
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
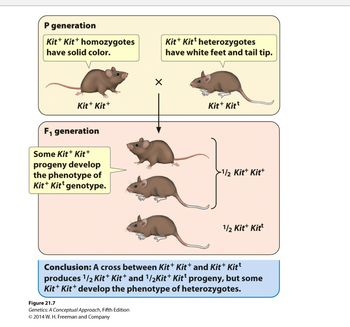
Transcribed Image Text:### Genetic Inheritance in Mice: An Educational Overview
#### P Generation (Parental Generation):
- **Kit⁺ Kit⁺ Homozygotes**:
- Description: Mice with solid color (uniform coat color).
- Genotype: Kit⁺ Kit⁺
- **Kit⁺ Kitᵗ Heterozygotes**:
- Description: Mice with white feet and tail tip.
- Genotype: Kit⁺ Kitᵗ
#### Crossbreeding:
- A cross is made between a Kit⁺ Kit⁺ homozygote and a Kit⁺ Kitᵗ heterozygote mouse.
#### F₁ Generation (First Filial Generation):
- **Offspring (Progeny) Outcomes**:
- Some of the crossbreeds show a **solid color** similar to Kit⁺ Kit⁺ genotype.
- Other offspring have **white feet and a white tail tip**, indicative of the Kit⁺ Kitᵗ genotype.
- **Genotype Ratio**:
- Half of the progeny (1/2) are Kit⁺ Kit⁺.
- The other half (1/2) are Kit⁺ Kitᵗ.
#### Conclusion:
- The cross between Kit⁺ Kit⁺ and Kit⁺ Kitᵗ parental mice results in a progeny that includes both Kit⁺ Kit⁺ (solid color) and Kit⁺ Kitᵗ (white feet and tail tip) genotypes.
- Interestingly, some Kit⁺ Kit⁺ progeny develop the phenotype typical of the Kit⁺ Kitᵗ genotype, i.e., white feet and tail tip.
#### Visual Explanation:
1. **Top Section (P Generation)**:
- Shows two mice, one labeled Kit⁺ Kit⁺ (solid color) and the other Kit⁺ Kitᵗ (white feet and tail tip), signifying the parental generation.
2. **Middle Section (Crossbreeding)**:
- Displays the cross (X) leading to the F₁ generation.
3. **Bottom Section (F₁ Generation)**:
- Illustrates three mice representing the F₁ offspring. Some show the solid color typically associated with the Kit⁺ Kit⁺ genotype, while others display the white feet and tail tip of heterozygotes.
- The genetic ratio is shown with brackets

Transcribed Image Text:### F1 Generation Analysis: Kit+Kit+ and Phenotypic Expression
#### Background Context
Refer to Figure 21.7 in your textbook and consult the associated PowerPoint lecture to understand the inheritance patterns and phenotypic expressions in the F1 generation.
#### Question Analysis
**Question:**
Explain how a Kit+Kit+ mouse in the F1 generation can have white feet and tail. Are both of the Kit+ alleles silenced in the F1 generation Kit+Kit+ mice?
#### Explanation
To address this question, consider the following points:
1. **Genotypic Background:**
- F1 generation mice carrying Kit+Kit+ genotype inherit one Kit+ allele from each parent.
2. **Phenotypic Expression:**
- The occurrence of white feet and tail in a Kit+Kit+ mouse might be attributed to variations in gene expression, regulation, or potential epistatic interactions with other genes influencing pigment production and distribution.
3. **Gene Silencing Mechanism:**
- It's essential to analyze if both Kit+ alleles are silenced. Typically, this would involve understanding if epigenetic modifications, such as methylation, are differentially affecting the alleles or if post-transcriptional regulation mechanisms are in play.
#### Conclusion
The observations of white feet and tail despite the Kit+Kit+ genotype suggest complex regulatory mechanisms. This underscores the importance of examining not just the genetic makeup but also gene expression and regulation to fully understand phenotypic outcomes in the F1 generation.
Note: Detailed explanation of any diagrams or graphs from Figure 21.7 should be provided by consulting the specific textbook or lecture slide referenced. This contextual information would be crucial for a holistic understanding.
Continue exploring these genetic phenomena by engaging with interactive discussions and practical examples provided in your educational resources.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- **GENETICS** why does the map distance calculated between 2 genes need to be adjusted using a mapping function if the calculated frequency is greater than .07 or 7 map units?arrow_forwardPlease help and explainarrow_forwardProvide the required information. Show the COMPLETE 7-step method of gene-interaction and epistasis Dog ears may either be drooping or erect. In terms of their barking, some always bark, otherssometimes bark, and still other are non-barking. Two dogs from the same species but of differentphenotypes were used in the cross: (See attached Image)arrow_forward
- Shown in the pictures below are the degrees of dominance in the inheritance of flower color in some plants. *Based on the phenotypes (or maybe genotype), differentiate between complete dominance, incomplete dominance, and codominance. Be able to discuss the difference briefly but concisely. You may also refer to the definition.arrow_forwardGive typed full explanation The Genes you are examining exhibit a continuous pattern of variation. For these Genes, a Dominant Allele represents a 1 foot increase in overall height. If you cross the following individuals, AaBb and AaBb, what percentage of the offspring will be 7 feet tall. Assume an individual with no Dominant Alleles (aabb) is 4 feet tall. Report your answer as a percentage i.e., 22.1%.arrow_forwardGene interaction and Epistasis Dog ears may either be drooping or erect. In terms of their barking, some always bark, others sometimes bark, and still other are non-barking. Two dogs from the same species but of different phenotypes were used in the cross: P1 phenotype drooping ears & Non-barking X erect ears & sometimes bark P1 genotype AABB aabb F1 phenotype 100% drooping ears & Non-barking F1 genotype AaBb Mating the male and female from F1 produced: F2 phenotypes F2 genotypes 4 drooping ears & non-barking A_B_ 1 drooping ears & always bark A_bb 2 erect ears & sometimes bark aaB_ aabb Using the same…arrow_forward
- Please explain how you do this question step by step I am very confused! thank you:) You have three independent mutant alleles in the Drosophila gene no-antenna: nan1, nan2 and nan3. You determine the phenotype of Drosophila that are heterozygous for the three alleles (heterozygous for a wild-type allele and a mutant allele), and that are homozygous for the three mutant alleles. The antenna is composed of three segments that are followed at the distal end by a feathery arista (that is the antenna is composed of three segments and an arista). Allele nan1 nan2 nan3 heterozygous Wild-type No arista Wild-type homozygous No arista No antenna No antenna nan1 is a __x__ allele, nan2 is a __y__ allele, and nan3 is a __z__ allele. X Y Z A Dominant negative Null Hypomorphic B Null Dominant negative Hypomorphic C Null Hypomorphic Dominant negative D Hypomorphic Dominant negative Null E Dominant negative Hypomorphic Null Referencing the table above, select the…arrow_forward. The human IGF2 gene is autosomal and maternallyimprinted. Copies of the gene received from themother are not expressed, but copies received fromthe father are expressed. You have found two allelesof this gene that encode two different forms of theIGF2 protein distinguishable by gel electrophoresis.One allele encodes a 60K (Kilodalton) blood protein;the other allele encodes a 50K blood protein. In ananalysis of blood proteins from a couple named Billand Joan, you find only the 60K protein in Joan’sblood and only the 50K protein in Bill’s blood. Youthen look at their children: Jill is producing only the50K protein, while Bill Jr. is producing only the 60Kprotein.a. With these data alone, what can you say about theIGF2 genotype of Bill Sr. and Joan?b. Bill Jr. and a woman named Sara have two children, Pat and Tim. Pat produces only the 60K protein and Tim produces only the 50K protein. Withthe accumulated data, what can you now say aboutthe genotypes of Joan and Bill Sr.?arrow_forwardplease make sure to read the question (THERE ARE OTHER VARIATIONS OF THE QUESTION ON DIFFERNT WEBSITES THAT ARE DIFFERENT THAN MINE)arrow_forward
- Answer in step by step with explanation. Don't use Ai and chatgpt.arrow_forward7. please answer thisarrow_forwardYou are interested in studying position effect variegation in Drosophila using the chromosome depicted below: Deactivation of the w+ gene gives a white eye phenotype and deactivation of the rst+ gene gives a rough eye phenotype; the normal phenotypes are red and smooth. Because the rst+ and w+ genes have now been placed close to a heterochromatic domain, some sections (or sectors) of the eye display mutant phenotypes due to gene deactivation while others display the normal, wild type phenotype. Which phenotype would you not expect to see rst w Inverted X chromosome white smooth eye sectors white rough eye sectors red smooth eye sectors red rough eye sectorsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education