
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Interference effects are produced at point P on a screen as a result of direct rays from a 490-nm source and reflected rays off a mirror, as shown in the figure below. If the source is L = 150 m to the left of the screen and h = 2.00 cm above the mirror, find the distance y (in millimeters) to the first dark band above the mirror.
answer in mm
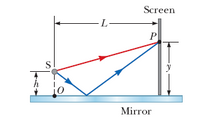
Transcribed Image Text:Screen
P
S
Mirror
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A tempered glass is placed atop a phone screen (n=1.52). Green light (540 nm) is incident from air onto the tempered glass (1.60). What is the minimum thickness of the tempered glass for the incident light to appear constructively? 0 [nm] 632 [nm] 169 [nm] 84 [nm]arrow_forwardLaser light is shone onto two slits separated by a distance of 8.0mm. The light is shone onto a screen 5.7m away. The distance to the m=3 bright fringe measured from the central bright spot is 7.9cm. Find the wavelength of the laser in nm.arrow_forwardPlease asaparrow_forward
- The following problem must be solved taking into consideration the modification given below: A student holds a laser that emits light of wavelength 545 nm. The laser beam passes though a pair of slits separated by 0.500 mm, in a glass plate attached to the front of the laser. The beam then falls perpendicularly on a screen, creating an interference pattern on it. The student begins to walk directly toward the screen at 2.00 m/s. The central maximum on the screen is stationary. Find the speed at which the 5th-order maxima changes its position on the screen. Do not use small angle approximation. Modification: Suppose there is a liquid in the space between the slits and the screen. Give such liquid any refractive index you desire (numerical value). Also suppose that the screen has a finite lenght (give another numerical value). Besides calculating the speed at which the 5th-order maxima changes its position on the screen also calculate the initial value of bright fringes according to the…arrow_forwardYou measure three segments of the distance between a diffraction slit an the screen on which the pattern forms: x1 = (15.8 ± 0.2) cm, x2 = (6.7 ± 0.1) cm, and x3 = (11.3 ± 0.1). What is the uncertainty of the total distance x1 + x2 + x3? Group of answer choices 0.4 cm 0.5 cm 0.2 cm 0.3 cm 0.1 cmarrow_forwardA slit of width 0.45 mm is illuminated with light of wavelength 544 nm, and a screen is placed 110 cm in front of the slit. Find the widths of the first and second maxima on each side of the central maximum. w1 = mm (1st maxima) w2 = mm (2nd maximaarrow_forward
- A thin film of glycerin (n = 1.473) of thickness 475 nm with air on both sides is illuminated with white light at near normal incidence. What wavelengths will be strongly reflected in the range 300 nm to 700 nm? nm (smallest value) nm nm (largest value) Need Help? Read Itarrow_forwardslit of width 0.46 mm is illuminated with light of wavelength 534 nm, and a screen is placed 114 cm in front of the slit. Find the widths of the first and second maxima on each side of the central maximum. w1 = mm (1st maxima) w2 = mm (2nd maxima)arrow_forwardA diffraction grating with n = 2.5E-05 lines/nm is used to separate two colors of light. The angle between their first maxima is Δθ ≡ θ1 - θ2 = 0.44 degrees, and the first light has wavelength λ1 = 618 nm. Part (a) Find θ1 using n and λ1 in radians. Part (b) Find θ2 in radians. Part (c) Find the value of the wavelength of the second color λ2 in nm.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON