
Database System Concepts
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780078022159
Author: Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
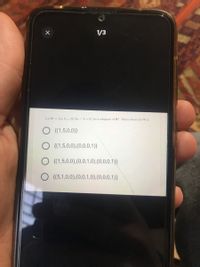
Transcribed Image Text:1/3
Let W = [(a, b, c, d)| 5a - b=0 ) be a subspace of R'. Then a basis for W is
O {(1,5,0,0)}
O {(1,5,0,0),(0,0,0,1)}
O {(1,5,0,0),(0,0,1,0),(0,0,0,1)}
{(5,1,0,0),(0,0,1,0),(0,0,0,1)}
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Need help with longest increasing subsequence problem in the image in O(n^2)arrow_forwardProblem 28. Prove that, for every IL FSC C = (Q,δ,ν,s) and every n ∈ N, there is an input string w ∈ {0,1}^n such that |C(w)|≥n−log2 |Q| .arrow_forward6. Find g •f (a) f:Ž– N, f(n) = n² + 1; g:N → Q, g(n) = g: (0, 1) → (0, 1), g(x) =1– x. (b) f:R → (0, 1), f(x)= 1/(x² + 1); (c) f:Q – {2} → Q*, f(x) = 1/(x – 2); (d) f:R → [1,00), f(x)= x² + 1; g: Q* → Q*, g(x) = 1/x. g:[1, 00) → [0, 0) g(x)= /r – 1. + [0, 00) g(x) = Vx – 1. (e) f:Q – {10/3} → Q – {3}, f(x) = 3x – 7; 2r /(т — 3). g: Q – {3} → Q – {2}, g(x) =arrow_forward
- The correct statements are: Let R = {(1,2), (2,3), (3,4)}. {(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4), (1, 3), (1, 4), (2, 4), (4,4)} is the transitive closure of R. Let R = {(1,2), (2,3), (3,4)}. {(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4), (1, 1), (2, 2), (3, 3), (4,4)} is the reflexive closure of R. Let R = {(1,2), (2,3), (3,4)}. {(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4), (2, 1), (3, 2), (4, 3), (4, 4)) is the symmetric closure of R.arrow_forwardFind a countermodel for each of the following wffs: Jx p(x) → Vx p(x) Vx (p(x, f(x)) → p(x, y))arrow_forwardLet i, j ∈ Za and w, x ∈ Zb with i, j different from each other and w, x different from each other. When a function f : Za → Zb is chosen at random, what is Pr[f(j) = x | f(i) = w]?arrow_forward
- For each function, indicate the class Θ(g(n)) the function belongs to. Prove each assertion. 1. f(n) = 2n ln(n+2)2 + (n+2)2 ln(n/2) 2. f(n) = 2n+1 + 3n+1 3. f(n) = floor(ln(n))arrow_forwardGiven interpretations (a) (Vx) (y) P(x, y) → (x)(Vy) P(x, y) (b) (Vx) [P(x) → Q(x)] → [(x) P(x) → (Vx)Q(x)] (c) (Vx)[A(x)]' → [(Vx)A(x)]' to prove that each of the following wffs is not valid.arrow_forwardIs it true that for any nfa M = (Q,E,8.90,F) the complement of L(M)is equal to the set {w e E*: 8* (40,w) n. F= Ø}? If so, prove it. If not, give a counterexample. Is it true that for every nfa M = (Q, £,8,40.F)the complement of L (M)is equal to the set {w e £* : 8*; (g0,w) e (Q – F) = Ø}? If so, prove it; if not, give a counterexample.arrow_forward
- Consider F = {BC -> D, B -> E, CE -> D, E -> CA, BF -> G} and R(A,B,C,D,E,F,G) 1.Find a minimal cover for F. 2.Find all many keys for R.arrow_forwardLet f (f(n) and g(n)) be asymptotically nonnegative functions. Using the basic definition of Θ notation, prove that max(f(n), g(n)) = Θ(f(n) + g(n)),arrow_forwardExercise 12.9 Given a weighted (connected) undirected graph G = (V, E, w), with m =n+ 0(1) edges (i.e., the number of edges is at most the number of vertices plus some constant), give an O(n)-time algorithm to compute the minimum spanning tree of G. Prove the correctness and the running time of your algorithm. (Hint: Think of how one can eliminate an edge from being in the MST.)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780134444321
Author:Tony Gaddis
Publisher:PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780132737968
Author:Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780133976892
Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337627900
Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education