
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
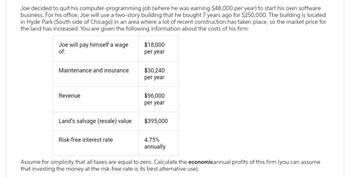
Transcribed Image Text:Joe decided to quit his computer-programming job (where he was earning $48,000 per year) to start his own software
business. For his office, Joe will use a two-story building that he bought 7 years ago for $250,000. The building is located
in Hyde Park (South side of Chicago) in an area where a lot of recent construction has taken place, so the market price for
the land has increased. You are given the following information about the costs of his firm:
Joe will pay himself a wage
of:
Maintenance and insurance
Revenue
Land's salvage (resale) value
Risk-free interest rate
$18,000
per year
$30,240
per year
$96,000
per year
$395,000
4.75%
annually
Assume for simplicity that all taxes are equal to zero. Calculate the economicannual profits of this firm (you can assume
that investing the money at the risk-free rate is its best alternative use).
SAVE
AI-Generated Solution
info
AI-generated content may present inaccurate or offensive content that does not represent bartleby’s views.
Unlock instant AI solutions
Tap the button
to generate a solution
to generate a solution
Click the button to generate
a solution
a solution
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Our firm produces two products: generators and solar panels. Name five economies of scale you would expect our company to leverage and explain how you would expect the company to leverage them. Our firm’s accountants have put together the following table of costs. Generators Solar Panels Fixed Costs $2 million $2 million Variable Costs $2 million $2 million Revenue $3 million $5 million The accountants have assured us that there are no places to save money. We are at our profit maximizing quantities of each product. We are as efficient as any firm could possibly be. In answering the questions below, do not just say lower costs or increase sales. Explain all your answers. If you cannot explain why you are taking an action, then you are just guessing.arrow_forwardI need help to see if I'm doing this correctly, also what his economic profit is as a financial advisor and if he should stay in the piano business or not. Thank you.arrow_forwardOnly typed answer and don't use chat gpt and please answer correctly Suppose that you can sell as much of a product (in integer units) as you like at $61 per unit. Your marginal cost (MC) for producing the qth unit is given by: MC=9q This means that each unit costs more to produce than the previous one (e.g., the first unit costs 9*1, the second unit (by itself) costs 9*2, etc.). If fixed costs are $50, what is the optimal output level? Please specify your answer as an integer. Also, assume that a competitive firm has the total cost function: TC = 1q3 - 40q2 + 710q + 1700 Suppose the price of the firm's output (sold in integer units) is $550 per unit. Using tables (but not calculus) to find a solution, what is the total profit at the optimal output level? Please specify your answer as an integer.arrow_forward
- Dr. Khan starts his own dental practice after quitting his $150,000 job at The Mall Dental Clinic. His revenues for the first year are $500,000. He paid $90,000 in rent for the dental office, $60,000 for his office manager's salary, $24,000 for the dental hygienist, $150,000 for insurance, and $6,000 for other miscellaneous costs. The normal profit from running his business is $20,000. A) His accounting profit is $350,000. B) His economic profit is $150,000. C) His economic profit is zero. D) His accounting profit is zero.arrow_forwardChris P. Nugget runs a small fast-food chicken restaurant named "Poultrygeist.". He hires one employee at a cost of $28,000 per year, pays annual rent of $25,000 for his shop, and spends $75,000 per year on other inputs (food, supplies, etc.). He has $100,000 of his own funds previously invested in equipment (ovens, serving counters, etc.) that could earn him $8,000 per year if these funds were alternatively invested. Chris has been offered $80,000 per year to work as a restaurant manager for a competitor. Total annual revenue from the restaurant is $200,000. For all answers, be specific and show your work. a. How much are Mr. Nugget's "explicit costs" this year? b. How much are Mr. Nugget's "implicit costs" this year? c. What is Mr. Nugget's "accounting profit" this year? d. What is Mr. Nugget's "economic profit" this year? e. Put into words what your answer to part d. means for Mr. Nugget's decision about whether to stay at his restaurant or to close and take the offer at his…arrow_forwardork (5.3) Part 1 of 3 A manufacturing company makes two types of water skis, a trick ski and a slalom ski. The relevant manufacturing data are given in the table. Labor Hours per Ski Maximum Labor-Hours Available per Day 120 25 Department Fabricating Finishing Answer parts (A), (B), and (C) below Trick Ski 5 1 Slalom Ski 4 1 CITT (A) If the profit on a trick ski is $50 and the profit on a slalom ski is $60, how many of each type of ski should be manufactured each day to realize a maximum profit? Wh is the maximum profit? The maximum profit is $ The maximum occurs when trick skis and slalom skis are produced. 4arrow_forward
- Use the table below to answer the next three questions. The below table displays the production schedule for Great Balls of Fire, a food truck that sells flaming meatballs. Great Balls of Fire has a lease on the truck itself that costs $1200 per week that must be paid whether or not the food truck produces and sells any meatballs. They may hire up to three workers to produce and sell the meatballs, workers cost $600 per week. The production schedule shows you how many meatballs would be produced with the varying levels of employees. Employees Meatballs Fixed Costs Variable Cost Total Cost Average Variab Cost 0 0 0 1 300 2 500 3 600 Completely fill out the table, please round all answers to the nearest cent. Do not enter any commas, dollar signs, or units (Ex. If your calculator says 12.376, just enter 12.38.) If your answer is an even dollar amount, you don't need to include the cents (Ex. you may enter 10 instead of 10.00)arrow_forwardUntil recently, Mark worked as a financial advisor, earning $65,000 annually. Then he inherited a piece of commercial real estate that had been renting for $14,000 annually. Mark decided to leave his job and operate a sea food restaurant in the space he inherited. At the end of the first year, his books showed total revenues of $300,000, and paid a total cost of $200,000 for food, utilities, cooks, and other supplies: Show all your work including formulas learned to support your answer for each of the following: A) Calculate his explicit costs: B) Calculate his implicit costs. C) Calculate his accounting profits. D) Calculate his economic profits.arrow_forwardSuppose that in 2018, you inherited from your grandfather a small planetarium that had been closed for several years. Your planetarium has a maximum capacity of 75 people and all the equipment is in working order. You decide to reopen the planetarium on the weekends as a new laser-tag venture called Shoot for the Stars, and much to your delight it has become an instant success, with admission tickets selling out quickly for each day you are open. Describe some of the decisions that you must make in the short run. What might you consider to be your “fixed factor”? What alternative decisions might you be able to make in the long run? Explainarrow_forward
- Only typed answerarrow_forwardDesmond works as an accountant making $80,000 per year. He is considering leaving his job to open an artisanal cheese shop. He estimates that he will need to spend $20,000 per year on space, $10,000 per year on supplies and $40,000 per year on staff. The shop will earn will earn $120,000 per year in revenue. Assuming his estimates are accurate, what will Desmond's accounting profit be? Assuming his estimates are accurate, what will Desmond's economic profit be? Please enter your solution without commas, dollar signs, or cents.arrow_forwardGloria decided to open her own business and earns $50,000 in accounting profit the first year. When deciding to open her own business, she turned down three separate job offers with annual salaries of $50,000, $60,000, and $70,000. What is Gloria's economic profit from running her own business? Question 5 options: a) -$75,000 b) -$20,000 c) $20,000 d) none of the abovearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education