
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
The common field cricket makes its characteristic loud chirping sound using a specialized vibrating structure in its wings. The motion of this structure—and the sound intensity that it produces—can be modeled as a damped oscillation. The sound intensity of such a cricket is as shown.
a. What is the frequency of the oscillations?
b. What is the time constant for the decay of these oscillations?
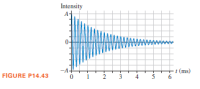
Transcribed Image Text:Intensity
A-
0-
I (ms)
5 6
-A-
FIGURE P14.43
2 3
4
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A mass (100 g) rests on a second mass (850 g) that is attached to a spring with k = 75.0 N/m. The coefficient of static friction between the two mass is 0.70. The masses are set into motion that is simple harmonic on a frictionless surface. a. What is the maximum amplitude the oscillation can have without the masses slipping against each other? b. What is the speed of the masses when they pass through the equilibrium position for the amplitude computed in part a?arrow_forward4. The displacement y(t) of an undamped oscillator of mass m>0 on a spring with spring constant k>0, and initial displacement a + 0 and initial velocity zero satisfies my" + ky = 0, y(0) = a, y'(0) = 0 %3D a. Solve this initial value problem. b. Show that the solution is periodic with period T, meaning that y(t+T)= y(t), and express Tin terms of m and k.arrow_forwardQ3, first three partsarrow_forward
- 10. A block hangs on a spring attached to the ceiling and is pulled down 6 inches below its equilibrium position. After release, the block makes one complete up-and-down cycle in 2 seconds and follows simple harmonic motion. a. What is the period of the motion? b. What is the frequency? c. What is the amplitude? С. d. Write a function to model the displacement d (in inches) as a function of the time t (in seconds) after release. Assume that a displacement above the equilibrium point is positive. е. Find the displacement of the block and direction of movement at t = 1 sec.arrow_forwardT 56. Damped sine wave The graph of f(t) = e¯' sin t is an example of a damped sine wave; it is used in a variety of applications, such as modeling the vibrations of a shock absorber. a. Use a graphing utility to graph ƒ and explain why this curve is called a damped sine wave. b. Compute f'(1) and use it to determine where the graph of f has a horizontal tangent. c. Evaluate lim e¯ª sin t by using the Squeeze Theorem. What does the result say about the oscillations of this damped sine wave?arrow_forwardAn object moves in simple harmonic motion described by the equation d=4 cos t, where t is measured in seconds and d in inches. Find the following. a. the maximum displacement b. the frequency c. the time required for one cycle a. in. b. cycles per second C. Enter your answer in the answer bos Save for Later Type here to searcharrow_forward
- B. E. 0.2727 m 0.3140 m 0.3497 m 0.3087 m C. F. 1--1 NUTOJ A 2.9 kg mass is attached to a spring with constant 24_N/m and is moving horizontally on a frictionless surface. If the object has speed 1.4_m/s as it passes through the equilibrium position, then what is the maximum displacement of the object? I 24. A. 0.4867_m D. 0.4348 m B. 0.1773 m E. 0.257_m C. 0.4112_m F. 0.5435 m JABBX Two objects are connected by a light string passing over a light, frictionless pulley. The 5.00-kg object is released from rest at a point 4.00 m above the floor. Find the speed of the 5.00-kg object when it is 1 meter above the floor. 5.00 kg Pigshow.jpeg Pig show.jpeg MacBook Proarrow_forwardA spring with spring constant 15 N/m hangs from the ceiling. A ball is attached to the spring and allowed to come to rest. It is then pulled down 9.5 cm and released. The ball makes 20 oscillations in 23 s seconds. You may want to review (Pages 403-404) Part A What is its the mass of the ball? Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. m = Submit Part B "i Vmax= μA Submit Value Request Answer What is its maximum speed? Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. μA Value Units Request Answer ? Units ?arrow_forwardWhich of the following four options is the correct one Which one or more? a. A spectrogram is a graph of frequency against amplitude and time with time on the x-axis, frequency on the y-axis and amplitude indicated by brightness or colour. b. A spectrogram is a graph of amplitude on the y axis against time on the x-axis. c. A spectrogram is a graph of frequency against amplitude and time with time on the x-axis, frequency on the y-axis and amplitude indicated by crosses. d. A spectrogram is a graph of amplitude against frequency and time with frequency on the x-axis, time on the y-axis and amplitude indicated by brightness or colour.arrow_forward
- Pendulum clocks use the repetitive motion of the oscillations to track time. Imagine you have one of these clocks and you move from the lower elevation of St. Catharines to the higher elevation of Calgary. Will you need to adjust the length of the pendulum to keep time correctly? If so, will you need to increase or decrease the length of the pendulum to ensure the pendulum keeps time correctly? O The length of the pendulum will need to be decreased. O The length of the pendulum will need to be increased. O The length of the pendulum will not need to be changed.arrow_forwardI would like some help with thus problem, thank you!arrow_forwardA mass of 1.64 Kg is connected to a spring of spring constant 9.02 N/m. An oscillation is started by pulling the mass to the right to amplitude 0.779 m before release and the oscillator moves in air. The oscillation decays to 16.7% of the original amplitude in 63.5 seconds. a. What would the position of the oscillation be 29.63 seconds after release?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON