
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
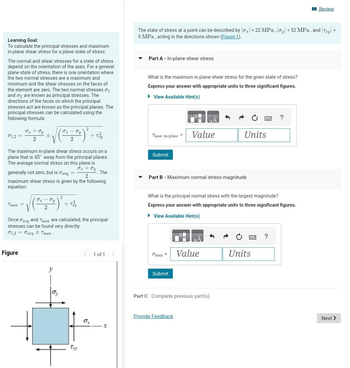
Transcribed Image Text:Learning Goal:
To calculate the principal stresses and maximum
in-plane shear stress for a plane state of stress.
The normal and shear stresses for a state of stress
depend on the orientation of the axes. For a general
plane state of stress, there is one orientation where
the two normal stresses are a maximum and
minimum and the shear stresses on the faces of
the element are zero. The two normal stresses 01
and 2 are known as principal stresses. The
directions of the faces on which the principal
stresses act are known as the principal planes. The
principal stresses can be calculated using the
following formula:
σ1,2 =
Tmax =
O₂ + Oy
2
±
Figure
The maximum in-plane shear stress occurs on a
plane that is 45° away from the principal planes.
The average normal stress on this plane is
O₂ + Oy
generally not zero, but is avg =
maximum shear stress is given by the following
equation:
. The
OT Ty
2
JI Ty
2
y
Oy
2
+ Tzu
Once avg and Tmax are calculated, the principal
stresses can be found very directly:
01,2 avg Tmax.
2
Txy
tiểu
< 1 of 1 >
Ox
X
The state of stress at a point can be described by |0₂| = 22 MPa, oy = 52 MPa, and Try =
9 MPa, acting in the directions shown (Figure 1).
Part A - In-plane shear stress
What is the maximum in-plane shear stress for the given state of stress?
Express your answer with appropriate units to three significant figures.
► View Available Hint(s)
=
Tmax in-plane 1
Submit
Part B - Maximum normal stress magnitude
max =
Value
Submit
What is the principal normal stress with the largest magnitude?
Express your answer with appropriate units to three significant figures.
► View Available Hint(s)
Provide Feedback
Units
Value
Part C Complete previous part(s)
Units
?
?
Review
Next >
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- His can you find answers for these please and explain how ? Thank youarrow_forwardQ1. The image below shows an example of "absolute dependent motion analysis", where the motions of two objects depend on each other, and the goal is to find the relations in their motions (i.e., in their positions, velocities, and accelerations). Please put the suggested steps of analysis in the correct order. VA A B VB Differentiate the entire equation with respect to time, and extract the relation in velocities. Repeat for acceleration if needed. Set up a coordinate (s) along the direction of motion from a fixed point (O) or a fixed datum line. Represent the positions of the objects respectively. In some cases intermediate objects need to be considered too and their positions need to be represented as well. Recognize the constant length(s) and find the depending geometric relations between the position variables.arrow_forwardThree forces are applied to a hook. F1 y 5 4 F2 5 12 13 F3 Values for the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value F1 45 lb F2 15 lb F3 140 lb a. Write each vector in Cartensian Vector Notation. Round your final answers to 3 significant digits/figures. F- ĝ lb = F- i lb F3 = j lb 3.arrow_forward
- 1- Water vapor at a flow rate of 20000 kg / hour enters a steam boiler with a specific volume of 150 kPa 0.001053 m3 / kg. With the energy it takes from the fuel in the combustion chamber of the boiler, it rises at 150˚C at 1200 kPa. If the boiler has poor insulation and loses 100 kW of heat to the environment, calculate the time required to increase 1 ton of water to 150 ° C in the boiler. A. 347 sB. 3752 sC. 1651 sD. 648 sE. 2494 sarrow_forwardSolve fast and accurate,it needs attentionarrow_forwardWhen a beam section is subjected to a shear load, a shear stress distribution is developed on the section. The distribution of the shear stress is not linear. Elasticity theory can be used to calculate the shear stress at any point. However, a simpler method can be used to calculate the average shear stress across the width of the section, a distance y above or below the neutral axis. The average VQ shear stress is given by T = Here V is the shear It force on the section, I is the moment of inertia of the entire section about the neutral axis, and t is the width of the section at the distance y where the shear stress is being calculated. Q is the product of the area of the section above (or below) y and the distance from the neutral axis to the centroid of that area (Figure 1). In short, Q is the moment of the area about the neutral axis. I Figure 1 of 1 An I-beam has a flange width b = 250 mm, height h = 250 mm, web thickness tw = 9 mm, and flange thickness tf = 14 mm. Use the…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY