
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
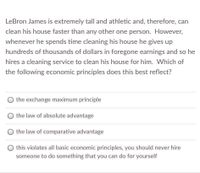
Transcribed Image Text:LeBron James is extremely tall and athletic and, therefore, can
clean his house faster than any other one person. However,
whenever he spends time cleaning his house he gives up
hundreds of thousands of dollars in foregone earnings and so he
hires a cleaning service to clean his house for him. Which of
the following economic principles does this best reflect?
the exchange maximum principle
the law of absolute advantage
the law of comparative advantage
this violates all basic economic principles, you should never hire
someone to do something that you can do for yourself
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Suppose two countries, France and Germany, use only capital and labor for production. Factor endowments of the nations are presented in the table below. Capital | Labor France 2200 800 Germany 880 220 a. Which country is labor-abundant? Which country is capital-abundant? b. Assume that both countries produce two goods, cars and wine. If cars are capital-intensive and wines are labor-intensive, which country should specialize in the production of cars? Which country should specialize in the production of wines? Explain why?arrow_forwardSuppose that Georgiania was a thriving empire in its golden age. Business was booming and it was the center of international trade under the leadership of Emperor Raphael III. His empire's pride and joy was the trading of green and black tea, and he decreed that their entire economy should be built around it. However, in the mid 1800s, Georgiania experienced a severe economic downturn when the other nations of the world created an embargo on tea from Georgiania, which led to civil strife due to thousands of workers being laid off. A downward fluctuation in the economy like this is known as economic growth. a recession. the invisible hand. market failure. The correct term is a key component of macroeconomics. both microeconomics and macroeconomics. microeconomics.arrow_forwardQ. 1arrow_forward
- If country A uses all of its resources efficiently, it can produce a maximum of 100 units of good X. If country A uses all of its resources efficiently, it can produce a maximum of 150 units of good Y. If country B uses all of its resources efficiently, it can produce a maximum of 75 units of good X. If country B uses all of its resources efficiently, it can produce a maximum of 125 units of good Y. Both countries have (linear) straight line PPFs. What is the opportunity cost of producing 10 units of X in country A? (hint: your answer should be measured in the positive number of units of good Y that must be given up - round your answer to two decimal places only if necessary)arrow_forwardDiego and Kris are roommates. They spend most of their time studying, but they leave some time for their favorite activities: making pizza and brewing root beer. Diego takes 4 hours to brew a gallon of root beer and 2 hours to make a pizza. Kris takes 6 hours to brew a gallon of root beer and 4hours to make a pizza. a) What is each roommate's opportunity cost of making a pizza? Who has the absolute advantage in making pizza? Who has the comparative advantage in making pizza? b) If Diego and Kris trade foods with each other, who will trade away pizza in exchange for root beer? c) The price of pizza can be expressed in terms of gallons of root beer, what is the highest price at which pizza can be traded that would make both roommates better off? What is the lowest price? Why?arrow_forwardSuppose there exist two imaginary countries, Congaree and Yosemite. Their labor forces are each capable of supplying four million hours per week that can be used to produce almonds, shorts, or some combination of the two. The following table shows the amount of almonds or shorts that can be produced by one hour of labor.arrow_forward
- Which of the following statements concerning location economies is FALSE? Explain Why? 1. Companies must determine where to sell and where to produce. 2.The Internet is an industry where companies must locate facilities near their foreign customers, so decisions on market and production location are connected. (difficult, page 382) 3.Companies may have excess production capacity already in place that will influence their ability to serve markets in different countries. 4. The process of determining an overall geographic strategy must be flexible because country conditions changearrow_forwardWhen a country has a comparative advantage in the production of a good, it means that it can produce this good at a lower opportunity cost than its trading partner. Then the country will specialize in the production of this good and trade it for other goods. The following graphs show the production possibilities frontiers (PPFs) for Glacier and Rainier. Both countries produce corn and basil, each initially (i.e., before specialization and trade) producing 18 million pounds of corn and 9 million pounds of basil, as indicated by the grey stars marked with the letter A. BASIL (Millions of pounds) 48 42 36 30 24 18 12 6 0 0 PPF 6 Glacier A 12 18 24 30 36 CORN (Millions of pounds) 42 48 ? BASIL (Millions of pounds) 48 42 36 30 24 18 12 6 0 0 PPF I + 6 Rainier 12 18 24 30 36 CORN (Millions of pounds) I 42 48 (?) Glacier has a comparative advantage in the production of while Rainier has a comparative advantage in the production of Suppose that Glacier and Rainier specialize in the production…arrow_forwardAlice and Bob each produce haircuts and landscaping services. Alice can provide 4 haircuts in one hour. Bob can provide 2 haircuts in one hour. It takes Alice 2 hours to landscape an acre of property. It takes Bob 1 hour to landscape an acre of property. Assume Alice and Bob both work a standard 8 hour day. If Alice and Bob were to combine forces and open their business "Heads and Hedges" together, how should Alice and Bob allocate their time to maximize the gains from trade with one another? (check all that apply) Alice should only spend her time cutting hair. Bob should only spend his time cutting hair. Bob should only spend his time landscaping. Alice should only spend her time landscaping.arrow_forward
- Suppose you have a team of two workers: one is a baker and one is a chef. Your baker is talented but is inexperienced. Your chef is not only an elite chef but is also faster at baking. If your kitchen specialized according to absolute advantage, who would do the cooking? Who would do the baking? If your kitchen specialized according to comparative advantage, who would do the cooking? Who would do the baking? Which approach above is more efficient? Explain your answer.arrow_forwardWhen a country specializes in the production of a good, this means that it can produce this good at a lower opportunity cost than its trading partner. Because of this comparative advantage, both countries benefit when they specialize and trade with each other. The following graphs show the production possibilities frontiers (PPFS) for Maldonia and Lamponia. Both countries produce lemons and sugar, each initially (i.e., before specialization and trade) producing 24 million pounds of lemons and 12 million pounds of sugar, as indicated by the grey stars marked with the letter A. (? (?) Maldonia Lamponia 64 64 56 56 48 PPF 48 40 40 32 32 24 24 PPF 16 16 16 24 32 40 48 56 64 16 24 32 40 48 56 64 LEMONS (Millions of pounds) LEMONS (Millions of pounds) Maldonia has a comparative advantage in the production of production of while Lamponia has a comparative advantage in the . Suppose that Maldonia and Lamponia specialize in the production of the goods in which each has a comparative advantage.…arrow_forwardPlease write your answers on a piece of paper. Your answers should be handwritten. Upload your answers as an attachment to the system. Firm A can produce 6 tables and 3 chairs in a day. Firm B can produce 8 tables and 2 chairs. Write your answers on a piece of paper and upload on the E-Learning system. a) Find the firms that have absolute advantage in producing tables and chairs. Discuss briefly. b) To maximize total production, which firms should produce which product? Analyze using comparative advantage concept. Show your calculations. Draw the production possibility frontier.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education