
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
A pipeline engineer working in Yemen for the oil giant BP wants to perform a present worth analysis on alternative pipeline routings the first predominately by land and the second primarily undersea. The undersea route is more expensive initially due to extra corrosion protection
and installation costs, but cheaper security and maintenance reduces annual costs. Use present
worth analysis with a MARR= 9% to determine which route should be selected
Use factors or formulas
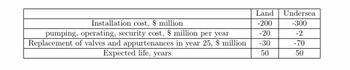
Transcribed Image Text:Installation cost, $ million
pumping, operating, security cost, $ million per year
Replacement of valves and appurtenances in year 25, $ million
Expected life, years
Land Undersea
-200
-300
-20
-30
50
-2
-70
50
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The product development group of a high-tech electronics company developed flve proposals for new products. The company wants to expand its product offerings, so it will undertake all projects that are economically attractive at the company's MARR of 12% per year. The cash flows (in $1000 units) associated with each project are estimated. Which projects, if any, should the company accept on the basis of a present worth analysis? Project Initial Investment Operating Cost, per Year Revenue, per Year Salvage Value Life A B $-200 $-70 $325 $10 $-300 $-130 $250 $22 10 years $-660 $-400 $475 $0 $-820 $-370 $550 $-900 $-770 $825 $90 $40 3 years 5 years 8 years 4 years The present worth of project A is $ The present worth of project B is $ The present worth of project C is $ The present worth of project D is $ The present worth of project E is $ Project A is (Click to select) Project B is (Click to select) Project C is (Click to select) Project D is (Click to select) ▼ Project E is (Click to…arrow_forwardCompare the alternatives C and D on the basis of a present worth analysis using an interest rate of 15.00% per year and a study period of 10 years. (Include a minus sign if necessary.) Alternative First Cost AOC, per Year Annual Increase in Operating Cost, per Year Salvage Value Life, Years The present worth of alternative C is $ с $-50000 $-8000 $-1500 $14000 10 $-21000 $-9000 $-200 $1500 5 and that of alternative D is $arrow_forwardUsing AW analysis. Texas Popcorn Corporation is planning to fully automate it process. The company CEO is currently looking into three options. Options A costs $450,000, AOC of $55,000, and salvage value of $85,000 after 3 years. Option B will cost $720,000 with an AOC of $68,000 and salvage of $95,000 after 4 years. Option C cost $800,000 with an AOC of $95,000 and salvage of $125,000 after 6 years. Which machine should the company select at an interest rate of 10% per year? Assume the project service life is 12 years.arrow_forward
- For some years, Mel has contracted with several major pizza retailers for home delivery services. He uses a MARR of 12% per year in all business dealings. His current van, purchased 10 years ago for $75,000, can be used for 3 more years, with an AOC of $23.000 and an estimated $25,000 trade-in value. A better-equipped van will cost $102,500, have an economic life of 6 years, an estimated trade- in value of $45,000, an AOC of $32,000 per year, and will generate an estimated $24,000 per year additional revenue. On the basis of these estimates, what market value now for the current van will make the new van equally attractive? Solve by spreadsheet or factors, as requested by your instructor. On equating the AW values of the current van and the new van, to calculate the market value now for the current van, the spreadsheet tool that should be used is GOAL SEEK The market value now for the current van that will make the new van equally attractive will be $ 62232.06 Oarrow_forwardWhat are the breakeven points and the range of profitability for below given Total profit general equation of a product is TP = - 0.00102 + 80D - 100?arrow_forwardDifferent types and capacities of crawler hoes are being considered for use in a significant excavation project to bury fiber-optic cable in Argentina. Several supervisors who have experience with similar projects have identified key attributes and their view of relative importance. Determine the weighted rank order (0 to 10 scale) and the normalized weights. Attribute Comment 1. Truck vs. hoe height 90% as important as trenching speed 2. Type of topsoil Only 10% of most important attribute 3. Type of subsoil 30% as important as trenching speed 4. Hoe cycle time Twice as important as type of subsoil 5. Hoe trenching speed Most important attribute 6. Cable-laying speed 80% as important as hoe cycle timearrow_forward
- An international textile company’s North America Division must decide which type of fabric cutting machines it will use—straight knife or round knife. The estimates are summarized below. Compare them on the basis of annual worths values at i = 10% per year using (a) factors, and (b) single-cell spreadsheet functions. Round Knife Straight Knife First cost, $ −250,000 −170,000 AOC, $/year −31,000 −35,000 Overhaul in year 2, $ — −26,000 Salvage value, $ 40,000 10,000 Life, years 6 4arrow_forwardAs supervisor of a facilities engineering department, you consider mobile cranes to be critical equipment. The purchase of a new, medium-sized truck-mounted crane is being evaluated. The economic estimates for the two best alternatives are shown in the following table. MARR is at 15% per year. You can use the assumption of repeatability in this case. Show that the same selection is made for the following methods:a. RORAI method b. AWC method c. PW methodarrow_forwardThe MARR is 7% per year, capital investment is $118,864, annual expense is $30,127, annual revenue is $89,754, salvage value is $18,093, The study period is 10 years. What is the AW?arrow_forward
- The PW-based relation for the incremental cash flow series to find A/* between the lower first-cost alternative X and alternative Y has been developed. 0=-38,000+9000(P/A,Ai*,10) + (-2000 (P/F,Ai*,10)) Determine the highest MARR value for which Y is preferred over X. Any MARR value less than % favors Y.arrow_forwardDecision D6, which has three possible choices (X, Y, or Z), must be made in year 3 of a 6-year study period in order to maximize EPW). Using an MARR of 18% per year, the investment required in year 3, and the estimated cash flows for years 4 through 6, determine which decision should be made in year 3. High Low High 06 Low 2 High Low Investment, Cash Flow, (Year Cash Flow, $1000 Cash Flow, Year 31 3) (Year 4) $1000 (Year 5) Cash Flow, $1000 (Year 6) Outcome Probability 3 4 5 6 High (X) $-150,000 $50 $50 $50 0.5 Low (X) $40 $30 $20 0.5 High (Y) $-73,000 $30 $40 $50 0.45 Low (Y) $30 $30 $30 0.55 High (Z) $-240,000 $190 $170 $150 0.7 Low (Z) $-30 $-30 $-30 0.3 The present worth of X is $arrow_forwardAbel and Family Perfumes wants to add one or more of four new products to its current line of colognes. Historically, Abel has used a 5-year project recovery period and a MARR of 20% per year. (a) Determine which of the four options the company should undertake on the basis of a present worth analysis, provided the total amount of investment capital available is $800,000. Use a hand solution, unless assigned otherwise. (b) What products are selected if the investment limit is increased to $900,000? Use a spreadsheet, unless assigned otherwise. (All cash flows are in $1000 units.) Product Line R1 S2 T3 U4 Investment, $ −200 −400 −500 −700 M&O cost, $/year −50 −200 −300 −400 Revenue, $/year 150 450 520 770arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education