
Concept explainers
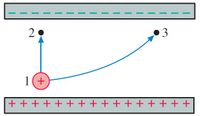
In two different situations a proton is released between the plates of a charged capacitor (uniform E-field). In the first situation, it is released with some initial velocity and travels from position 1 to position 2. In the second situation, it is released with some initial velocity and travels from position 1 to position 3. In both situations the initial speed is the same.
1. The potential energy change () :
A. is equal for both paths
B. is greater from 1 to 2
C. is greater from 1 to 3
D. cannot be determined by given information
2. The kinetic energy of the proton () :
A. increases from 1 to 3, but decreases from 1 to 2
B. increases from 1 to 2, but decreases from 1 to 3
C. increases form 1 to 2 and 1 to 3
D. does not change along these paths
3. At the end of each trajectory ():
A. the speed of first proton is greater
B. the speed of second proton is greater
C. the protons have same speed
D. cannot be determined speed by given information
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

- V(V) 10 II III I 5 0. 4 6 . 8 x(cm) -5- -104 I II III 4 x(cm) A B В С D In the figure above, the top panel of graph shows the potential V as a function of position x in three regions I, II, and III. Accordingly, four parallel plates, A through D, can be setup to realized the distribution of potential, as schematically drawn in the bottom panel of the figure. The unit of the distance is cm, and the unit of potential is V. What direction does the electric field point in region I? Right O No field O Left 2.arrow_forwardThe figure shows the equipotential lines of a charge distribution, each of which are 20 Volts apart. The inner equipotential line has the lowest voltage. W- B What direction does the electric field have at position D? South North West East Submit Answer Tries 0/2 About how much work is needed to move a charge of 7 mC from position C to position F?arrow_forwardFigure 3.0 cm -2.0 nC 1.0 nC + 3.0 cm < 3.0 cm -2.0 nC 1 of 1 Part A What is the electric potential at the point indicated with the dot in the figure? (Figure 1) Express your answer with the appropriate units. μA Value Units ?arrow_forward
- As shown, two protons are launched with the same speed from point 1 inside a parallel-plate capacitor. One proton moves along the path from 1 to 2, the other from 1 to 3. Points 2 and 3 are the same distance from the positive plate.a. Is ΔU1→2, the change in potential energy along the path 1 → 2, larger than, smaller than, or equal to ΔU1→3 ? Explain.b. Is the proton’s speed ν2 at point 2 larger than, smaller than, or equal to the proton’s speed ν3 at point 3? Explain.arrow_forwardPlease answer this within 30 mins ! I will upvote !arrow_forwardC1= 3 uf, C2=6 uf, C3=5uf, C4=4 uf A) Find the total energy (in mJ) stored in the system B) find the energy (in mJ) stored by each capacitorarrow_forward
- An electronic flash unit for a camera contains a capacitor with a capacitance of 780 μF. When the unit is fully charged and ready for operation, the potential difference between the capacitor plates is 310 V. A) What is the magnitude of the charge on each plate of the fully charged capacitor? Express your answer using two significant figures. B) Find the energy stored in the "charged-up" flash unit. Express your answer using two significant figures.arrow_forwardA moving particle encounters an external electric field that decreases its kinetic energy from 9450 eV to 6990 eV as the particle moves from position A to position B. The electric potential at A is -43.0 V, and that at B is +39.0 V. Determine the charge of the particle. Include the algebraic sign (+ or -) with your answer. Number i Units Lower potential Higher potential VB E SUBROLarrow_forwardI Review A 13.0 nC charge is at x = Ocm and a -1.4 nC charge is at = 3.0 cm Part A At what point or points on the a-axis is the electric potential zero? Express your answer in centimeters. If there is more than one answer, give each answer separated by a comma. Vα ΑΣφ ? x0 = cm Submit Request Answerarrow_forward
- The electric potential in a region of space is V = Part A E= Submit What is the strength of the electric field at (x, y) = (2.7 m, 2.8 m)? Express your answer using two significant figures. Part B 0= 2 of 15 || ΑΣΦ 4 → C Request Answer 15. ΑΣΦ Submit (300 V-m) √x² + y² 2 Request Answer What is the direction of the electric field at (x, y) = (2.7 m, 2.8 m)? Give the direction as an angle ccw from the positive x-axis. Express your answer in degrees using two significant figures. BALAD where and y are in meters. ? V/m ccw from the positive z-axisarrow_forwardThe figure by James Clerk Maxwell shows the electric field lines and equipotentials of a pair of positive charges. Charge A has four times the magnitude of charge B. Assume the electric potential is zero infinitely far from the charge configuration. At which point would a negative charge have the greatest electric potential energy? 6 8 If a positive charge has a velocity at point 8, moving to which point would result in the greatest kinetic energy loss? 2 A moving charged particle would experience no net change in kinetic energy when moving between which pairs of points? and 6 4 2 and 4 3 and 7 6 and 8 2 and 8 2 Lines of Force and Equipotential Surfaces. A- 20. P..Point of Equilibrium. AP=3 AB.arrow_forwardA proton with an initial speed of 850,000 m/s is brought to rest by an electric field. ▾ Part A Did the proton move into a region of higher potential or lower potential? O Because the proton is a positive charge and it slows down as it travels, it must be moving from a region of higher potential to a region of lower potential. O Because the proton is a negative charge and it accelerates as it travels, it must be moving from a region of higher potential to a region of lower potential. O Because the proton is a negative charge and it accelerates as it travels, it must be moving from a region of lower potential to a region of higher potential. Because the proton is a positive charge and it slows down as it travels, it must be moving from a region of lower potential to a region of higher potential. Submit ✓ Correct Here we learn how to determine the distribution of the electric potential based on the movement of a charged particle. Part B Previous Answers What was the potential difference…arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





