
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
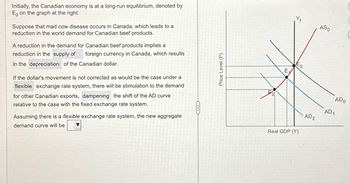
Transcribed Image Text:Initially, the Canadian economy is at a long-run equilibrium, denoted by
E, on the graph at the right.
Suppose that mad cow disease occurs in Canada, which leads to a
reduction in the world demand for Canadian beef products.
A reduction in the demand for Canadian beef products implies a
reduction in the supply of foreign currency in Canada, which results
in the depreciation of the Canadian dollar.
If the dollar's movement is not corrected as would be the case under a
flexible exchange rate system, there will be stimulation to the demand.
for other Canadian exports, dampening the shift of the AD curve
relative to the case with the fixed exchange rate system.
Assuming there is a flexible exchange rate system, the new aggregate
demand curve will be
Price Level (P)
2
Yf
ASO
E
Eo
Real GDP (Y)
ADO
AD1
AD2
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- There is a flexible exchange rate system and only two countries in the world, the United States and Mexico. If the inflation rate in the United States rises relative to the inflation rate in Mexico, it follows that both the dollar and the peso will appreciate, although the peso will appreciate before the dollar appreciates. both the dollar and the peso will depreciate, although the peso will depreciate before the dollar depreciates. the dollar will appreciate, and the peso will depreciate. There is not enough information to answer the question. the dollar will depreciate, and the peso will appreciate.arrow_forwardThe autonomous region of Catalonia has recently declared independence from Spain, and is looking for an exchange rate policy that would best fit their needs. The Catalans’ main goal is to stabilise the price level in the long-run, but constantly experience fluctuations in the price of foreign goods imported from Spain and other European countries. Would it be better for the Catalans to fix the exchange rate against the Euro, or to adopt a floating exchange rate? Justify your answer briefly.arrow_forwardSuppose the foreign exchange market is characterized by the following equations: Qd = 12.5 – 1.25R Qs = 3.5 + 1.25R where Qd is the demand function for foreign exchange, Qs is supply function of foreign exchange, and R is exchange rate in units of domestic currency per unit of foreign currency (quantity is in million units of foreign currency). ===================== The foreign exchange market described above is Select one: stable unstable unpredictable none of the abovearrow_forward
- To prevent an appreciation of the British pound, the U.S. Federal Reserve has to: Sell U.S. currency Buy British currency Sell British currency Devalue the U.S. dollararrow_forwardSuppose that at some point the spot exchange rate is equal to 100 yen per one U.S. dollar, while the interest rate in dollars is 6% and the interest rate in yen is 1%. What is the approximate forward rate that is consistent with this situation?arrow_forwardAssume that in 2010, Country A had an exchange rate of 0.770.77 units of national currency (UNC) per U.S. dollar (USD). By 2015, Country A's budget deficit increased, and Country A decided to issue bonds to finance the deficit. As a result, the exchange rate changed by UNC0.06UNC0.06. Calculate the 2015 exchange rate.arrow_forward
- Suppose the exchange rate value of the dollar depreciates. Instructions: In order to receive full credit, you must make a selection for each option. For correct answer(s), click the option once to place a check mark. For incorrect answer(s), click the option twice to empty the box. Who are the winners? People who want to buy foreign assets Firms that export goods People who want to buy assets in this country People who travel abroad Firms that import goods People who travel to this countryarrow_forwardRelative inflation rates affect interest rates, exchange rates, the overall economic health of a country, and the operations and profitability of multinational companies. Consider the following statement: Countries with lower inflation rates will have lower interest rates. If companies borrow from countries with low interest rates, the potential gains from the interest savings will likely be (multiplied or offset) by the losses from currency appreciation.arrow_forwardAccording to the purchasing-power-parity theory, the U.S. dollar maintains its purchasing-power parity if it depreciates by an amount equal to the excess of: Question 3 options: a) Foreign inflation over U.S. inflation b) Foreign interest rates over U.S. interest rates c) U.S. interest rates over foreign interest rates d) U.S. inflation over foreign inflationarrow_forward
- Relative inflation rates affect interest rates, exchange rates, the overall economic health of a country, and the operations and profitability of multinational companies. Consider the following statement: Countries with lower inflation rates will have lower interest rates. Based on your understanding of the relationship between relative inflation rates and exchange rates, identify whether the preceding statement is valid or invalid. The statement is invalid, because the nominal interest rate is independent of the inflation rate. The statement is valid, because the nominal interest rate is the sum of the real interest rate plus inflation, so lower inflation rates would result in lower interest rates.arrow_forwardAssume that you are studying exchange rates between India and the US. Assume that the equilibrium exchange rate in India is 76 Indian rupees per US dollar. Now suppose that the inflation rate falls in India. Which of the following choices shows a change we would expect to see in the Indian forex market? The demand for the US dollar would rise, leading to a depreciation of the Indian rupee. The demand for the Indian rupee would increase leading to an appreciation of the US dollar. The supply of the Indian rupee would rise leading to an appreciation of the Indian rupee. The supply of the US dollar would rise leading to an appreciation of the Indian rupeearrow_forwardBy controlling the exchange rate of the Yuan and “pegging” it to the U.S. Dollar: a) is helping the United States improve its balance of trade b) the Yuan is overvalued c) the Yuan is undervalued d) the Yuan is properly valued e) China is hurting their ability to exportarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education