
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
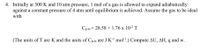
Transcribed Image Text:4. Initially at 300 K and 10 atm pressure, 1 mol of a gas is allowed to expand adiabatically
against a constant pressure of 4 atm until equilibrium is achieved. Assume the gas to be ideal
with
Cp.m = 28.58 +1.76 x 10-2 T
(The units of T are K and the units of Cp,m are J K-l mol-'.) Compute AU, AH, q and w.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please write full calculations and explain math At 700 K, the reaction2SO2(g) + O2(g) ⇌ 2SO3(g) has the equilibrium constant K = 4.3 × 106, and the following initial partial pressures present: pSO2 = 0.010 bar; pO2 = 0.010 bar; pSO3 = 10. bar. Calculate Q and predict in what direction the reaction will proceed to reach equilibrium.arrow_forwardAt 4000C and 350 bar, a 1:3 mixture of nitrogen and hydrogen gases react to form an equilibrium a mixture containing ammonia at a mole fraction of 0.75. Assuming perfect gas behavior, calculate the equilibrium constant K for: N2(g) + 3 H2(g) ⇄ 2 NH3(g)arrow_forwardI am doing a calculation wrong somewhere. It keep getting the wrong answer.arrow_forward
- For the following reaction: A(g) + 3 B(g) magnitude of Kp (don't report the units) assuming the following composition at equilibrium: PA = 0.735 bar PB = 0.603 bar Pc = 0.627 bar PD 0.87 bar = 2 C(g) + D(g) Calculate the =arrow_forwardAs you are walking across your laboratory, you notice a 5.25 L flask containing a gaseous mixture of 0.0205 mole NO2 (9) and 0.750 mol N2O4 (q) at 25°C. 4 (g) Is this mixture at equilibrium? If not, will the reaction proceed towards forming more products, or more reactants? N2O4 4 (9) → 2NO2 (9) Ko = 4.61 x 103 at 25°Carrow_forwardWhat is Boyle's law constant, kp if a sealed rigid container with a volume, Vof 0.600 L has a pressure, Pof 130.0 kPa? V = kg(1/P) BIUA - A - I E E E X x, = E 12pt Paragraph fx MacBook Airarrow_forward
- The initial concentrations or pressures of reactants and products are given for each of the following systems. Calculate the reaction quotient and determine the direction in which each system will proceed to reach equilibrium. (The system is considered in equilibrium if Kc and Qc are within 5% of each other.) (a.) 2 SO3(g) 2 SO2(g) + O2(g) Pi(SO3) = 0.100 atm, Pi(SO2) = 1.10 atm, Pi(O2) = 1.20 atm, Kp = 5.5 atm What is the reaction quotient? What direction will the reaction shift to? LEFT or RIGHT? (b.) 2 NO(g) + Cl2(g) 2 NOCl(g) Pi(NO) = 1.25 atm, Pi(Cl2) = 1.25 atm, Pi(NOCl) = 0 atm, Kp = 3.1 ✕ 103 What is the reaction quotient? What direction will the reaction shift to? LEFT or RIGHT? (c.) N2(g) + O2(g) 2 NO(g) [N2]i = 0.120 M, [O2]i = 0.240 M, [NO]i = 1.20 M, Kc = 0.050 What is the reaction quotient? What direction will the reaction shift to? LEFT or RIGHT?arrow_forwardConsider the following reaction where K, = 9.52×10-2 at 350 K: %3D CH4(g) + CC14(g) 2CH2C1½(g) If the three gases are mixed in a rigid container at 350 K so that the partial pressure of each gas is initially one atm, what will happen? Indicate True (T) or False (F) for each of the following: • 1. A reaction will occur in which CH,Cl2(g) is consumed. v 2. K, will increase. • 3. A reaction will occur in which CH, is consumed. • 4. Q is less than K. v 5. The reaction is at equilibrium. No further reaction will occur.arrow_forwardConsider the equilibrium system described by the chemical reactionbelow. Calculate the value of Qc for the initial set reaction conditions in3.00 L container:8.65 g C2H4, 11.2 g O2, and 5.68 g CH3CHO. 2 C2H4(g) + O2(g) = 2 CH3CHO(g)arrow_forward
- Parrow_forwardDetermine the equilibrium partial pressure of NH3 in a reaction vessel that initially contained 0.900 atm N2 and 0.500 atm H2 at 648 K.arrow_forwardCalculate the pressure equilibrium constant KP for the equilibrium between nitrogen monoxide, oxygen, and nitrogen dioxide has the final temperature of the mixture round your answer to two significant digits.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY