
The drug Finasteride is marketed as Propecia to help protect against male pattern baldness, and it also may protect against prostate cancer. A large sampleof healthy men over age 55 were randomly assigned to receive either a daily Finasteride pill or a placebo. The study lasted seven years and the men had annual check-ups and a biopsy at the end of the study. Prostate cancer was found in 804 of 4368 men taking Finasteride and in 1145 of the 4692 men taking a placebo.
Suppose that the investigators want to control for whether a subject is over 60 years old in the logistic model from part (g) above. Let the variable Over60 = 1 if a subject is over 60 and 0 otherwise. They fit a logistic model with both Finasteride and Over60 as the predictors and obtain the following:
Coefficients:
| Estimate | Std. Error | z value | Pr(>|z|) | ||
| (Intercept) | -1.88067 | 0.05075 | -37.059 | < 2e-16 | *** |
| Finasteride | -0.34736 | 0.05355 | -6.486 | 8.79e-11 | *** |
| Over60 | 1.32285 | 0.05589 | 23.670 | < 2e-16 | *** |
What is the estimated odds ratio associated with the coefficient for the Over60 predictor? What is the interpretation?
Suppose that you decide to fit a logistic regression model using these data. Let Y = 1 if a subject develops cancer and 0 otherwise. Let Finasteride = 1 if a subject received Finasteride and 0 if they received placebo. The estimated logistic model is (below). What is the value of hat-b, a, b, c, d, or e?
a.) -0.331 b.) -0.329 c.) -0.123 d.) -0.347 e.) -0.358
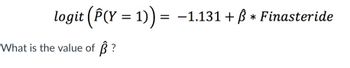
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

- Whirling disease is a deadly disease that affects trout in Montana riversIn a follow-up to a 2006 study conducted by the Montana Department of FishWildlife and Parks (FWP)researchers sought to determine if the proportion of trout afflicted by whirling disease in the Gallatin river differs between rainbow trout and brown trout. To test this theory, researchers collected a representative sample of 527 rainbow trout and 459 brown trout. Of the 527 rainbow trout collected, 120 had developed whirling disease; of the 459 brown trout collected, 74 had developed whirling disease Calculate the relative risk of whirling disease for rainbow trout compared to brown trout in this sample.arrow_forwardFrom the U.S. Census Bureau's American Community Survey in 2019 it was found that 33.13% of United States residents over the age of 25 had an educational attainment of a bachelor's degree or higher. In the District of Columbia, the percentage of residents over the age of 25 who had attained a bachelor's degree or higher was 59.67%. An investigator for the U.S. Census Bureau took a random sample of seven residents from the District of Columbia and asked them their highest educational degree they had obtained. When there is no data set posted for an investigation, open a blank StatCrunch page by clicking "Open StatCrunch" on the StatCrunch home page. a) Verify that the sample from the District of Columbia satisfies the conditions of the binomial experiment. Write one sentence to check each requirement in context of the investigation. b) Assuming the sample from the District of Columbia is a binomial experiment, build the probability distribution in a single table and include the table in…arrow_forwardAn epidemiologist found five cases of “big toe cancer” in the Yukon Territory. Because there were only a few cases, the epidemiologist decided to conduct a matched case-control study to determine whether shoe size larger than 9 is a risk factor for big toe cancer. Cases were individually matched to one control for daily activity, history of athlete’s foot, and history of ingrown toenails. The following data were gathered: Shoe size > 9 Pair Case Control 1 Yes No 2 No No 3 No Yes 4 Yes Yes 5 No Yes Compute the proper measure of association. Interpret your results. If you were to investigate a rare cancer in Lynchburg, where might you look for data? What would be necessary legally and ethically to be able to utilize this data set(s)? Submit your thread by 11:59 p.m. (ET) on Thursday of Module/Week 3, and submit your replies by 11:59 p.m. (ET) on Sunday of the same module/week. 1arrow_forward
- Travelers who have no intention of showing up often fail to cancel their hotel reservations in a timely manner. These travelers are known, in the parlance of the hospitality trade, as “no-shows”. To protect against no-shows and late cancellations, hotels invariably overbook rooms. A recent study examined the problems of over-booking rooms in the hotel industry. The following data, extracted from the study represent the daily numbers of late cancellations and no-shows for a random sample of 10 days at a hotel: 18, 16, 16, 16, 14, 18, 16, 18, 14, 19. c) Count the number of measurements that actually fall within the interval(x¯−2s, x¯+2s){ and express the interval count as a percentage of total number of measurementsarrow_forwardCalcium is the most abundant mineral in the body and also one of the most important. The recommended daily allowance (RDA) of calcium for adults is 800 milligrams (mg). A random sample of 18 people with incomes below the poverty level gives the following daily calcium intakes: 686, 433, 743, 647, 734, 641, 993, 620, 574, 634, 850, 858, 992, 775, 1113, 672, 879, 609 At the 1% significance level, do the data provides sufficient evidence to conclude that the mean calcium intake of all people with income levels below the poverty level is less than the RDA of 800 mg? Step 1 : Step 2: 3.Critical Value approach: 4.Conclusion:arrow_forwardFrom public records, individuals were identified as having been charged with drunken driving not less than 6 months or more than 12 months from the starting date of the study. Two random samples from this group were studied. In the first sample of 25 individuals, the respondents were asked in a face-to-face interview if they had been charged with drunken driving in the last 12 months. Of these 25 people interviewed face to face, 11 answered the question accurately. The second random sample consisted of 40 people who had been charged with drunken driving. During a telephone interview, 26 of these responded accurately to the question asking if they had been charged with drunken driving during the past 12 months. Assume the samples are representative of all people recently charged with drunken driving. (a) Categorize the problem below according to parameter being estimated, proportion p, mean μ, difference of means μ1 – μ2, or difference of proportions p1 – p2. Then solve the problem.…arrow_forward
- please help!!arrow_forwardAn industrial psychologist feels that a big factor in job turnover among assembly-line workers is the individual employees' self-esteem. He thinks that workers who change jobs often (population A) have, on the average, lower self-esteem, as measured by standardized test, than workers who do not (population B). To determine whether he can support his belief with statistical analysis, he draws a simple random sample of employees from each population and gives a test measuring self-esteem. The results are as follows. At 0.05 level of significance and assuming equal variances. Mean Standard Deviation Sample size A 52.3 9.23 10 69.47 11.78 17 Provide the tabular and computed value of the test statistic. O a. 1.703; 3.05 O b. 2.06; 3.94 O . 1.708; 4.01 O d. 2.052; 3.46arrow_forwardAn article included data from a survey of 2587 hiring managers and human resource professionals.The article noted that many employees are using social networks to screen job applicants and that this practice is becoming more common. Of the 2587 people who participated in the survey, 1300 indicated that they use social networking sites ( such as Facebook, MySpace, and LinkedIn) to research job applicants. For the purposes of this exercise, assume that the sample is representative of hiring managers and human resource professionals. d. suppose that researchers wanted to estimate the proportion of hiring managers and human resource professionals who screen job applicants using social networks. determine the sample size required to estimate the proportion of employers using social networks to screen job applicants to within .03 with 99% confidence. ( round your answer up to the nearest whole number ) hint: use formula that is used when the p estimate is unknownarrow_forward
- Travelers who have no intention of showing up often fail to cancel their hotel reservations in a timely manner. These travelers are known, in the parlance of the hospitality trade, as “no-shows”. To protect against no-shows and late cancellations, hotels invariably overbook rooms. A recent study examined the problems of over-booking rooms in the hotel industry. The following data, extracted from the study represent the daily numbers of late cancellations and no-shows for a random sample of 10 days at a hotel: 18, 16, 16, 16, 14, 18, 16, 18, 14, 19. a) Compute s, the sample s.d. for the data setarrow_forwardIdentify whether the studies described here are based on (1) single samples, (2) paired samples, or (3) independent samples. Cardiovascular disease risk factors are compared in husbands and wives. A nutritional exam is applied to a random sample of individuals. Results are compared to the results of the whole nation. An investigator compares vaccination histories in 30 autistic schoolchildren to a simple random sample of non-autistic children from the same school district.arrow_forwardResearchers investigate how the presence of cell phones influence the quality of human interaction. Subjects are randomly selected from a population and divided into an experimental group that is asked to leave their phones in the front of the room and a control group that are not asked to leave their cell phones at the front of the room. Subjects are left alone for 10 minutes and then asked to take a survey designed to measure quality of interactions they had with others in the experiment. What statistical test is appropriate?arrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





