
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
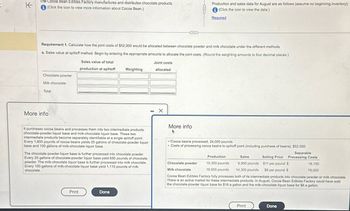
Transcribed Image Text:K
The Cocoa Bean Edibles Factory manufactures and distributes chocolate products.
(Click the icon to view more information about Cocoa Bean.)
Production and sales data for August are as follows (assume no beginning inventory):
(Click the icon to view the data.)
Required
Requirement 1. Calculate how the joint costs of $52,000 would be allocated between chocolate powder and milk chocolate under the different methods.
a. Sales value at splitoff method. Begin by entering the appropriate amounts to allocate the joint costs. (Round the weighting amounts to four decimal places.)
Sales value of total
Joint costs
Chocolate powder
Milk chocolate
Total
More info
production at splitoff
Weighting
-
allocated
More info
It purchases cocoa beans and processes them into two intermediate products:
chocolate-powder liquor base and milk-chocolate liquor base. These two
intermediate products become separately identifiable at a single splitoff point.
Every 1,600 pounds of cocoa beans yields 25 gallons of chocolate-powder liquor
base and 100 gallons of milk-chocolate liquor base.
The chocolate-powder liquor base is further processed into chocolate powder.
Every 25 gallons of chocolate-powder liquor base yield 690 pounds of chocolate
powder. The milk-chocolate liquor base is further processed into milk chocolate.
Every 100 gallons of milk-chocolate liquor base yield 1,110 pounds of milk
chocolate.
Cocoa beans processed, 24,000 pounds
•Costs of processing cocoa beans to splitoff point (including purchase of beans), $52,000
Separable
Selling Price Processing Costs
$11 per pound $
$8 per pound $
Production
Chocolate powder
10,350 pounds
16,650 pounds
Sales
6,900 pounds
14,300 pounds
Milk chocolate
18,150
78,000
Cocoa Bean Edibles Factory fully processes both of its intermediate products into chocolate powder or milk chocolate.
There is an active market for these intermediate products. In August, Cocoa Bean Edibles Factory could have sold
the chocolate-powder liquor base for $16 a gallon and the milk-chocolate liquor base for $6 a gallon.
Print
Done
Print
Done
SAVE
AI-Generated Solution
info
AI-generated content may present inaccurate or offensive content that does not represent bartleby’s views.
Unlock instant AI solutions
Tap the button
to generate a solution
to generate a solution
Click the button to generate
a solution
a solution
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Need help with question B sales vale at split off point. Please show how you got the numbers. I really need help calculating cost per liter for each product. Thanksarrow_forwardRalston Dairy gathered this data about the two products that it produces: Products Current SalesValue Estimated AddedProcessing Costs Sales Value IfProcessing Further Frozen yogurt $8,100 $1,900 $10,900 Ice cream 11,900 7,100 17,900 Which of the products should be processed further? because profits $fill in the blank 3.arrow_forwardPlease help mearrow_forward
- 9. Ralston Dairy gathered this data about the two products that it produces: Product Current Sales Value Estimated Added Processing Cost Sales Value If Processed Further Frozen yogurt $8,000 $2,000 $11,000 Ice Cream 12,000 7,000 18,000 PLEASE NOTE: All dollar amounts are rounded to whole dollars and shown with "$" and commas as needed (i.e. $12,345). If needed, a Net Loss or decrease will be shown in whole dollars with "$" and parentheses - ($12,345). If processed further, what is the Frozen Yogurt's incremental profit or loss? If processed further, what is the Ice Cream's incremental profit or loss? Which of the products should be processed further? . Please note: Your answer is either "Frozen Yogurt" or "Ice Cream" - capital first letters and no quotes.arrow_forwardSolve all pleasearrow_forwardPlease help mearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education