
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
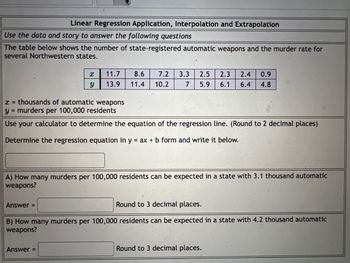
Transcribed Image Text:Linear Regression Application, Interpolation and Extrapolation
Use the data and story to answer the following questions
The table below shows the number of state-registered automatic weapons and the murder rate for
several Northwestern states.
x
11.7 8.6 7.2 3.3 2.5 2.3 2.4 0.9
13.9 11.4 10.2 7 5.9 6.1 6.4 4.8
Y
x = thousands of automatic weapons
y = murders per 100,000 residents
Use your calculator to determine the equation of the regression line. (Round to 2 decimal places)
Determine the regression equation in y = ax + b form and write it below.
A) How many murders per 100,000 residents can be expected in a state with 3.1 thousand automatic
weapons?
Answer =
Round to 3 decimal places.
B) How many murders per 100,000 residents can be expected in a state with 4.2 thousand automatic
weapons?
Answer =
Round to 3 decimal places.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Check for accuracy and respond the last questions 2. For this problem, use Chapter 11 Data Set 3. We want to know if urban and rural residents both have the same attitude toward gun control. a. What is the null hypothesis? The null hypothesis concludes that there is no difference in attitudes toward gun control between urban and rural residents. b. What is the research hypothesis? The research hypothesis suggests that there is a difference in attitudes toward gun control between urban and rural residents. c. Will you be conducting a one-tailed or a two-tailed test? Why? In this case I would conduct a two-tailed test because i’m interested in whether there is a difference in attitudes toward gun control between urban and rural residents, regardless of which direction that difference follows. e.- What is the p-value (hint: it is under “sig” in the output table)? The P-value is 0.44. Do you reject the null hypothesis or fail to reject the null? What do you conclude about urban and…arrow_forwardChallenge The following box plots show monthly average high temperature from January to December in degrees Fahrenheit for two U.S. cities. Which city should you live in if you want the most variability in temperature? City X City Y 10 15 20 25 40 45 50 55 60 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 Degrees Fahrenheit Degrees Fahrenheit Which city should you live in if you want the most variability in temperature? O A. City X and City Y, because they have the same variability in te O B. City Y OC. City Xarrow_forwardThe data below represent the number of days absent, x, and the final grade, y, for a sample of college students at a large university. Complete parts (a) through (e) below. У, No. of absences, x 1 2 4 6. 7 8 9. Final grade, y 88.8 85.9 83.0 80.6 77.7 73.3 63.5 68.3 65.4 62.6 (Round to three decimal places as needed.) A. For every unit change in the final grade, the number of days absent falls by days, on average. B. For every day absent, the final grade falls by on average. C. For zero days absent, the final score is predicted to be 88.778 . D. For a final score of zero, the number of days absent is predicted to be days. E. It is not appropriate to interpret the y-intercept. (c) Predict the final grade for a student who misses five class periods and compute the residual. Is the observed final grade above or below average for this number of absences? The predicted final grade is |. This observation has a residual of, which indicates that the final grade is average. (Round to one decimal…arrow_forward
- Researchers wondered whether the size of a person's brain was related to the individual's mental capacity. They selected a sample of 5 females and 5 males and measured their MRI image pixel counts and IQ scores. Females Males MRI IQ MRI IG The data is reported to the right. Complete parts (a) through (d) below 139 858,472 140 955,003 935,494 924,059 1.079.550 1,001.121 Click the icon to view the critical values table. 991,305 138 141 857,782 833,868 790,619 133 135 132 141 135 140 AMRI 1,080,000- AIO 145 AIO 145- AMRI 1,080,000 780,000 130 130 780,000 130 780,000 780,000 130 1,080,000 145 1,080,000 MRI 145 MRI (b) Compute the linear correlation coefficient between MRI count and IQ. Are MRI count and IQ linearly related? Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your choice. (Round to three decimal places as needed.) A. Yes, MRI count and IQ are linearly related since the linear correlation coefficient is O B. No. MRI count and IQ are not…arrow_forwardLesson 7Q8 Identify the well-known consistent estimators. A.Sample mean B.Sample variance C.Sample mean and sample variance D.Population mean and population variancearrow_forwardA study was done to look at the relationship between number of movies people watch at the theater each year and the number of books that they read each year. The results of the survey are shown below. Movies 10 7 6 10 0 9 1 6 Books 0 0 -0 0 9 0 9 -0 Use the model to predict the number of books read per year for someone who watches 3 movies per year.Books per year = (Please round your answer to the nearest whole number.) Interpret the slope of the regression line in the context of the question: The slope has no practical meaning since people cannot read a negative number of books. As x goes up, y goes down. For every additional movie that people watch each year, there tends to be an average decrease of 0.98 books read. Interpret the y-intercept in the context of the question: The y-intercept has no practical meaning for this study. If someone watches 0 movies per year, then that person will read 8 books this year. The best prediction for a person who doesn't watch…arrow_forward
- I need help with this problemarrow_forwardIdentify the type of observational study (cross-sectional, retrospective, or prospective) described below. A research company uses a device to record the viewing habits of about 10,000 households, and the data collected over the next 10 years will be used to determine whether the proportion of households tuned to a particular children's program decreases. Which type of observational study is described in the problem statement? O A prospective study O A retrospective study A cross-sectional study F4 F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 DELL F10 (... F11 -O F12 O PrtScr Insert Delete PgUp 。 Next PgDn Hoarrow_forwardWhich of the following must be entries from the original data set? the mode the range the third quartile the median the maximumarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman