
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
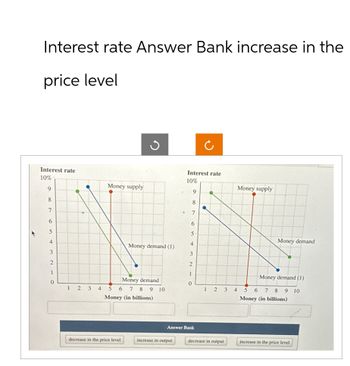
Transcribed Image Text:Interest rate Answer Bank increase in the
price level
Interest rate
10%
9
8
D
ง
2
Interest rate
10%
Money supply
9
8
Money supply
7
7
6
6
5
5
4
Money demand (1)
4
3
3
2
2
1
0
Money demand
0
1
2
345
6 7 8 9 10
1
2
3
4
Money (in billions)
Money demand
Money demand (1)
5 6 7 8 9 10
Money (in billions)
Answer Bank
decrease in the price level
increase in output
decrease in output
increase in the price level
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Typed plz and Asap Thanksarrow_forward11. Inflation and unemployment Suppose that the government believes the economy is producing goods and services beyond its optimal level. The government therefore decides to decrease the quantity of money in the economy. This monetary policy_______ the economy's demand for goods and services, leading to________ product prices. In the short run, the change in prices induces firms to produce______ goods and services. This, in turn, leads to a_______ level of unemployment. In other words, the economy faces a trade-off between inflation and unemployment: Lower inflation leads to________ unemployment.arrow_forwardInterest Rate 4% 3 2. O2 percent 0 percent 4 percent a 3 percent MS b d Refer to Figure 15-1. At which interest rate is there an excess money supply? Money Demand Quantity of Moneyarrow_forward
- 6. Monetary policy in the long run Consider a hypothetical economy that produces at its long-run macroeconomic equilibrium at a price level of 100. Suppose that the central bank in this economy is expanding the money supply by 4% each year. In order for the price level to be maintained at 100, real GDP must grow at an annual rate of (percentage?) if the velocity of money remains constant. Suppose the central bank enacts an unanticipated restrictive monetary policy. As a result, the supply of loanable funds (decreases/ Increase) , leading to a (rise/fall) in short-term interest rates. This in turn (reduces/raises) the opportunity cost of holding money. As people hold (Lower/ higher) money balances, the (velocity of money/ Price level/ aggregate output) will (rise/fall). True or false?: The shift in monetary policy exerts an impact on output and the general level of prices with a time lag. 6. Monetary policy in the long run Consider a hypothetical economy that produces at its…arrow_forward2arrow_forwardInterest rate 2% 4 6 8 C) 6 percent. D) 8 percent. 10 Transaction demand for money $220 220 220 220 220 Asset demand for money $300 280 260 240 220 1. Refer to the above table. The equilibrium interest rate is: B) 4 percent. Money supply $460 460 460 460 460 A) 2 percent.arrow_forward
- I only need Help with part (B)arrow_forwardThe following table gives the quantity of money demanded at various price levels (P), the money demand schedule. In the following table, fill in the column labeled Value of Money. Price Level (P) Value of Money (1/P) 0.80 1.00 1.33 2.00 Now consider the relationship between the quantity of money that people demand and the price level. The lower the price level, the required to complete transactions, and the money people will want to hold in the form of currency or demand deposits. Assume that the Federal Reserve initially fixes the quantity of money supplied at $3.5 billion. VALUE OF MONEY 8 Use the orange line (square symbol) to plot the initial money supply (MS) set by the Fed. Then, referring to the previous table, use the blue connected points (circle symbol) to graph the money demand curve. 2.00 1.75 1.50 1.25 1.00 0.75 Quantity of Money Demanded (Billions of dollars) 1.5 2.0 3.5 0.50 025 0 7.0 3 QUANTITY OF MONEY (Billions of dollars) 7 101 MS, Money Demand M money ?arrow_forwardA bank that expects interest rates to increase in the future will wants to hold more rate sensitive asset and fewer rate sensitive liabilities. (Choose the correct option) 1. Disagree. Rate sensitivve assets will increase the revenue this holding more of them as assets while reducing them as liabilities will decrease bank profits 2. Disagree. In any case it is more profitable for banks to reduce the number of rate sensitive assets and liabilities and increase assets and liabilities with fixed interest 3. Agree. Rate sensitive assets will increase the revenue thus holding more of them as assets while reducing them as liabilities will increase bank profits 4. Agree. Rate sensitive assets will increase in value thus holding more of them as assets, while reducing them as liabilities will decrease interest rate riskarrow_forward
- Value of Money 2 1 I MS1 1 19 U MS2 D Money Demand Quantity of Money money supply is MS1 and the value of money is 1, then there is a shortage in Select one: a. supply of money that is represented by the distance between points A and C. b. demand for money that is represented by the distance between points C and D. c. supply of money that is represented by the distance between points C and D. d. demand for money that is represented by the distance between points A and C. Refer to figure. If thearrow_forward15arrow_forward2. Money supply, money demand, and adjustment to monetary equilibrium The following table shows a money demand schedule, which is the quantity of money demanded at various price levels (P). Fill in the Value of Money column in the following table. Quantity of Money Demanded Price Level (P) Value of Money (1/P) (Billions of dollars) 1.00 2.0 1.33 2.5 4.0 2.00 4.00 8.0 Now consider the relationship between the price level and the quantity of money that people demand. The lower the price level, the Y money the typical transaction requires, and the y money people will wish to hold in the form currency or demand deposits.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education