
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Luis, Gabi, and Katherine form a partnership. Luis and Gabi give equipment and a building, respectively. Katherine agrees to perform all of the accounting and office work in exchange for a 10% interest.
| FMV | Basis | Partnership % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Luis’s equipment | $ 66,000 | $ 11,000 | 45% |
| Gabi’s building | $ 66,000 | $ 44,000 | 45% |
| Katherine’s services | $ 0 | $ 0 | 10% |
Required:
- What amount of gain, if any, do each of the partners recognize? Note: Leave no cells blank - be certain to enter "0" wherever required.
- What is the basis for each partner in his or her partnership interest?
- What is the basis to the partnership of each asset?
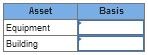
Transcribed Image Text:Asset
Basis
Equipment
Building
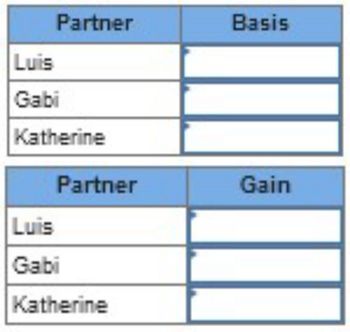
Transcribed Image Text:Luis
Gabi
Partner
Basis
Katherine
Partner
Gain
Luis
Gabi
Katherine
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- This year Sheila's income from her partnership is $225.000 Sheila's business deductions from the partnership total $440,000. Sheila also earns $170,000 of W-2 income and has $65,000 of investment income What is the amount of the excess business loss that is carried forward as a NOL? A.$0 B. $150.000 C. $200.000 D. $216.000arrow_forwardProblem 14-50 (LO 14-1, 14-4) Dennis, Suzy, and Katherine form a partnership. Dennis and Suzy give equipment and a building, respectively. Katherine agrees to perform all of the accounting and office work in exchange for a 10% interest. Dennis's equipment Suzy's building Katherine's services Required: FMV $ 100,000 $ 100,000 $ 0 Basis $ 10,000 $ 45,000 Partnership 45% 451 $ 0 10% a. What amount of gain, if any, do each of the partners recognize? b. What is the basis for each partner in his or her partnership interest? c. What is the basis to the partnership of each asset? Answer is complete but not entirely correct. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required a Required b Required c What amount of gain, if any, do each of the partners recognize? Partner Dennis Suzy Gain $ 10,000 $ 45,000 Katherine $ 20,000 Required a Required b>arrow_forwardQ1. Keith owns three partnership interests that are passive activities. He sells Partnership 3 and realizes a loss of $8,000. His income is: Form W-2 wages Schedule C proprietorship Partnership 1 Partnership 2 Partnership 2 loss carryforward Partnership 3 loss on sale What is Keith's total income? $30,000 20,000 5,000 (2,000) (3,000) (8,000)arrow_forward
- Problem 14-54 (LO 14-2, 14-3) Wade has a beginning basis in a partnership of $23,000. His share of income and expense from the partnership consists of the following amounts: Ordinary income Guaranteed payment Long-term capital gain 5 1231 gain Charitable contributions $ 179 expense Cash distribution Required: a. What is Wade's self-employment income? $ 43,000 12,000 15,500 4,300 2,000 b. Calculate Wade's basis at the end of the year. 18,000 6,000 a. Self-employment income b. Ending basis Amountarrow_forwardacc1arrow_forward11. Help me selecting the right answer. Thank youarrow_forward
- Katie, Berry and Betty agree to share profits and losses: Tom and Betty have $60 and $30 salary allowances Berry has a bonus of 50% of profits in excess of $500 Each have interest allowances of 10% of beginning capital Tom Capital, 1/1 $400 Betty Capital, 1/1 $350 Berry capital, 1/1 400 Remaining profits or losses are shared Tom 30%, Betty 40% and Berry 30%. Partnership profits are $800 for the year.arrow_forward1 John and Mary are equal partnership in a partnership. John's beginning basis is 50,000 and Mary's beginning basis is 70,000 Sales 200,000 Long term capital gain Short term capital loss 6,000 -4,000 Dividend income 2,000 salaries 50,000 Rent Expense 20,000 Interest income 5,000 Depreciation Section 179 expense 30,000 20,000 Distribution to Mary 40,000 Distrbution to John 30,000 1 Calculate ordinary income 2 Calculate Separately Reported Items 3 Calculate ending basis for John and Mary.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education