
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Show the solution for the derivatives. Note not dY*/dG, dY*/dY... but dY/dG, dY/Y, dY/dS
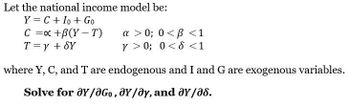
Transcribed Image Text:Let the national income model be:
Y = C + Io + Go
C = x +B(Y-T)
T = y + SY
a >0; 0<B<1
Y>0; 0 < d < 1
where Y, C, and T are endogenous and I and G are exogenous variables.
Solve for ay/aGo, Y/Oy, and ay/a8.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Given that a country will analyze the total benefit of its oil supply-demand in two periods of time by using the following data: Period I Deman curve: P = -0.2 Q₁ + 210 Suply curve: P = 0.04 Q₁ + 30 Interest rate : 10%, Oil reserve : 3.6 billion barrels of oil Units: P in USD, Q in million barrel Period II Deman curve: P = -0.2 Q₂ +210 Suply curve: P = 0.05 Q₂ + 30 Find the efficient allocation! (Q₁, Q₂, P₁, P₁, NB₁, NB₂, TNB), draw a graphical illustration!arrow_forwardHow many points (out of the 6 shown) can be explicitly plotted to form the IS curve given the goods market equilibrium?A goods market equilibrium is shown below: A, B, C, D, E, F 32- A goods market equilibrium is shown below: S₁ (Y= 400) 28- Real Interest Rate, r (%) S2(Y=600) S3 (Y = 800) 226 24- A 20- B C 16- 12- E 4- 0- 0 l(r) F 50 100 150 200 250 300 Desired national saving / desired investment We recommend that you drow out the IS curve before answeringarrow_forwardWhenever the interest charge for any interest period (a year, for example) is based on the remaining principal amount plus any accumulated interest charges up to the beginning of that period, the interest is said to be: a. effective interest b. compound interest c. simple interest d. nominal interest e. none of the choicesarrow_forward
- 2. C = 50 + .8YD = 50 + .8(Y – T) %3D | = 150 %3D G = 200 T = 200 a) Calculate AY if AG = 100 (assuming that G could change all by itself). b) Calculate AY if AT = 100 (assuming that T could change all by itself). c) Calculate AY for AG = AT = 100.arrow_forwardHello, can you explain how I’m supposed to figure this out? How am I supposed to know which Qs and Qd correlate?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education