
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
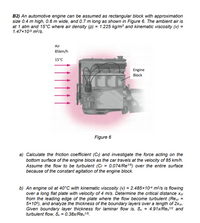
Transcribed Image Text:B2) An automotive engine can be assumed as rectangular block with approximation
size 0.4 m high, 0.6 m wide, and 0.7 m long as shown in Figure 6. The ambient air is
at 1 atm and 15°C where air density (P) = 1.225 kg/m and kinematic viscosity (v) =
1.47x105 m2/s.
Air
85km/h
15°C
Engine
Block
Figure 6
a) Calculate the friction coefficient (C) and investigate the force acting on the
bottom surface of the engine block as the car travels at the velocity of 85 km/h.
Assume the flow to be turbulent (Cr = 0.074/Re5) over the entire surface
because of the constant agitation of the engine block.
b) An engine oil at 40°C with kinematic viscosity (v) = 2.485×104 m³/s is flowing
over a long flat plate with velocity of 4 m/s. Determine the critical distance xer
from the leading edge of the plate where the flow become turbulent (Recr =
5x105), and analyze the thickness of the boundary layers over a length of 2xer.
Given boundary layer thickness for laminar flow is, öx = 4.91x/Re,2 and
turbulent flow, õ., = 0.38x/Re,15.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Problem 1: Streamlining From dimensional analysis, we know the drag force is FD- CopAV2/2, where Cp is a dimensionless coefficient of drag. The two space shuttles below have the same area A, the same velocity V, and are flying through the same air. Which has a smaller Co and why? (<25 words) thine earrow_forwardPlease solve and write out equations used. Thanksarrow_forward% ParametersD = 0.1; % Diameter of the tube (m)L = 1.0; % Length of the tube bundle (m)N = 8; % Number of tubes in the bundleU = 1.0; % Inlet velocity (m/s)rho = 1.2; % Density of the fluid (kg/m^3)mu = 0.01; % Dynamic viscosity of the fluid (Pa.s) % Define the grid size and time stepdx = D/10; % Spatial step size (m)dy = L/10; % Spatial step size (m)dt = 0.01; % Time step size (s) % Calculate the number of grid points in each directionnx = ceil(D/dx) + 1;ny = ceil(L/dy) + 1; % Create the velocity matrixU_matrix = U * ones(nx, ny); % Perform the iterationsfor iter = 1:100 % Calculate the velocity gradients dUdx = (U_matrix(:, 2:end) - U_matrix(:, 1:end-1)) / dx; dUdy = (U_matrix(2:end, :) - U_matrix(1:end-1, :)) / dy; % Calculate the pressure gradients dpdx = -mu * dUdx; dpdy = -mu * dUdy; % Calculate the change in velocity dU = dt * (dpdx / rho); % Update the velocity matrix U_matrix(:, 2:end-1) = U_matrix(:, 2:end-1) + dU; % Apply…arrow_forward
- For the below low-speed wind tunnel (Fig. 1), Settling chamber (reservoir) V₁ PI Nozzle V₂ P2. A2 Test section Diffuser Figure 2: Low-Speed Wind Tunnel P3 A3 A) Derive a mathematical expression to determine the flow velocity at the test section? B) At the sea level conditions, calculate the velocity at the test section when A1/A2=10 and the pressure difference is 4.9 kPa? C) What is a critical Reynolds number on an airfoil? D) If the airfoil has a critical Reynolds number of 550,000, how far aft of the airfoil's leading edge will transition occur?arrow_forwardAir at atmospheric pressure and temperature of 25 oC flows at a speed of 10 m/s along a flat plate that is 4 m long and has a uniform surface temperature of 140 oC. Ifcritical Reynolds number of 200,000:a) the local heat transfer kingdom at x = 2; 3; and 4 m from the front rim.b) the average heat transfer balance is 4 m long.c) the rate of heat transfer from the surface of the plate to the air if the width of the plate surface is 2 m.d) game problems b) and c) flow velocity 5 and 20 m/se) What is your analysis and conclusion on this case?arrow_forwardFrom Table A.3, the density of glycerin at standard conditionsis about 1260 kg/m3 . At a very high pressure of 8000 lb/in2 , itsdensity increases to approximately 1275 kg/m3 . Use this datato estimate the speed of sound of glycerin, in ft/s.arrow_forward
- The heat transfer coefficient is a nondimensional parameter which is a function of viscosity ? , specific heat cp (kJ/kg·K), and thermal conductivity k (W/m·K). This nondimensional parameter is expressed as (a) cp/? k (b) k/? cp (c) ? /cpk (d ) ? cp/k (e) cpk/?arrow_forwardPy Flow FIGURE 6.2 Portion of a fluid distribution system showing variations in velocity, pressure, and elevation. Reference level 2.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY