
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
infoPractice Pack
Question
infoPractice Pack
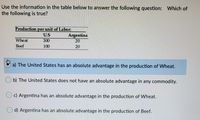
Transcribed Image Text:Use the information in the table below to answer the following question: Which of
the following is true?
per unit of Labor:
U.S
Production
Argentina
20
Whe at
300
Beef
100
20
a) The United States has an absolute advantage in the production of Wheat.
O b) The United States does not have an absolute advantage in any commodity.
c) Argentina has an absolute advantage in the production of Wheat.
d) Argentina has an absolute advantage in the production of Beef.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Includes step-by-step video
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 19arrow_forwardIn the following table, select the amount of each good that each country exports and Imports In the boxes across the row marked "Trade Action," and enter each country's final consumption of each good on the line marked "Consumption." When the two countries did not specialize, the total production of jeans was 17 million palrs per week, and the total production of rye was 46 million bushels per week. Because of specialization, the total production of jeans has increased by 3 million pairs per week, and the total production of rye has increased by 18 million bushels per week. Because the two countries produce more jeans and more rye under specialization, each country is able to gain from trade. Calculate the gains from trade-that is, the amount by which each country has increased its consumption of each good relative to the first row of the table. In the following table, enter this difference in the boxes across the last row (marked "Increase in Consumption"). Dolorium Arcadia Jeans Rye…arrow_forward3. Gains from trade Consider two neighboring island countries called Felicidad and Arcadia. They each have 4 million labor hours available per month that they can use to produce jeans, corn, or a combination of both. The following table shows the amount of jeans or corn that can be produced using 1 hour of labor. Jeans Corn Country (Pairs per hour of labor) (Bushels per hour of labor) Felicidad 5 20 Arcadia 8 16 Initially, suppose Arcadia uses 1 million hours of labor per month to produce jeans and 3 million hours per month to produce corn, while Felicidad uses 3 million hours of labor per month to produce jeans and 1 million hours per month to produce corn. Consequently, Felicidad produces 15 million pairs of jeans and 20 million bushels of corn, and Arcadia produces 8 million pairs of jeans and 48 million bushels of corn. Assume there are no other countries willing to trade goods, so, in the absence of trade between these two countries, each country consumes the amount of jeans and…arrow_forward
- QUESTION 23 Maximum Feasible Hourly Production Rates for either Tablets or TVs Using All AvailableResources United States Product Mexico Tablets TVs 6. Refer to the above table. Assuming that opportunity costs are constant, which of the following is a correct statement? O Mexico has a comparative advantage in producing both goods. O The United States has a comparative advantage in TV production. O The United States has a comparative advantage in producing both goods. O Mexico has a comparative advantage in producing TVs.arrow_forwardexplain the comparative advantage and the conditions under which it is beneficial for parties to trade. use an examplearrow_forwardParts a and b in the attached image pleasearrow_forward
- What is comparative advantage based on? A. dollar price B. labour costs C. opportunity costs D. capital costsarrow_forwardCanada Japan Labour hours needed to make 1 unit: Cars 30 40 Airplanes 120 160 Refer to Table 3-5. If Canada and Japan trade based on the principle of comparative advantage, what could Japan gain from importing an airplane?arrow_forwardThe chart is already done. I need help with the last two questionsarrow_forward
- Macmillan Learning The Power of Trade and Comparative Advantage: Work It Out 5 Here's another specialization and exchange problem. This problem is wholly made-up, so that you won't be able to use your intuition about the names of countries or the products to figure out the answer. Consider the following productivity table: Mandovia Ducennia Number of Hours to Make One Rotid Output of rotids for Mandovia: Total rotid output: 50 150 Number of Hours to Make One Tauron d. Now allow specialization. One billion hours of labor are available for making products in Mandovia, and 2 billion hours of labor are available for making products in Ducennia. If each country completely specializes in the product in which it holds the comparative advantage, what will the total output of rotids be? Of taurons? Is the total output of each product higher than before? million 100 million 200 Output of rotids for Ducennia: millionarrow_forwardAutomobiles Computers USA 20 15 Germany 15 5 if both countries produce according to the respective comparative advantages, what…arrow_forward***Please look at the screenshot for graphs*** Fill in the charts below with values based on the two Production Possibilities Frontiers above. Motor Vehicle Production in the United States (in millions) Cars Trucks 0 4 0 Motor Vehicle Production in Mexico (in millions) Cars Trucks 0 2 0 Which country has the absolute advantage in producing cars? Which country has the absolute advantage in producing trucks? Which country has the comparative advantage in producing cars? Which country has the comparative advantage in producing trucks? Should these two countries trade? Why or Why not?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education