
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
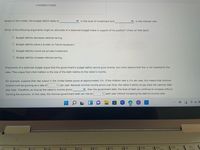
Transcribed Image Text:LOANABLE FUNDS
Based on this model, the budget deficit leads to
in the level of investment and
in the interest rate.
Which of the following arguments might an advocate of a balanced budget make in support of his position? Check all that apply.
Budget deficits decrease national saving.
Budget deficits place a burden on future taxpayers.
Budget deficits crowd out private investment.
Budget deficits increase national saving.
Proponents of a balanced budget argue that the government's budget deficit cannot grow forever, but critics believe that this is not necessarily the
case. They argue that what matters is the size of the debt relative to the nation's income.
For example, suppose that real output in the United States grows at approximately 3%. If the inflation rate is 2% per year, this means that nominal
income must be growing at a rate of % per year. Because nominal income grows over time, the nation's ability to pay back the national debt
also rises. Therefore, as long as the nation's income grows
than the government debt, the level of debt can continue to increase without
harming the economy. In this case, the nominal government debt can rise by % each year without increasing the debt-to-income ratio.
O
F12
F1
F9
(F3
F4
F6
F5
F8
F10
F11
Fn
$
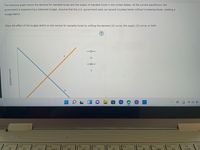
Transcribed Image Text:The following graph shows the demand for loanable funds and the supply of loanable funds in the United States. At the current equilibrium, the
government is experiencing a balanced budget. Assume that the U.S. government bails out several troubled banks without increasing taxes, creating a
budget deficit.
Show the effect of the budget deficit on the market for loanable funds by shifting the demand (D) curve, the supply (S) curve, or both.
D
S
INTEREST RATE
F2
-O-
F3
Ö+
F4
C
D
F5
a
F6
N
F7
51-
F8
5+
F9
Ⓒ
F10
-0.
F11
F12
Fn
Lock
Ins
P
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1) The government's budget deficit increases, and at the same time the trade deficit grows. This will lead to a(n) _____ in the demand and a(n) _____ in the supply of loanable funds in domestic markets. increase; increase decrease; increase decrease; decrease 2) A temporary decrease in government purchases would cause: a rightward shift in the saving curve and a leftward shift in the investment curve. a rightward shift in the saving curve and a rightward shift in the investment curve. no shift in the saving curve, but a leftward shift in the investment curve.arrow_forwardFor a closed economy, GDP is $18 trillion, consumption is $13 trillion, taxes are $2 trillion and the government runs a deficit of $1 trillion. What are private saving and national saving?arrow_forwardIn the Savings-Investment model, what is the effect of an increase in government spending on investment? Why?arrow_forward
- Question 21 An increase in real per capita GDP in an economy would __________ the average standard of living and would _________ life expectancy. raise; have little effect on raise; shorten raise; increase have no effect on; increase lower; shorten Question 22 An increase in _________ would lead to an increase in long-run economic growth. consumer spending and borrowing government taxes and fees resources and technology imports and exports prices and interest rates Question 23 Which of the following are the three major categories of resources? physical capital, technology, institutions land, labor, technology institutions, human capital, land natural resources, physical capital, human capital labor, physical capital, technologyarrow_forwardIn the long-run framework, budget surpluses: Choose the Correct and Explain why its correct should be run whenever output dips below potential output. should never be run since they crowd out investment in the short run. are better than budget deficits over the long run because unlike budget deficits, they increase saving and investment. should be run on a permanent basis since they boost saving and investment and stimulate economic growth.arrow_forwardExplanation it correctlyarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education