
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
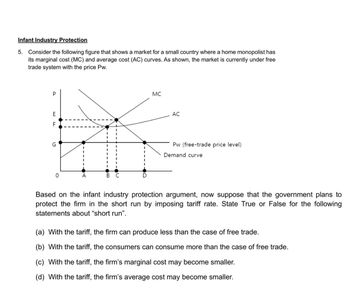
Transcribed Image Text:Infant Industry Protection
5. Consider the following figure that shows a market for a small country where a home monopolist has
its marginal cost (MC) and average cost (AC) curves. As shown, the market is currently under free
trade system with the price Pw.
P
E
யம
F
G
B
MC
AC
Pw (free-trade price level)
Demand curve
Based on the infant industry protection argument, now suppose that the government plans to
protect the firm in the short run by imposing tariff rate. State True or False for the following
statements about "short run".
(a) With the tariff, the firm can produce less than the case of free trade.
(b) With the tariff, the consumers can consume more than the case of free trade.
(c) With the tariff, the firm's marginal cost may become smaller.
(d) With the tariff, the firm's average cost may become smaller.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- i need this in words\ not handwritten solution pleasearrow_forwarde. Determine the deadweight loss to society (if any) when the regulated price is $10 per unit.arrow_forwardSofia, a political science student, thinks that the government should intervene to revive declining industries like video stores and print newspapers. The government, she reasons, can resolve the coordination problem of getting the agents in these markets to trade. Do you agree with her? Explain your answer. OA. No, these industries are declining not because of coordination problems but, rather, because of falling demand. OB. Yes, the coordination problems of these industries suggest that the invisible hand is failing, so government intervention would revive these industries. OC. Yes, government intervention is necessary to generate more buyers for these industries, thus coordinating buyers with existing sellers. OD. No, these declining industries are plagued by coordination problems, but government intervention is never the answer.arrow_forward
- Suppose five construction companies have the ability to build a factory overseas to produce a manufactured good The marginal cost of building a factory for each construction company is shown in the table below: Producer Company 1 Company 2 Company 3 Company 4 Company 5 Marginal Cost S1,000,000 $1.250,000 $1,300,000 $1,350.000 $1.500.000 If the market price of an overseas factory is $1.425,000, what is the surplus for these five companies? Producer surplus is S (Enter your response an a whole numberarrow_forwardWe want to model the oil markets of the 19th century. And let the inverse demand for oil be P = 300 - 2Q, and the marginal cost of producing oil be MC = Q. Standard Oil, during the second half of the 19th century, can be modeled as a monopsony. If we assume the oil market is a monopsony, what is the quantity produced in equilibrium? Give the exact value up to two sig figs after the decimal point.arrow_forwardWhat is meant by consumer surplus and producer surplus? Using a diagram show that there is a deadweight loss to society from monopoly in terms of total surplus.arrow_forward
- consider a market with a large number of firms, an upward sloping supply curve S0, and a downward sloping demand curve D0. Assume that the market is perfectly competitive; hence, the supply curve S0 is the sum of the marginal cost curves of all the firms. Indicate the original competitive equilibrium price P0, equilibrium quantity Q0, the resulting Consumer Surplus CS0, the resulting Producer Surplus PS0, and the “socially optimal” output (the output the Benevolent Dictator would choose) QSO on your graph. Graphically indicate the size of Dead-Weight Loss DWL0 if there is such a loss. In the narrative, please explain how you determined the socially optimal output level and the presence (or absence) of dead-weight loss in this situation.arrow_forwardSuppose Eckerd Pharmacy is the only pharmacy in a particular market, but CVS Pharmacy is thinking about entering the market. Absent entry, Eckerd Pharmacy can maximize profits by producing a small quantity. However, by producing a large quantity, Eckerd Pharmacy can attempt to deter entry by reducing prices and, consequently,. profits. E: $47 C: $47 Enter Eckerd Pharmacy must choose how much to produce first and then cVS Pharmacy will choose whether to enter the industry. The strategies and corresponding profits for Eckerd (E) and CVS Pharmacy (C) are depicted in the decision tree to the right. What is the Nash equilibrium of the game? Small Quantity E: $85 C: $0 Stay Out! E O A. Eckerd Pharmacy will choose the small quantity and CVS Pharmacy will Enter E: $O C: -$10 not enter. Large Quantity O B. Eckerd Pharmacy will choose the large quantity and CVS Pharmacy will not enter. Stay Out E: $65 C: $0 OC. Eckerd Pharmacy will choose the large quantity and CVS Pharmacy will enter. O D.…arrow_forward1. Rank the following in ascending order of Home welfare and justify your answers. If two items are equivalent, indicate this accordingly. a. Tariff t in a small country with perfect competition b. Tariff t in a small country with a Home monopoly c. Quota with the same imports M in a small country, with a Home monopoly d. Tariff t in a country facing a Foreign monopolyarrow_forward
- To justify the subsidies it has received from European governments, the Airbus Company has used all of the following arguments, except a. Airbus' subsidies were totally repaid as the firm realized profits on its aircraft sales. b. its subsidies have prevented U.S. aircraft firms from holding a world-wide monopoly. c. without subsidies to Airbus, Europe would be dependent on the United States as a supplier of aircrafts. d. U.S. aircraft firms have benefited from military-sponsored programs of the U.S. government. Note:- Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism. Answer completely. You will get up vote for sure.arrow_forwardAntidumping laws O allow foreign firms to easily enter the domestic market. O allows domestic firms to be protected from foreign competition by lowering their competitors' costs. O allows foreign firms to be more competitive in the domestic market. O allow domestic firms to be protected from foreign competition by raising their competitors' costs.arrow_forwardplease answer in text form and in proper format answer with must explanation , calculation for each part and steps clearlyarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education