
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
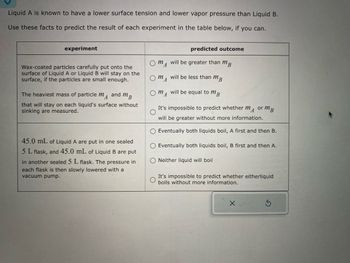
Transcribed Image Text:### Experiment Analysis: Surface Tension and Vapor Pressure
**Background**:
Liquid A has a lower surface tension and lower vapor pressure compared to Liquid B. These properties affect how particles behave on the surface of the liquids and their boiling points under reduced pressure.
#### Experiment 1: Surface Tension
**Objective**:
Determine the heaviest mass of particles (\(m_A\) and \(m_B\)) that can remain on the surface of Liquid A and Liquid B without sinking.
- **Predicted Outcomes**:
- \(m_A\) will be greater than \(m_B\)
- \(m_A\) will be less than \(m_B\)
- \(m_A\) will be equal to \(m_B\)
- It's impossible to predict whether \(m_A\) or \(m_B\) will be greater without more information
#### Experiment 2: Boiling Point under Reduced Pressure
**Objective**:
Assess the boiling behavior of equal volumes of Liquids A and B when placed in separate 5 L sealed flasks and subjected to a gradual pressure reduction using a vacuum pump.
- **Predicted Outcomes**:
- Eventually both liquids boil, A first and then B.
- Eventually both liquids boil, B first and then A.
- Neither liquid will boil.
- It's impossible to predict whether either liquid boils without more information.
These experiments utilize the distinct properties of liquid A and B to predict behaviors crucial in chemical and physical processes. Further data or experimental results are needed for conclusive predictions.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please answer question 3.arrow_forwardPlease don't provide handwriting solutionarrow_forwardPhysical states and phase changes (1) The forces that cause butter to melt on a slice of hot bread are (2) The forces that prevent O2 molecules in the upper atmosphere from forming O atoms are (3) A dog regulates its body temperature by panting, exhaling moisture through its tongue. This phase change is called + . In this process, energy is (4) Frost forms on your car's windshield overnight in the winter. This phase change is called In this process, energy isarrow_forward
- If 145 KJ Of Energy Is Added To Water, What Mass Of Water Can Be Heated From 35 °C To 100 C And Then Vaporized At 100°C A.arrow_forwardLiquid X is known to have a higher viscosity and higher surface tension than Liquid Y. Use these facts to predict the result of each experiment in the table below, if you can. experiment predicted outcome Omx will be greater than my Wax-coated particles carefully put onto the surface of Liquid X or Liquid Y will stay on the surface, if the particles are small enough. my will be less than my The heaviest mass of particle m т mx will be equal to My and my that will stay on each liquid's surface without sinking are measured. It's impossible to predict whether my or my will be greater without more information. Sy will be greater than Sy Small amounts of Liquid X and Liquid Y are sprayed into the air, where they form perfect spheres with a volume of 10.0 µL. The diameters of these drops are measured with a high-speed camera, and their surface areas Sy will be less than Sy Sy will be equal to Sy Sy and Sy calculated. It's impossible to predict whether Sy or Sy will be greater without more…arrow_forwardDetermain the boiling point of water at 672 mm Hg.arrow_forward
- - Suppose a small sample of pure X is held at -236.°C and 2.0 atm. What will be the state of the sample (solid, liquid, or gas)? - Suppose the temperature is held constant at -236.°C but the pressure is decreased by 1.2 atm. What will happen to the sample (nothing, it will melt, it will freeze, it will boil, it will condense, it will sublime, or it will deposit)? - Suppose, on the other hand, the pressure is held constant at 2.0 atm but the temperature is increased by 137°C. What will happen to the sample (nothing, it will melt, it will freeze, it will boil, it will condense, it will sublime, or it will deposit)? All these are part of one question.arrow_forwardCohesive forces in matter are related to potential energy from particle attractions. potential energy from particle repulsions. Okinetic energy. More than one response is correct.arrow_forward3. It is a quantity of heat need to convert a mole of liquid into gas phase at a specified temperature? a. molar enthalpy of vaporization b. molar enthalpy of boiling c. molar enthalpy of freezing d. molar enthalpy of evaporationarrow_forward
- 3) If water is placed in a test tube, covered with a piece of stiff рaper paper and inverted, the paper and water will not fall from the test tube. Why does it remain in the test tube?arrow_forward2. How are attractive forces related to the motion and the amount of kinetic energy of the particles?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY