.0 N must be applied to the top block. The assembly of blocks is now placed %3D on a horizontal, frictionless table (see the figure). Find the magnitudes of (a) the maximum horizontal force F that can be applied to the lower block so that the blocks will move together and (b) the resulting acceleration of the blocks. (a) Number i Units (b) Number i Units >arrow_forwardProblem 12: A box slides down a plank of length d that makes an angle of 0 with the horizontal, as shown. The kinetic and static coefficients of friction are µk and us, respectively. Omin = 1 Part (a) Enter an expression for the minimum angle at which the box, if initially at rest, will begin to slide. ^^^ 4 acotan(us) atan(us) cos(a) ( ) 7 8 9 cos(p) cos(0) sin(a) 5 6 sin(o) sin(0) 0 α 1 2 3 Mk d t Hints: 0% deduction per hint. Hints remaining: 2 Submit m Hint + * 0 BACKSPACE DEL HOME Feedback END CLEAR I give up! Feedback: 0% deduction per feedback. m 0 Part (b) Enter an expression for the nonconservative work done by kinetic friction as the block slides down the plank. Assume the box starts from rest, and is large enough that it will slide down the plank. the angle Part (c) For a plank of any length, at what angle, in degrees, will the final speed of the box at the bottom of the plank be 0.51 times the final speed of the box when there is no friction present? Assume μ = 0.39.arrow_forwardDuring a storm, a tree limb breaks off and comes to rest across a barbed wire fence at a point that is not in the middle between two fence posts. The limb exerts a downward force of 292 N on the wire. The left section of the wire makes an angle of 10.5° relative to the horizontal and sustains a tension of 412 N. Find the (a) magnitude and (b) direction (as an angle relative to horizontal) of the tension that the right section of the wire sustains.arrow_forward
- For the next three items: A 200 kg plank is projecting a distance L = 5.0 m from a wall which is held steadily by a string that is connected to it at an angle = 30° from the horizontal. The plank is actually fasted to the wall where an unknown force F is exerted on the plank by the wall. If a 60 kg mass is placed on the plank at a distance d = 1.0 m, find the tension force on the string. Ө d O 1300 N O 4200 N O 1600 N O2200 N L-arrow_forwardA loaded penguin sled weighing 72.0 N rests on a plane inclined at angle 0 = 22.0° to the horizontal (see the figure). Between the sled and the plane, the coefficient of static friction is 0.270, and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.140. (a) What is the minimum magnitude of the force , parallel to the plane, that will prevent the sled from slipping down the plane? (b) What is the minimum magnitude F that will start the sled moving up the plane? (c) What value of F is required to move the sled up the plane at constant velocity? (a) Number i (b) Number i (c) Number i Units Units Units +arrow_forwardA block with mass m1 = 8.7 kg is on an incline with an angle θ = 37° with respect to the horizontal. The coefficients of friction are: μk = 0.36 and μs = 0.396. Another block with mass m2 = 15.5 kg is attached to the first block. The new block is made of a different material and has a greater coefficient of static friction. What minimum value for the coefficient of static friction is needed between the new block and the plane to keep the system from accelerating?arrow_forward
- A donkey is harnessed to a sled having a mass of 251 kg, including supplies. The donkey must exert a force exceeding 1230 N at an angle of 34.3° (above the horizontal) in order to get the sled moving. Treat the sled as a point particle. (a) Calculate the normal force (in N) on the sled when the magnitude of the applied force is 1230 N. (Enter the magnitude.) (b) Find the coefficient of static friction between the sled and the ground beneath it. (c) Find the static friction force (in N) when the donkey is exerting a force of 6.15 ✕ 102 N on the sled at the same angle. (Enter the magnitude.)arrow_forwardAs shown above an adhesive has been applied to contacting faces of two blocks so that the blocks interact with an adhesive force that has a magnitude, Fadhesion. A tension, T, is exerted by a wire attached to the upper blocks causing the blocks to remain at rest. The two blocks have weights, Wbottom and Wtop. Which of the following must be true? Wtop=T Wbottom=Fadhesion T=Wtop−Fadhesion T=Wbottom+Wtop+Fadhesionarrow_forwardIn a two-dimensional tug-of-war, Alex, Betty, and Charles pull horizontally on an automobile tire at the angles shown in the picture. The tire remains stationary in spite of the three pulls. Alex pulls with force F A of magnitude 215 N, and Charles pulls with force F cof magnitude 181 N. Note that the direction of F cis not given. What is the magnitude of Betty's force F B if Charles pulls in (a) the direction drawn in the picture or (b) the other possible direction for equilibrium? Alex Charles 141° Betty (a) Number i Units (b) Number i Unitsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios