
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
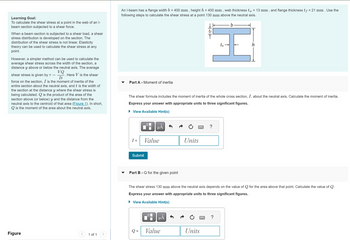
Transcribed Image Text:Learning Goal:
To calculate the shear stress at a point in the web of an l-
beam section subjected to a shear force.
When a beam section is subjected to a shear load, a shear
stress distribution is developed on the section. The
distribution of the shear stress is not linear. Elasticity
theory can be used to calculate the shear stress at any
point.
However, a simpler method can be used to calculate the
average shear stress across the width of the section, a
distance y above or below the neutral axis. The average
VQ
shear stress is given by T = Here V is the shear
It
force on the section, I is the moment of inertia of the
entire section about the neutral axis, and ₺ is the width of
the section at the distance y where the shear stress is
being calculated. Q is the product of the area of the
section above (or below) y and the distance from the
neutral axis to the centroid of that area (Figure 1). In short,
Qis the moment of the area about the neutral axis.
Figure
1 of 1
An I-beam has a flange width b = 400 mm, height h = 400 mm, web thickness tw = 13 mm, and flange thickness tƒ = 21 mm . Use the
following steps to calculate the shear stress at a point 130 mm above the neutral axis.
Part A - Moment of inertia
I =
Submit
Value
The shear formula includes the moment of inertia of the whole cross section, I, about the neutral axis. Calculate the moment of inertia.
Express your answer with appropriate units to three significant figures.
► View Available Hint(s)
O
μA
Part B - Q for the given point
=
0
μÅ
Units
Value
上を下
H
www ?
The shear stress 130 mm above the neutral axis depends on the value of Q for the area above that point. Calculate the value of Q.
Express your answer with appropriate units to three significant figures.
► View Available Hint(s)
Units
b
tr
?
h
Transcribed Image Text:Figure
H
<
1 of 1
Part C-Shear stress
Use the results from Parts A and B to calculate the shear stress at a point 130 mm above the neutral axis if the shear force on the section is
V = 5.8 KN.
Express your answer with appropriate units to three significant figures.
► View Available Hint(s)
T =
O
μA
Value
Submit
< Return to Assignment
Units
Provide Feedback
?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 14 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Needs Complete typed solution with 100 % accuracy. Handwritten solution is completely prohibited.arrow_forward3) Calculations for the red dog food can rolling down the slope in the Rube Goldberg design are as follows (we will name it Step 1): DO Step 1 (calculations are given): Coefficient of friction → μ = 0.14 Mass of the object → m = 368 gm = 0.368kg Initial height of the object (red can on top of books) → h=8.89, cm = 0.0889 m Slope of the file folder → 0 = 14° Travelling Distance by the object = 11.5 inch = 0.292 m And length that the object will travel = h/sin 0 = 0.0889/ sin14° = 0.367 m So, the radius of the object → R = 0.367 -0.292 = 0.075 m Initial Velocity of red can → u=0 Velocity and Force Calculations for Step 1: -From total mechanical energy conservation: → Initial mechanical energy = final mechanical energy → mg - In case of pure rolling, the velocity of the center of mass: →→V=Ro=0.075 x 14.28 = 1.07 m/s. -Hence the change in force acting on the object for the travel: →F=mgsine = 0.368 x 9.81 × sin14° =0.89 N Step 2: The Selective Step (Step 2) in this design and for the…arrow_forward5) Calculations for the red dog food can rolling down the slope in the Rube Goldberg design are as follows (we will name it Step 1): Step 1 (calculations are given): Coefficient of friction → μ = 0.14 Mass of the object → m = 368 gm = 0.368kg Initial height of the object (red can on top of books) → h=8.89, cm = 0.0889 m Slope of the file folder → 0= 14° Travelling Distance by the object = 11.5 inch = 0.292 m And length that the object will travel = h/sin 0 = 0.0889/ sin14° = 0.367 m So, the radius of the object → R = 0.367 -0.292 = 0.075 m Initial Velocity of red can → u = 0 Velocity and Force Calculations for Step 1: -From total mechanical energy conservation: → Initial mechanical energy = final mechanical energy → mg - In case of pure rolling, the velocity of the center of mass: →V=Roo= 0.075 x 14.28 = 1.07 m/s. -Hence the change in force acting on the object for the travel: →F=mgsine = 0.368 x 9.81 × sin14° =0.89 N Step 2: The Selective Step (Step 2) in this design and for the…arrow_forward
- Consider the impact of a 2 kg bird at the free end of an aircraft wing. The bird is moving at a speed of 10 m/s towards the aircraft. Speed of aircraft is 105 m. Model the aircraft wing as a beam of rectangular cross section having 3 m length, 0.05 m thickness and 0.5m width. During impact, compute a) the static equivalent force on the aircraft wing b)the maximum deflection of the wingarrow_forwardP= 4 kN w= 0.8 kN/m a) Start with the shear diagram. To use a segment of the left end of the beam to develop the expression for the shear, the vertical reaction at A must be known. Calculate the vertical reaction at A. Let a positive force act up. b)Write an expression for the internal shear for an arbitrary point between A and B c)Write an expression for the internal shear for an arbitrary point between B and C.arrow_forwardLearning Goal: To determine an I-beam's maximum bending moment, moment of inertia using the parallel-axis theorem, and the maximum stress at a given location using the flexure formula. As shown, I-beam ABC supports a sign that weighs S = 30 lb . The I-beam is 24 in. long and is further supported by a rod that is attached 18 in. from the wall. Assume that all forces acting on the I-beam act along its centroid and that the I-beam's weight is negligible. Let the dimensions of the I-beam be w = 4 in., g = 0.8 in., h = 2.9 in., j = 1 in., c = 6 in. c A ·a b B Part A - Free-body diagram of beam ABC S C H j- W h Before the problem can be analyzed, a free-body diagram must be drawn to understand the forces and reactions that act on the I-beam. Draw the free-body diagram of beam ABC. A free-body diagram includes the forces acting on the object, in this case the beam. Start your vectors at the black dots. You will not be graded on vector length. Ignore all reaction forces in the x direction, and…arrow_forward
- mhm 4.31 System for Exercise 4.24 (left) and Exercise 4.25 (right). m, the force required to deflect the end, as is illustrated in Figure 4.32 is In Chapter 11 we are much smarter and are able to show that for a cantilever ЗЕЛ L3 X, 4.32 Cantilever beam subjected to a at the end. F = ere E is the modulus of elasticity, which is a property of the material used, I is area moment of inertia of the cross-section of the beam, and L is the length. If a mass m,is attached to the end of the beam, what is the equation of motion the vertical motion of the beam? If the length is doubled, what is the change in quency of the free vibration of the beam? =kX 2 Guieds x=0 F-XX F x = L Fig. 4.33 Rotatin 4.28. Referring the end of a ca elasticity of the length is L = 1 1. Determine t 2. Determine t @= 1000 r 4.29. Determin 1. On the sam 2. Identify the the part youarrow_forwardLearning Goal: To use Hooke's law to determine the value of an axial load applied to a rectangular shape and to determine its lateral expansion. The element shown below is subjected to the axial compressive force P, which causes the shape to contract longitudinally in the direction a distance of 8 = 0.720 mm. Let h = 144.5 mm, w = 88.50 mm, and L = 298.0 mm. Assume the element is made from steel that has a modulus of elasticity of E= 200 GPa and a value of Poisson's ratio of v=0.32. ♥ Part A Value of the axial load Determine the value of the axial load P. Express your answer to four significant figures and include the appropriate units. View Available Hint(s) P = Submit P μÀ Value Units ? Part B Lateral expansion in the y direction Determine the lateral expansion in the y direction due to the axial load. Express your answer to four significant figures and include the appropriate units. View Available Hint(s) dy = Submit d₂ = Value Part C - Lateral expansion in the z direction μA Submit…arrow_forwardA simply supported beam hinged at A and supported at C, is carrying a distributed load and a point load (see Fig. 1). The beam has a Young Modulus E = 80 GPa and a constant depth of 400 mm. The moment of inertia of the beam is limited to be I = 255 x 10-4 m*. 1. P- 120 KN 9 15 KN/m 4 (m) 2 (m) Figure 1 (a) (i) Write the bending moment expression using Macauley's method. (ii) Determine the bending moment at A. (ii) Determine the bending moment at B. (iv) Determine the bending moment at C. (v) Derive the deflection equation and find the value of the integration constants. (vi) Find the deflection atarrow_forward
- 6. Two close-coiled helical springs are arranged, parallel (one inside the other) about the same longitudinal axis. Both springs have the same number of coils and same overall length, but the mean coil diameter of the outer spring, which is made of steel wire, is twice that of the inner spring, which is made of bronze wire. The springs are designed to act together when a tensile force is applied, so that both suffer the same change in length and each carries half the force. Determine the ratio of the wire diameters, and the retio of the stresses produced in the wires, if Esteel = 2 x Ebronzearrow_forwardQ: Draw shear force and bending moment diagrams for the beam shown below and then find max. shear force and bending moment. 100 N 45 1.0 16 KN 1.2 1.7 1.9arrow_forwardStrength of Materials First theree number 187 First tow number 18 Please solve it very quickly . Read questions carefully. . Draw neat, labelled diagrams. . Write relevant equations. . Be clear and specific and include units in answers. . Give explanatory notes where necessary.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY