
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
N2(g)+O2(g)+heat⇌2NO(g)
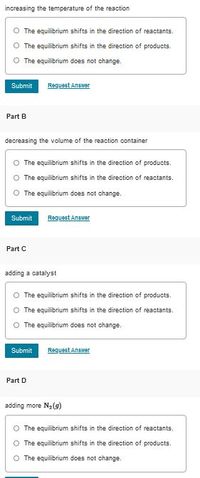
Transcribed Image Text:increasing the temperature of the reaction
The equilibrium shifts in the direction of reactants.
The equilibrium shifts in the direction of products.
The equilibrium does not change.
Submit
Reguest Answer
Part B
decreasing the volume of the reaction container
O The equilibrium shifts in the direction of products.
The equilibrium shifts in the direction of reactants.
The equilibrium does not change.
Submit
Request Answer
Part C
adding a catalyst
The equilibrium shifts in the direction of products.
O The equilibrium shifts in the direction of reactants.
O The equilibrium does not change.
Submit
Request Answer
Part D
adding more Na(9)
The equilibrium shifts in the direction of reactants.
The equilibrium shifts in the direction of products.
O The equilibrium does not change.
O O O
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Octane (112.224 g/mol) undergoes combustion to form carbon dioxide gas and water vapor: 2 C8H18 (l) + 25 O2 (g) → 16 CO2 (g) + 18 H2O (g) ΔH°rxn = -1.01 x 105 kJ Given that the density of octane is 0.703 g/mL, what volume of octane must undergo combustion to produce 524 kJ of heat?arrow_forwardEnergy cannot be created nor destroyed, but it can be transferred between a system and its surroundings. The change in internal energy, AU, is positive if the system absorbs energy, and it is negative if the system releases energy. (Figure 1) The total change in internal energy is the sum of the heat, q, and work, w: AU =q+w. Figure 1 of 1 Surroundings AU pystem u System >0 Surroundings AU system System u <0 AU = q + warrow_forwardCaSO4.5H2O + heat → ____ CaSO4(s) + ____ H2Oarrow_forward
- Nitric oxide (NO) can be formed from nitrogen, hydrogen and oxygen in two steps. In the first step, nitrogen and hydrogen react to form ammonia: N₂(g) + 3H₂(g) 2 NH3(g) In the second step, ammonia and oxygen react to form nitric oxide and water: 4 NH3(g) + 50₂(g) → 4 NO(g) + 6 H₂O(g) ΔΗ = - 92. kJ kJ Calculate the net change in enthalpy for the formation of one mole of nitric oxide from nitrogen, hydrogen and oxygen from these reactions. Round your answer to the nearest kJ. X AH = -905. kJarrow_forwardGiven the following thermochemical equations: 2 OF2 (g) →→→ 02 (g) + 2 F2 (g) 2 CIF (g) + O2 (g) → C120 (g) + OF2 (g) CIF 3 (g) + O2 (g) → Cl20 (g) + 3/2 OF2 (g) AH = -49.4 kJ AH = +205.6 kJ AH = +266.7 kJ Calculate the enthalpy change (in kJ) for this reaction: CIF (g) + F2 (g) → CIF3 (g) Show your complete solution. Express your answer in two decimal places.arrow_forwardWhen methanol, CH, OH, is burned in the presence of oxygen gas, O₂, a large amount of heat energy is released. For this reason, it is often used as a fuel in high performance racing cars. The combustion of methanol has the balanced, thermochemical equation CH₂OH(g) + O₂(g) → CO₂(g) + 2 H₂O(1) AH = -764 kJ How much methanol, in grams, must be burned to produce 983 kJ of heat? mass: garrow_forward
- Nitric oxide (NO) can be formed from nitrogen, hydrogen and oxygen in two steps. In the first step, nitrogen and hydrogen react to form ammonia: N₂(g) + 3 H₂(g) 2NH,(9) In the second step, ammonia and oxygen react to form nitric oxide and water: 4NH3(g) + 5O₂(g) 4 NO(g) + 6H₂O(g) ΔΗ=-905. kJ Calculate the net change in enthalpy for the formation of one mole of nitric oxide from nitrogen, hydrogen and oxygen from these reactions. Round your answer to the nearest kJ. kJ ΔΗ= -92. kJ Xarrow_forwardThe following thermochemical equation is for the reaction of carbon dioxide(g) with hydrogen (g) to form acetylene(g) (C₂H₂) and water(g). 2CO₂(g) + 5H₂(g)→→→→→→ C₂H₂(g) + 4H₂O(g) ΔΗ = 46.5 kJ When 10.9 grams of carbon dioxide (g) react with excess hydrogen (g), kJ of energy are Hint: An amount of energy is expressed as a positive number. The sign of AH in the thermochemical equation indicates whether the energy is absorbed or evolved.arrow_forwardCoffee cup calorimetry was used to determine the enthalpy of solution of lithium iodide (LiI): A) First, the coffee cup was calibrated. 50.0 mL of water (s=4.184J/g×0 C) was heated to 95.50C and mixed with 50.0 mL of cool water at 22.30 C. The temperature of the contents of the coffee cup stabilized at 49.40 C. Determine the heat capacity of the coffee cup. B) Next, the enthalpy of solution of lithium iodide (LiI) was determined. 0.0g of solid lithium iodide was added to 100mL of water at 23.20 C in the coffee cup, and the temperature increased to 32.10 C. Calculate the enthalpy of the solution of lithium iodide.arrow_forward
- In one box of nails, there are 75 iron nails weighing 0.280 lblb . The density of iron is 7.86 g/cm3g/cm3. The specific heat of iron is 0.452 J/g∘CJ/g∘C. The melting point of iron is 1535 ∘C∘C. A)How much heat, in joules, must be added to the nails in the box to raise their temperature from 16 ∘C∘C to 123 ∘C∘C? B)How much heat, in joules, is required to heat one nail from 31 ∘C∘C to its melting point?arrow_forwardYou are given the following data: H₂(g) 2H (g) Br₂(g) → 2 Br (g) H₂(g) + Br₂(g) 1 kJ mol → → 2 HBr (g) Calculate AH° for the reaction. H(g) + Br(g) HBr (g) Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. x10 ΔΗ° = 436.4 X ΔΗ° = 192.5 ΔΗ° = - 72.4 kJ mol kJ mol kJ molarrow_forwardThe conversion of sulfur dioxide to sulfur trioxide is exothermic: SO2 (g) + ½ O2 (g) → SO3 (g) ΔH°rxn = ??? A certain exothermic reaction occurs in a coffee cup calorimeter that contains 425 mL of water. When the reaction reaches completion, the temperature of the water has increased by 2.37°C. If 3.47 g of SO3 are produced in the reaction, what is ΔH°rxn?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY