
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
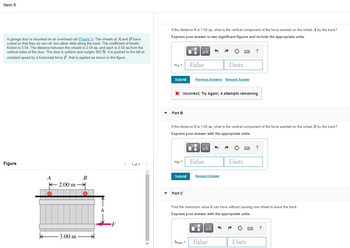
Transcribed Image Text:Item 9
A garage door is mounted on an overhead rail (Figure 1). The wheels at A and B have
rusted so that they do not roll, but rather slide along the track. The coefficient of kinetic
friction is 0.54. The distance between the wheels is 2.00 m, and each is 0.50 m from the
vertical sides of the door. The door is uniform and weighs 900 N. It is pushed to the left at
constant speed by a horizontal force F, that is applied as shown in the figure.
Figure
B
k
A
K 2.00 m
-3.00 m
h
F
1 of 1
If the distance his 1.60 m, what is the vertical component of the force exerted on the wheel A by the track?
Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units.
μA
?
nA =
Value
Units
Submit
Previous Answers Request Answer
X Incorrect; Try Again; 4 attempts remaining
Part B
If the distance h is 1.60 m, what is the vertical component of the force exerted on the wheel B by the track?
Express your answer with the appropriate units.
μÅ
?
nB =
Value
Units
Submit
Request Answer
Part C
Find the maximum value h can have without causing one wheel to leave the track.
Express your answer with the appropriate units.
μA
Imax =
Value
Units
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A uniform ladder stands on a rough floor and rests against a frictionless wall as shown in the figure. N2 mg d b Since the floor is rough, it exerts both a normal force N, and a frictional force f, on the ladder. However, since the wall is frictionless, it exerts only a normal force N, on the ladder. The ladder has a length of L = 4.70 m, a weight of W = 68.0 N, and rests against the wall a distance d = 3.75 m above the floor. If a person with a mass of m = 90 kg is standing on the ladder, determine the following. (a) the forces exerted on the ladder when the person is halfway up the ladder (Enter the magnitude only.) N1 N2 = f1 %3D (b) the forces exerted on the ladder when the person is three-fourths of the way up the ladder (Enter the magnitude only.) N1 = N N2 = f1arrow_forwardThe figure shows a horizontal beam of mass M = 54.5 kg and length L = 6.3 m supported at its left end by a frictionless pin and at the other end by an ideal cable attached to wall h = 6 m above the beam. A mass m = 28.9 kg is suspended from the beam a distance d = 3.7 m from the wall. Find the tension in the cable. h T = m M -L- Narrow_forwardA 11.0-kg monkey climbs a uniform ladder with weight w = 1.40 × 102 N and length L = 2.60 m as shown in the figure below. The ladder rests against the wall and makes an angle of 0 = 60.0° with the ground. The upper and lower ends of the ladder rest on frictionless surfaces. The lower end is connected to the wall by a horizontal rope that is frayed and can support a maximum tension of only 80.0 N. Rope (a) Draw a force diagram for the ladder. Choose File no file selected This answer has not been graded yet. (b) Find the normal force exerted on the bottom of the ladder. (c) Find the tension in the rope when the monkey is two-thirds of the way up the ladder. N (d) Find the maximum distance d (along the ladder) that the monkey can climb up the ladder before the rope breaks. (e) If the horizontal surface were rough and the rope were removed, how would your analysis of the problem change? What other information would you need to answer parts (c) and (d)? This answer has not been graded yet.…arrow_forward
- A uniform stationary ladder of length L and mass M leans against a smooth vertical wall, while its bottom legs rest on a rough horizontal floor. The coefficient of static friction between floor and ladder is μ. The ladder makes an angle θ with respect to the floor. A painter of mass 1/2M stands on the ladder a distance d from its base.arrow_forwardcan you please solve (c) ?arrow_forwardA 10.0-kg monkey climbs a uniform ladder with weight w = 1.09 x 10 N and length L = 3.40 m as shown in the figure below. The ladder rests against the wall at an angle of 6 = 60°. The upper and lower ends of the ladder rest on frictionless surfaces, with the lower end fastened to the wall by a horizontal rope that is frayed and that can support a maximum tension of only 80.0 N. Rope (a) Draw a force diagram for the ladder. (Submit a file with a maximum size of 1 MB.) (b) Find the normal force exerted on the bottom of the ladder. N (c) Find the tension in the rope when the monkey is two-thirds of the way up the ladder. N (d) Find the maximum distance that the monkey can climb up the ladder before the rope breaks. m (e) If the horizontal surface were rough and the rope were removed, how would your analysis of the problem be changed and what other information would you need to answer Parts (c) and (d)?arrow_forward
- As shown below, a beam of length L is in equilibrium and is attached to a cable which is pulling it against a frictionless wall. The beam is not attached to the wall and the wall is only exerting a normal force on the beam. Additionally, there is a 702 N box hanging on a wire from the end of the beam. Determine the cable tension & the beam weight. 0.89 L 45° tension = beam weight = 702 Narrow_forwardChapter 12, Problem 037 GO In the figure, a uniform plank, with a length L of 6.83 m and a weight of 386 N, rests on the ground and against a frictionless roller at the top of a wall of height h = 2.78 m. The plank remains in equilibrium for any value of e = 70.0° or more, but slips if e < 70.0°. Find the coefficient of static friction between the plank and the ground. Roller Number Units the tolerance is +/-2% Click if you would like to Show Work for this question: Open Show Workarrow_forwardA ladder leans against a wall 5 meters above the ground so a homeowner can clear his gutters of leaves from last fall. The bottom of the ladder just begins to slip when it is 7.1 meters from the wall. What is the coefficient of static friction between the bottom of the ladder and the ground?arrow_forward
- A uniform ladder stands on a rough floor and rests against a frictionless wall as shown in the figure. Since the floor is rough, it exerts both a normal force N1 and a frictional force f1 on the ladder. However, since the wall is frictionless, it exerts only a normal force N2 on the ladder. The ladder has a length of L = 4.1 m, a weight of WL = 61.0 N, and rests against the wall a distance d = 3.75 m above the floor. If a person with a mass of m = 90 kg is standing on the ladder, determine the following. (a) the forces exerted on the ladder when the person is halfway up the ladder (Enter the magnitude only.) N1 = N N2 = N f1 = N (b) the forces exerted on the ladder when the person is three-fourths of the way up the ladder (Enter the magnitude only.) N1 = N N2 = N f1 = Narrow_forwardThere is this ladder with a length L = 3.5 m and mass M= 15 kg leans against a smooth vertical wall, while its bottom legs rest on a rough horizontal floor. There is also static friction between floor and ladder is u = 0.47. The ladder makes an angle 0 = 55° with respect to the floor. A person of mass 8M stands on the ladder a distance d from its base. What is the magnitude of the normal force N, in newtons, exerted by the floor on the ladder? What is the largest distance up the ladder dmax, in meters, that the person can stand without the ladder slipping?arrow_forwardA 14.0 m uniform ladder weighing 520 N rests against a frictionless wall. The ladder makes a 65.0°-angle with the horizontal. (a) Find the horizontal and vertical forces (in N) the ground exerts on the base of the ladder when an 850-N firefighter has climbed 3.80 m along the ladder from the bottom. horizontal force magnitude direction N towards the wall vertical force magnitude direction up N (b) If the ladder is just on the verge of slipping when the firefighter is 9.40 m from the bottom, what is the coefficient of static friction between ladder and ground? (c) What If? If oil is spilled on the ground, causing the coefficient of static friction to drop to half the value found in part (b), what is the maximum distance (in m) the firefighter can climb along the ladder from the bottom before the ladder slips? marrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON