
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
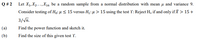
Transcribed Image Text:Let X1, X2...,X16 be a random sample from a normal distribution with mean µ and variance 9.
Consider testing of Ho: µ < 15 versus H,:4 > 15 using the test Y: Reject H, if and only if X > 15+
Q # 2
3/Vn.
(a)
Find the power function and sketch it.
(b)
Find the size of this given test Y.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Parts (a) and (b) are both related to normal distribution but are not directly connected to each other. Please complete both parts. Sketch two normal pdfs, both with u=-1, but one with (a) o=2 and the other with o =7. Label the curves. (b) Compute P(|Z| < 2.43). Assume that Z is a standard normal random variable. 2.arrow_forwardThe average age of the library books is μ = 20 in California. This distribution is negatively skewed. But the librarian at the local elementary school claims that, on average, the books in the library are more than 20 years old. To test this claim, this librarian takes a sample of n = 16 books and records the publication date for each. The sample produces an average age of M = 23.8 years with a variance of s² = 67.5. Do the data from this sample provide evidence that the age of books in this local elementary school is older than the average age of population? Use α = .01arrow_forwardDo a two-sample test for equality of means assuming unequal variances. Calculate the p-value using Excel. (a-1) Comparison of GPA for randomly chosen college juniors and seniors: x⎯⎯1x¯1 = 4.5, s1 = .20, n1 = 15, x⎯⎯2x¯2 = 4.9, s2 = .30, n2 = 15, α = .025, left-tailed test.(Negative values should be indicated by a minus sign. Round down your d.f. answer to the nearest whole number and other answers to 4 decimal places. Do not use "quick" rules for degrees of freedom.) d.f. t-calculated p-value t-critical (a-2) Based on the above data choose the correct decision. Do not reject the null hypothesis Reject the null hypothesis (b-1) Comparison of average commute miles for randomly chosen students at two community colleges: x⎯⎯1x¯1 = 23, s1 = 5, n1 = 22, x⎯⎯2x¯2 = 32, s2 = 7, n2 = 19, α = .05, two-tailed test.(Negative values should be indicated by a minus sign. Round down your d.f. answer to the nearest whole number and other answers to 4…arrow_forward
- Let X1, X2, .. ., Xn be a random sample from a normal distribution with mean u and variance o?. Find an estimator for o? using the method of moments. Is this estimator bi- ased/unbiased? Is it consistent?arrow_forwardDo a two-sample test for equality of means assuming unequal variances. Calculate the p-value using Excel. (a-1) Comparison of GPA for randomly chosen college juniors and seniors: x⎯⎯1x¯1 = 4.5, s1 = .20, n1 = 15, x⎯⎯2x¯2 = 4.9, s2 = .30, n2 = 15, α = .025, left-tailed test.(Negative values should be indicated by a minus sign. Round down your d.f. answer to the nearest whole number and other answers to 4 decimal places. Do not use "quick" rules for degrees of freedom.) d.f. Not attempted t-calculated Not attempted p-value Not attempted t-critical Not attempted (a-2) Based on the above data choose the correct decision. Do not reject the null hypothesis Reject the null hypothesisarrow_forwardLet x = age in years of a rural Quebec woman at the time of her first marriage. In the year 1941, the population variance of x was approximately ?2 = 5.1. Suppose a recent study of age at first marriage for a random sample of 41 women in rural Quebec gave a sample variance s2 = 2.9. Use a 5% level of significance to test the claim that the current variance is less than 5.1. Find the value of the chi-square statistic for the sample. (Round your answer to two decimal places.) What are the degrees of freedom?arrow_forward
- Suppose that X₁,..., Xn are i.i.d. from a normal population with mean μ and variance o². Calculate the expected value and the variance of the sample mean X and find the distribution of √n(X − µ).arrow_forwardLet X1, X2,..., Xn be a random sample of size n > 3 from a normal distribution with unknown mean μ and known variance equal to 2. Show that is an unbiased estimator of μ and compute its variance. parrow_forwardIf X is a negative binomial rv, then Y= r+Xis the total number of trials necessary to obtainr S’s. Obtain the mgf of Y and then its mean valueand variance. Are the mean and variance intuitively consistent with the expressions for E(X)and V(X)? Explainarrow_forward
- Let X1, X2, X3, ..., X, be a random sample from a distribution with known variance Var(X,) = o², and unknown mean EX, = 0. Find a (1 – a) confidence interval for 0. Assume that n is large.arrow_forwardCompute the standard score (Z-score) for x, when x = 21, the mean of the distribution = 27, and the variance (S2) = 9. Z = %3D O 2 -2 .67 -.67arrow_forwardThe table below shows the number of hours per day 11 patients suffered from headaches before and after 7 weeks of soft tissue therapy. At x = 0.01, is there enough evidence to conclude that soft tissue therapy helps to reduce the length of time patients suffer from headaches? Assume the samples are random and dependent, and the population is normally distributed. Complete parts (a) through (f). Patient 8 9 10 11 Q 1 Daily headache hours (before) 2.3 3.4 3.3 2.6 1.8 Daily headache hours (after) 1.8 2.7 1.8 1.6 1.9 1.9 1.2 2.5 2.2 2.0 1.1 2 3 4 5 6 7 4.1 3.2 3.5 2.4 3.7 2.6 C (a) Identify the claim and state Ho and Ha The claim is "The therapy the length of time patients suffer from headaches." Let μd be the hypothesized mean of the patients' daily headache hours before therapy minus their daily headache hours after it. State Ho and H₂. Choose the correct answer below. OA. Ho: Hd=d O C. Ho: Hd ≤0 OB. Ho. Họ sở Ha: Hd >d Ha: Hdd Ha: Hd>0 OD. Ho: Hd #d Ha:Hd=d O E. Ho: Hd zd Ha: Hd 3.169…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman