
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Exercise A.2 .
Sinergy and Dinaco are the only two companies in a high-tech industry. They are faced with the following matrix of results when deciding their research budget:
After analizing the graph, answer the following questions...
a) Does Sinergy have a dominant strategy? Reason your answer.
b) Does Dinaco have a dominant strategy? Reason your answer.
c) Is there a Nash equilibrium in this scenario? Reason your answer.
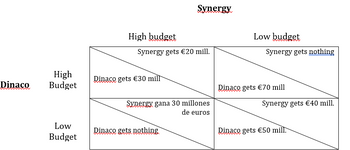
Transcribed Image Text:Dinaco
High
Budget
Low
Budget
High budget
Synergy gets €20 mill.
Dinaco gets €30 mill
Synergy
Synergy gana 30 millones
de euros
Dinaco gets nothing
Low budget
Synergy gets nothing
Dinaco gets €70 mill
Synergy gets €40 mill.
Dinaco gets €50 mill.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- below cost? That is, explain a rationale of loss leaders, using your U4. The coconut-milk carts from Exercise S7 set up again the next day. Nearly 172 [CH. 5] SIMULTANEOUS- MOVE GAMES a dollars of a pound of cheese. (a) Initially, L'Épicerie runs La Boulangerie and La Fromagerie as if the were separate firms, with independent managers who each try to maximize their own profit. What are the Nash equilibrium quanti- ties, prices, and profits for the two divisions of L'Épicerie, given the new quantity equations? (b) The owners of L'Épicerie think that they can make more total profit by coordinating the pricing strategies of the two Yuppietown divi- sions of their company. What are the joint-profit-maximizing prices for bread and cheese under collusion? What quantities do La Bou- langerie and La Fromagerie sell of each good, and what is the profit that each division earns separately? (c) In general, why might companies sell some of their goods at prices below cost? That is, explain a…arrow_forwardAnswer the following questions: 1.What is the Nash Equilibrium of this game? 2. Does Starbucks have dominant pricing strategy, given these predicted payoffs? Does Dunkin' Donuts have a dominant pricing strategy, given these payoffs? Explain. 3. Is this game an example of a prisoner's dilemma? Why or why not?arrow_forwardIdentify a real-world situation in which you see game theory/strategic behavior in action. Explain the game: Who are the players ? What are the strategies they have at their disposal? How are payoffs determined? What, if any, is the Nash equilibrium? Note, this article from Up Journey might help you come up with an example: https://upjourney.com/game-theory-examples-in-real-lifearrow_forward
- Japan's Elpida Memory entered court management and was acquired by Micron. The media reportedthat it was the result of the semiconductor chicken game.■Question (a) Where is the Nash Equilibrium?■Question (b) What is the mixed-strategy equilibrium? – find out x and y■Question (c) What is the probability of a chicken game?arrow_forwardCompare and contrast P and Q determination in a strategic situation like an oligopoly and that in a purely competitive situation. Give examples for each type of scenarios.arrow_forwardQuestion 2 (Choices Involving Strategy): Suppose there are two competing Gyms in a local town. Each gym is individually owned and has three pricing levels to choose from: Low, Medium and High (PL,PM, and PH). Consider the table below as the outcomes for each combination of strategies (they are yearly profits in the thousands). Can you predict the outcome using ONLY iteratively dominated strategies? Why or why not? Find the Nash Equilibrium(a) using best responses. Is this the best outcome? Now, suppose that there was a sudden increase in the cost of equipment that meant the low price was no longer viable, and both choosing the medium price level meant only 50 (thousand) profit for each gym. Nothing else changes. What is the pure and mixed strategy Nash equilibrium of this new game? Gym 1 is on the left and Gym 2 is on the top. The first number inside every box is Gym 1's profit and the second (after the comma) is Gym 2's profit. (10 Marks) PL PMPH PL 125, 125 200, 75 375,50 PM 75, 250…arrow_forward
- I am struggling with this question for a Game Theory course. It would be great to have a visual breakdown of how to solve it so that I understand what to do for the rest of the problems.arrow_forwardThe payoff matrix in the figure to the right shows the payoffs for a pricing game. If you were firm A, which strategy would you choose? Firm A should A. price high because this is their maximin strategy. B. price low because this is their tit-for-tat strategy. C. price high because this is their dominant strategy. D. price low because this is their dominant strategy. E. price low because this maximizes profits of both firms. Firm B's dominant strategy is to price If this game were repeated a large number of times and you were firm A and you could change your strategy, what might you do? Firm A should O A. use a tit-for-tat strategy by responding in kind to firm B's play. B. use a maximin strategy by maximizing the minimum gain that can be earned. C. use a tit-for-tat strategy by selecting a price that minimizes firm B's profits. D. use a maximin strategy by by responding in kind to firm B's play. E. use a tit-for-tat strategy by maximizing the minimum gain that can be earned. C Price…arrow_forwardQ:3 a,b and carrow_forward
- Two rival companies competing in the same market need to decide their plans for future expansion of their stores. The Table below shows the possible outcomes of their mutually interdependent actions (payoffs are profits in £m) Giga Company Titanic Conglomerate No Change Refurbishment of existing stores Large Expansion No Change 30, 40 25, 35 15, 24 Refurbishment of existing stores 35, 30 28, 32 18, 33 Large Expansion 12, 22 18, 20 20, 25 The Nash equilibrium: (A) does not exist. (B) occurs when both firms choose Refurbishment of existing stores. (C) occurs when both firms choose Large Expansion. (D) occurs when both firms choose No Change.arrow_forward8) Consider the following game: There are 10 players. Each player is asked to write a number between 0 and 100. The player whose choice is closest to half of the average is the winner. Describe the game and discuss what would you expect to be the average number if the game were played in class with your colleagues. Do you expect them to play the Nash equilibrium strategy? Explain.arrow_forwardSolve all this question......you will not solve all questions then I will give you down?? upvote...arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education