
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
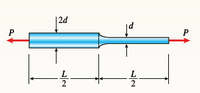
A bar with a circular cross section having two
different diameters d and 2d is shown in the figure.
The length of each segment of the bar is L/2, and the
modulus of elasticity of the material is E.
(a) Obtain a formula for the strain energy U of the
bar due to the load P.
(b) Calculate the strain energy if the load
P = 27 kN, the length L = 600 mm, the
diameter d = 40 mm, and the material is
brass with E = 105 GPa.
Transcribed Image Text:L.
2
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The two bars shown in the figure are used to support a load P. When unloaded, joint B has coordinates (0, 0). After load P is applied, joint B moves to the coordinate position (0.20 in., -0.55 in.). Assume a = 9 ft, b = 6 ft, and h = 7 ft. Determine the normal strain in each bar. B P b harrow_forwardA plastic rod AB of length L = 0.5 m has a diameter d1 = 30 mm (see figure). A plastic sleeve CD of length c = 0.3 m and outer diameter d2 = 45 mm is securely bonded to the rod so that no slippage can occur between the rod and the sleeve (b = 0.1 m). The rod is made of an acrylic with modulus of elasticity E, = 3.1 GPa and Poisson's ratio v = 0.3, and the sleeve is made of a polyamide with E2 = 2.5 GPa. Determine the elongation (8) of the rod AB and the new diameter (d,') of the AC or DB segment, when the rod is pulled by axial forces P = 12 kN. Note: take n = 3.1415926. di d2 C D A В b- -L-arrow_forwardSolve the following problems The composite bar in the figure is made of two segments AB and BC, having a diameter of 12 mm and 8 mm respectively. The you modulus of elasticity EAB = 90 GPa and EBC= 80GPa Critically evaluate the deformation of the bar shown under the given loads. the missing force F1 325KN. F=40KN F= kN A 4m 4.2marrow_forward
- 4(a) A solid circular bar is experiencing axial load F=3 kN as in Figure 4(a). Find the strain energy in the bar, E=200GPa. F= 3 kN F= 3 kN Solid circular bar 6 = 40 mm Figure 4(a) 4(b) A simple ABCD structure is being loaded built in at D and loaded with load P at A, as in Figure 4b. The structure is made of steel solid round cross section with 100mm diameter with E= 200GPA, o, = 250 MPa. AB = Im, BC= 1.5m, CD= 2.5m Neglect the energy from the shear and axial load, find the ; i) Vertical deflection of point A i) Horizontal deflection of point A iii) Slope of point C D Figure 4b A в P=10Narrow_forwardA circular aluminum tube with a length of L = 420 mm is loaded in compression by forces P (see figure). The hollow segment of length LB has outside and inside diameters of 60 mm and 35 mm, respectively. The solid segment of length 2L/3 has a diameter of 60 mm. A strain gage is placed on the outside of the hollow segment of the bar to measure normalstrains in the longitudinal direction.(a) If the measured strain in the hollow segment is6jy=470*10 , what is the strain in the solid part? Hint: The strain in the solid segment is equal to that in the hollow segment multiplied by the ratio of the area of the hollow to that of the solid segment.(b) What is the overall shortening of the bar?(c) If the compressive stress in the bar cannot exceed 48 MPa, what is the maximum permissible value of load P?arrow_forwardA rigid bar ACE is supported by three vertical wires and is initially horizontal, as shown in the figure. Then, a force P is applied at the center of the bar. All wires are made from the same material with modulus of elasticity E = 200 GPa and have the same cross-sectional area, A = 10 mm². You may assume that the deformations are small and that the stresses are within the elastic range for this problem. 1.5 m A D F 1.0 m 1.0 m H C E P A 2.0 m Figure 3.1: Rigid bar supported by three vertical wires a) Find the normal stresses and the axial displacements in the wires if P = 15 kN. b) Knowing that AB is the critical wire, and its yield stress is oy maximum P that can be applied. = 1500 MPa, find thearrow_forward
- A 5-mm-thick rectangular alloy bar is subjected to a tensile load P by pins at A and B, as shown in the figure. The width of the bar is w= 26 mm. Strain gages bonded to the specimen measure the following strains in the longitudinal (x) and transverse (y) directions: &x = 840 με and Ey = -265 με. (a) Determine Poisson's ratio for this specimen. (b) If the measured strains were produced by an axial load of P = 18 kN, what is the modulus of elasticity for this specimen? P Answers: (a) v = (b) E= 0.315 i .044 y e Textbook and Media Save for Later GPa B P Attempts: 2 of 5 used Submit Answerarrow_forwardFor the truss in figure below, the cross-sectional area of the truss members is A = 500 mm2 and Young’s modulus E = 200 GPa. Let P = 95.8 kN. Determine: a) Strain energy for truss AC. Enter your answer in J to 2 decimal places. b) Strain energy for truss AB. Enter your answer in J to 2 decimal places. c) Strain energy for truss BC. Enter your answer in J to 2 decimal places. d) Strain energy for truss BD. Enter your answer in J to 2 decimal places. e) Strain energy for truss DC. Enter your answer in J to 2 decimal places. f) Strain energy for truss DF. Enter your answer in J to 2 decimal places. g) Strain energy for truss FC. Enter your answer in J to 2 decimal places. h) Strain energy for truss CE. Enter your answer in J to 2 decimal places. i) The displacement at point A. Enter your answer in mm to 2 decimal places.arrow_forwardConsider the two bars of identical material with their elastic modulus E as shown in Figure below. Both bars have the same circular cross-section with diameter of d. The length of the longer bar is 2L and the length of the shorter bar is L. The angle between the bars is B. The system is subjected to a vertical force acting at point Pas shown in the figure with a magnitude of F. Calculate horizontal and vertical components of the displacement of point P. Use engineering notation (ENG display mode on scientific calculators) with 3 significant figures after the decimal point. E (psi) 1.50E+06 d (in) 1.25 L (in) 12 Beta (degrees) 30 F (Ibf) 110 F P L 2Larrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY