
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question

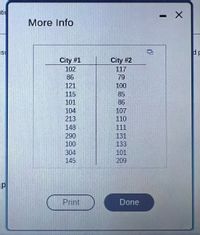
Transcribed Image Text:Listed in the data table are amounts of strontium-90 (in millibecquerels, or mBq, per gram of calcium) in a simple random sample of baby teeth obtained from
residents in two cities. Assume that the two samples are independent simple random samples selected from normally distributed populations. Do not assume that the
population standard deviations are equal. Use a 0.10 significance level to test the claim that the mean amount of strontium-90 from city #1 residents is greater than
the mean amount from city #2 residents.
Click the icon to view the data table of strontium-90 amounts.
What are the null and alternative hypotheses? Assume that population 1 consists of amounts from city #1 levels and population 2 consists of amounts from city #2.
O A. Ho: H1= H2
H1: H1> H2
O B. Ho: H1 H2
H1: H1> H2
O D. Ho: H1= H2
O C. Ho: H1SH2
H1: H1> H2
H1: H1##2
Transcribed Image Text:nti
More Info
S
City #1
102
City #2
117
79
86
121
100
115
101
85
86
104
213
107
110
111
131
148
290
100
304
145
133
101
209
up
Print
Done
中
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 8 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 4arrow_forwardThe blood platelet counts of a group of women have a bell-shaped distribution with a mean of 245.4 and a standard deviation of 63.6. (All units are 1000 cells/μL.) Using the empirical rule, find each approx. percentage below. a. What is the approx. percentage of women with platelet counts within 3 standard deviations of the mean, or between 54.6 and 436.2? b. what is the approx. percentage of women with platelet counts between 118.2 and 372.6?arrow_forwardA company that makes cola drinks states that the mean caffeine content per 12-ounce bottle of cola is 45 milligrams. You want to test this claim. During your tests, you find that a random sample of thirty 12-ounce bottles of cola has a mean caffeine content of 46.7 milligrams. Assume the population is normally distributed and the population standard deviation is 7.7 milligrams. At α=0.05, can you reject the company's claim? Complete parts (a) through (f). (a) Identify H0 and Ha. (b) Find the critical value(s). Select the correct choice below and fill in the answer box within your choice. c) Identify the rejection region(s). Choose the correct answer below. d) Find the standardized test statistic. e) Decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis. f) Interpret the decision in the context of the original claim.arrow_forward
- A company that makes cola drinks states that the mean caffeine content per 12-ounce bottle of cola is 35 milligrams. You want to test this claim. During your tests, you find that a random sample of thirty 12-ounce bottles of cola has a mean caffeine content of 33.4 milligrams. Assume the population is normally distributed and the population standard deviation is 7.9 milligrams. At α=0.05, can you reject the company's claim? -Identify Ho and Ha. -Find the critical value and sketch the region -Calculate the test statistic -Do you reject Ho or fail to reject Haarrow_forwardAn SRS of size 10 is drawn from a population that has a normal distribution. The sample has a mean of 139 and a standard deviation of 7. Give the standard error of the mean 7 , 1arrow_forwardA company that makes cola drinks states that the mean caffeine content per 12-ounce bottle of cola is 35 milligrams. You want to test this claim. During your tests, you find that a random sample of thirty 12-ounce bottles of cola has a mean caffeine content of 35.4 milligrams. Assume the population is normally distributed and the population standard deviation is 7.9 milligrams. At α=0.05, can you reject the company's claim? Complete parts (a) through (e). Part 1(a) Identify H0 and Ha. Choose the correct answer below. A.) H0:μ≥35.4 Ha:μ<35.4 B.) H0:μ≠35 Ha:μ=35 C.) H0:μ=35 Ha:μ≠35 D.) H0: μ≥35 Ha: μ<35 E.) H0: μ≠35.4 Ha:μ=35.4 F.) H0: μ=35.4 Ha:μ≠ 35.4 (b) Find the critical value(s). Select the correct choice below and fill in the answer box within your choice. (c) Find the standardized test statistic. z= (d) Decide whether to reject or fail to reject…arrow_forward
- A researcher compares two compounds (1 and 2) used in the manufacture of car tires that are designed to reduce braking distances for SUVS equipped with the tires. The mean braking distance for SUVs equipped with tires made with compound 1 is 71 feet, with a population standard deviation of 11.0. The mean braking distance for SUVs equipped with tires made with compound 2 is 74 feet, with a population standard deviation of 12.3. Suppose that a sample of 70 braking tests are performed for each compound. Using these results, test the claim that the braking distance for SUVS equipped with tires using compound 1 is shorter than the braking distance when compound 2 is used. Let μ₁ be the true mean braking distance corresponding to compound 1 and μ₂ be the true mean braking distance corresponding to compound 2. Use the 0.05 level of significance. Step 2 of 5: Compute the value of the test statistic. Round your answer to two decimal places. Answer How to enter your answer (opens in new window)…arrow_forwardThe average size of a farm in one county is 162 acres with a standard deviation of 38 acres. The average size of a farm in a second county is 180 acres with a standard deviation of 40 acres. Assume the data were obtained from two samples that had 30 farms each. Can it be concluded that the average size of the farms in the two counties is different? (Let α = 0.05)arrow_forwardThe daily sleep duration among college students is normally distributed with a mean of 8.13 and standard deviation of 1.87. You want to use a sample size such that 95% of the averages fall within ±15±15 minutes (.25 of an hour) of the true mean of 8.13. Determine the smallest number of students you need to sample.arrow_forward
- The daily sleep duration among college students is normally distributed with a mean of 7.13 hours and standard deviation of 1.67 hours. You want to use a sample size such that 95% of the averages fall within ±15±15 minutes (.25 of an hour) of the true mean of 7.13 hours. Determine the smallest number of students you need to sample.arrow_forwardTo compare the dry braking distances from 30 to 0 miles per hour for two makes of automobiles, a safety engineer conducts braking tests for 35 models of Make A and 35 models of Make B. The mean braking distance for Make A is 43 feet. Assume the population standard deviation is 4.6 feet. The mean braking distance for Make B is 46 feet. Assume the population standard deviation is 4.5 feet. At α=0.10, can the engineer support the claim that the mean braking distances are different for the two makes of automobiles? Assume the samples are random and independent, and the populations are normally distributed. The critical value(s) is/are Find the standardized test statistic z for μ1−μ2.arrow_forwardA company that makes cola drinks states that the mean caffeine content per 12-ounce bottle of cola is 35 milligrams. You want to test this claim. During your tests, you find that a random sample of thirty 12-ounce bottles of cola has a mean caffeine content of 33.4 milligrams. Assume the population is normally distributed and the population standard deviation is 7.4 milligrams. At α=0.09, can you reject the company's claim? Identify Ho and Ha Find the critical values and rejection regions Find standardized test statistic Decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis. interpret the decision in the context of the original claim.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman