
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Transcribed Image Text:=
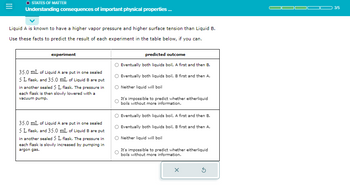
STATES OF MATTER
Understanding consequences of important physical properties ...
Liquid A is known to have a higher vapor pressure and higher surface tension than Liquid B.
Use these facts to predict the result of each experiment in the table below, if you can.
experiment
35.0 mL of Liquid A are put in one sealed
5 L flask, and 35.0 mL of Liquid B are put
in another sealed 5 L flask. The pressure in
each flask is then slowly lowered with a
vacuum pump.
35.0 mL of Liquid A are put in one sealed
5 L flask, and 35.0 mL of Liquid B are put
in another sealed 5 L flask. The pressure in
each flask is slowly increased by pumping in
argon gas.
O
predicted outcome
Eventually both liquids boil, A first and then B.
Eventually both liquids boil, B first and then A.
Neither liquid will boil
It's impossible to predict whether eitherliquid
boils without more information.
Eventually both liquids boil, A first and then B.
Eventually both liquids boil, B first and then A.
Neither liquid will boil
It's impossible to predict whether eitherliquid
boils without more information.
5
3/5
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please don't provide handwritten solution...arrow_forwardThe pressure above a pure sample of solid Substance X at -10. °C is lowered. At what pressure will the sample melt? Use the phase diagram of X below to find your answer. pressure (atm) 04- 02- 6 0 atm solid liquid 400 temperature (K) Note: your answer must be within 0.025 atm of the exact answer to be graded correct. gas 600arrow_forwardThe pressure above a pure sample of solid Substance X at -146. °C is lowered. At what pressure will the sample sublime? Use the phase diagram of X below to find your answer. pressure (atm) solid 200 liquid temperature (K) 400 gas Note: your answer must be within 0.5 atm of the exact answer to be graded correct.arrow_forward
- Four liquids are described in the table below. Use the second column of the table to explain the order of their freezing points, and the third column to explain the order of their boiling points. For example, select '1' in the second column next to the liquid with the lowest freezing point. Select '2' in the second column next to the liquid with the next higher freezing point, and so on. In the third column, select '1' next to the liquid with the lowest boiling point, '2' next to the liquid with the next higher boiling point, and so on. Note: the density of water is 1.00 g/mL. solution 7.3 g of sodium chloride (NaCl) dissolved in 350. mL of water 7.3 g of hydrobromic acid (HBr) dissolved in 350. mL of water 7.3 g of glucose (C6H1206) dissolved in 350. mL of water 350. mL of pure water freezing point (choose one) € (choose one) (choose one) (choose one) @ X boiling point (choose one) (choose one) (choose one) (choose one) C Śarrow_forwardFour liquids are described in the table below. Use the second column of the table to explain the order of their freezing points, and the third column to explain the order of their boiling points. For example, select '1' in the second column next to the liquid with the lowest freezing point. Select '2' in the second column next to the liquid with the next higher freezing point, and so on. In the third column, select '1' next to the liquid with the lowest boiling point, '2' next to the liquid with the next higher boiling point, and so on. Note: the density of water is 1.00 g/mL. solution 2.1 g of potassium nitrate (KNO3) dissolved in 150. mL of water 2.1 g of potassium chloride (KCI) dissolved in 150. mL of water 2.1 g of hydroiodic acid (HI) dissolved in 150. mL of water 150. mL of pure water freezing point (choose one) ✓ (choose one) ✓ (choose one) (choose one) boiling point (choose one) (choose one) (choose one) (choose one) ✓arrow_forwardThis graph shows how the vapor pressure of three liquids varies with temperature: vapor pressure, torr 900- 800- 700- 600 500 400. 300 200 100. 0+ 100 130 temperature, °C Use the graph to answer the following questions: 110 120 Which liquid is the most volatile? Which is the least volatile? What is the normal boiling point of each liquid? Note: your answer must be within 1°C of the exact answer to be Suppose a beaker of isobutyl alcohol is put inside a sealed tank containing isobutyl alcohol gas at 106. degree C and 701. torr. After ten minutes, will there be more liquid in the beaker, less liquid, or the same amount? ▪ethylbenzene - isobutyl alcohol orthoxylene 140 most volatile: least volatile: ethylbenzene: isobutyl alcohol: orthoxylene: more less the same ✓ choose one ethylbenzene isobutyl alcohol orthoxylene °C °Carrow_forward
- Four liquids are described in the table below. Use the second column of the table to explain the order of their freezing points, and the third column to explain the order of their boiling points. For example, select '1' in the second column next to the liquid with the lowest freezing point. Select '2' in the second column next to the liquid with the next higher freezing point, and so on. In the third column, select '1' next to the liquid with the lowest boiling point, '2' next to the liquid with the next higher boiling point, and so on. Note: the density of water is 1.00 g/mL. olo solution freezing point boiling point Ar 5.5 g of hydroiodic acid (HI) dissolved in 200. mL of water (choose one) (choose one) 5.5 of calcium chloride (CaCl2) dissolved in 200. mL of water (choose one) (choose one) 5.5 g of potassium hydroxide (KOH) dissolved in 200. mL of water (choose one) (choose one) 200. mL of pure water (choose one) (choose one) ?arrow_forwardTry Again Your answer is incorrect. The enthalpy of vaporization of Substance X is 23.0 Round your answer to 2 significant digits. 0.32 atm x10 X kJ and its normal boiling point is 10. °C. Calculate the vapor pressure of Xat - 18. °C. mol Sarrow_forwardRefer to the following phase diagram (not to scale!) for sulfur dioxide: P atm 78 1.00 0.0017 197.6 200.4 Choose all that apply T Kelvin A sample of sulfur dioxide at a pressure of 1.70×10-3 atm and a temperature of 266 K is compressed at constant temperature to a pressure of 83.7 atm. Which of the following are true? 263.1 430.7 The sample is initially a gas. The liquid initially present will vaporize. The final state of the substance is a liquid. The sample is initially a solid. One or more phase changes will occur.arrow_forward
- Compound Molar Mass (g/mol) Boiling point (degrees C) CH3CH2CH2OH (1-propanol) 60.1 97 CH3(CH2)2CH3 (butane) 58.1 -0.5 CH3COCH3 (acetone) 58.1 56.2 a)Identify all intermolecular forces present in a pure sample of these compounds. b)Explain the difference in boiling points of these three compounds. c)Which substance will have the highest vapor pressure?arrow_forwardFour liquids are described in the table below. Use the second column of the table to explain the order of their freezing points, and the third column to explain the order of their boiling points. For example, select '1' in the second column next to the liquid with the lowest freezing point. Select '2' in the second column next to the liquid with the next higher freezing point, and so on. In the third column, select '1' next to the liquid with the lowest boiling point, '2' next to the liquid with the next higher boiling point, and so on. Note: the density of water is 1.00 g/mL. solution freezing point boiling point 2.0 g of ethylene glycol (C2H602) dissolved in 300. mL of water (choose one) (choose one) 2.0 g of potassium acetate (KCH3CO2) dissolved in 300. mL of water (choose one) (choose one) 2.0 g of glucose (C6H1206) dissolved in 300. mL of water (choose one) (choose one) 300. mL of pure water (choose one) (choose one)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY