
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
In this problem, assume that the distribution of differences is approximately normal. Note: For degrees of freedom d.f. not in the Student's t table, use the closest d.f. that is smaller. In some situations, this choice of d.f. may increase the P-value by a small amount and therefore produce a slightly more "conservative" answer.
A survey of houses and traditional hogans was made in a number of different regions of the modern Navajo Indian Reservation. The following table is the result of a random sample of eight regions on the Navajo Reservation.
I need help with (c), sketching and (d) and (e)

Transcribed Image Text:In this problem, assume that the distribution of differences is approximately normal. Note: For degrees of freedom d.f. not in the Student'st table, use the closest d.f. that is smaller. In some situations, this choice of d.f. may increase the P-value by a small amount
and therefore produce a slightly more "conservative" answer.
A survey of houses and traditional hogans was made in a number of different regions of the modern Navajo Indian Reservation. The following table is the result of a random sample of eight regions on the Navajo Reservation.
Area on Navajo Reservation
Bitter Springs
Rainbow Lodge
Number of Inhabited Houses
Number of Inhabited Hogans
16
11
18
14
Kayenta
Red Mesa
68
46
32
Black Mesa
11
15
Canyon de Chelly
Cedar Point
Burnt Water
28
47
50
17
50
18
Does this information indicate that the population mean number of inhabited houses is greater than that of hogans on the Navajo Reservation? Use a 5% level of significance. (Let d = houses - hogans.)
(a) What is the level of significance?
State the null and alternate hypotheses. Will you use a left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed test?
O Ho: Hd > 0; H,: Hd = 0; right-tailed
O Ho: Hd = 0; H: Hg < 0; left-tailed
O Ho: Hd = 0; H: Hd > 0; right-tailed
O Ho: Hd = 0; H,: Hg + 0; two-tailed
(b) What sampling distribution will you use? What assumptions are you making?
O The Student's t. We assume that d has an approximately normal distribution.
O The standard normal. We assume that d has an approximately normal distribution.
O The Student's t. We assume that d has an approximately uniform distribution.
O The standard normal. We assume that d has an approximately uniform distribution.
What is the value of the sample test statistic? (Round your answer to three decimal places.)
(c) Find (or estimate) the P-value.
O p-value > 0.250
O 0.125 < Pp-value < 0.250
O 0.050 < P-value < 0.125
O 0.025 < P-value <0.050
O 0.005 < p-value < 0.025
O p-value < 0.005
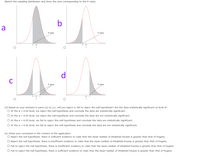
Transcribed Image Text:Sketch the sampling distribution and show the area corresponding to the P-value.
b
a
P-value
P-value
-t
-t
d
P-value
P-value
-t ot
(d) Based on your answers in parts (a) to (c), will you reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis? Are the data statistically significant at level a?
O At the a = 0.05 level, we reject the null hypothesis and conclude the data are statistically significant.
O At the a = 0.05 level, we reject the null hypothesis and conclude the data are not statistically significant.
O At the a = 0.05 level, we fail to reject the null hypothesis and conclude the data are statistically significant.
O At the a = 0.05 level, we fail to reject the null hypothesis and conclude the data are not statistically significant.
(e) State your conclusion in the context of the application.
O Reject the null hypothesis, there is sufficient evidence to claim that the mean number of inhabited houses is greater than that of hogans.
O Reject the null hypothesis, there is insufficient evidence to claim that the mean number of inhabited houses is greater than that of hogans.
O Fail to reject the null hypothesis, there is insufficient evidence to claim that the mean number of inhabited houses is greater than that of hogans.
O Fail to reject the null hypothesis, there is sufficient evidence to claim that the mean number of inhabited houses is greater than that of hogans.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In this problem, assume that the distribution of differences is approximately normal. Note: For degrees of freedom d.f. not in the Student's t table, use the closest d.f. that is smaller. In some situations, this choice of d.f. may increase the P-value by a small amount and therefore produce a slightly more "conservative" answer. Are America's top chief executive officers (CEOs) really worth all that money? One way to answer this question is to look at row B, the annual company percentage increase in revenue, versus row A, the CEO's annual percentage salary increase in that same company. Suppose a random sample of companies yielded the following data: B: Percent increasefor company 24 25 25 18 6 4 21 37 A: Percent increasefor CEO 21 25 22 14 −4 19 15 30 What is the value of the sample test statistic? (Round your answer to three decimal places.)=__ (c)Find (or estimate) the P-value. A-P-value > 0.500 B-0.250 < P-value < 0.500 C- 0.100 < P-value < 0.2500.050 <…arrow_forwardIn this problem, assume that the distribution of differences is approximately normal. Note: For degrees of freedom d.t. not in the Student's t table, use the dosest d.f. that is smaller. In some situations, this choice of d.f. may increase the P value by a small amount and therefore produce a ightly more "conservative" answer. A survey of houses and traditional hogans was made in a number of different regions of the modern Navajo Indian Reservation. The following table is the result of a random sample of eight regions on the Navajo Reservation. Area on Navajo Reservation Bitter Springs Rainbow Lodge Kayenta Red Mesa Number of Inhabited Houses Number of Inhabited Hogans 18 16 12 44 32 Black Mesa 11 15 Canyon de Chelly Cedar Point 28 47 17 Burnt Water A USE SALT Does this information indicate that the population mean number of inhabited houses is greater than that of hogans on the Navajo Reservation? use a 5% level of significante. (Let d= houses- hogans.) (a) What is the level of…arrow_forwardIn this problem, assume that the distribution of differences is approximately normal. Note: For degrees of freedom d.f. not in the Student's t table, use the closest d.f. that is smaller. In some situations, this choice of d.f. may increase the P-value by a small amount and therefore produce a slightly more "conservative" answer. Are America's top chief executive officers (CEOs) really worth all that money? One way to answer this question is to look at row B, the annual company percentage increase in revenue, versus row A, the CEO's annual percentage salary increase in that same company. Suppose a random sample of companies yielded the following data:arrow_forward
- In this problem, assume that the distribution of differences is approximately normal. Note: For degrees of freedom d.s. not in the Student's t table, use the closest d.f. that is smaller. In some situations, this choice of d.r. may increase the Pvalue by a small amount and therefore produce a slightly more "conservative" answer. Are America's top chief executive officers (CEOS) really worth all that money? One way to answer this question is to look at row B, the annual company percentage increase in revenue, versus row A, the CEO's annual percentage salary increase in that same company. Suppose a random sample of companies yielded the following data: B Percent increase 24 25 25 18 6 for company 21 37 4 A: Percent increase 23 for CEO 22 14 -4 19 15 30 A USE SALT Do these data indicate that the population mean percentage increase in corporate revenue (row B) is different from the population mean percentage increase in CEO salary? Use a 5% level of significance. (Let d - B - A.) (a) What…arrow_forwardIn this problem, assume that the distribution of differences is approximately normal. Note: For degrees of freedom d.f. not in the Student's t table, use the closest d.f. that is smaller. In some situations, this choice of d.f. may increase the P-value by a small amount and therefore produce a slightly more "conservative" answer.Is fishing better from a boat or from the shore? Pyramid Lake is located on the Paiute Indian Reservation in Nevada. Presidents, movie stars, and people who just want to catch fish go to Pyramid Lake for really large cutthroat trout. Let row Brepresent hours per fish caught fishing from the shore, and let row A represent hours per fish caught using a boat. The following data are paired by month from October through April. Oct Nov Dec Jan Feb March April B: Shore 1.7 1.8 2.0 3.2 3.9 3.6 3.3 A: Boat 1.6 1.4 1.7 2.2 3.3 3.0 3.8 a) What is the value of the sample test statistic? (Round your answer to three decimal places.)b) Find (or estimate) the…arrow_forwardIn this problem, assume that the distribution of differences is approximately normal. Note: For degrees of freedom d.f. not in the Student's t table, use the closest d.f. that is smaller. In some situations, this choice of d.f. may increase the P-value by a small amount and therefore produce a slightly more "conservative" answer.Is fishing better from a boat or from the shore? Pyramid Lake is located on the Paiute Indian Reservation in Nevada. Presidents, movie stars, and people who just want to catch fish go to Pyramid Lake for really large cutthroat trout. Let row B represent hours per fish caught fishing from the shore, and let row A represent hours per fish caught using a boat. The following data are paired by month from October through April. Oct Nov Dec Jan Feb March April B: Shore 1.5 1.8 2.1 3.2 3.9 3.6 3.3 A: Boat 1.4 1.5 1.7 2.2 3.3 3.0 3.8 Use a 1% level of significance to test if there is a difference in the population mean hours per fish caught using a boat…arrow_forward
- Which of the following is NOT true about statistical graphs? Choose the correct answer below. O A. They can be used to identify extreme data values. O B. Similar graphs can be constructed in order to compare data sets. O C. They utilize areas or volumes for data that are one-dimensional in nature. O D. They can be used to consider the overall shape of the distribution. ...arrow_forwardIn this problem, assume that the distribution of differences is approximately normal. Note: For degrees of freedom d.f. not in the Student's t table, use the closest d.f. that is smaller. In some situations, this choice of d.f. may increase the P-value by a small amount and therefore produce a slightly more "conservative" answer. Are America's top chief executive officers (CEOs) really worth all that money? One way to answer this question is to look at row B, the annual company percentage increase in revenue, versus row A, the CEO's annual percentage salary increase in that same company. Suppose a random sample of companies yielded the following data: B: Percent increasefor company 24 25 25 18 6 4 21 37 A: Percent increasefor CEO 21 25 22 14 −4 19 15 30 Do these data indicate that the population mean percentage increase in corporate revenue (row B) is different from the population mean percentage increase in CEO salary? Use a 5% level of significance. (Let d = B − A.)…arrow_forwardWhich of these choices below would be the best choice to address such errors of measurement? a. Broaden the range (i.e., spread) between the control limits. b. Reduce the range between the specification limits. c. Reduce the spread between the control limits. d. Broaden the range between the specification limits. Choices c, and d are true (i.e., reduce the spread between the control limits and broaden the range between the specification limits).arrow_forward
- In this problem, assume that the distribution of differences is approximately normal. Note: For degrees of freedom d.f. not in the Student's t table, use the closest d.f. that is smaller. In some situations, this choice of d.f. may increase the P-value by a small amount and therefore produce a slightly more "conservative" answer. Are America's top chief executive officers (CEOs) really worth all that money? One way to answer this question is to look at row B, the annual company percentage increase in revenue, versus row A, the CEO's annual percentage salary increase in that same company. Suppose a random sample of companies yielded the following data: B: Percent increasefor company 24 25 23 18 6 4 21 37 A: Percent increasefor CEO 21 23 22 14 −4 19 15 30 Do these data indicate that the population mean percentage increase in corporate revenue (row B) is different from the population mean percentage increase in CEO salary? Use a 5% level of significance. (Let d = B −…arrow_forwardIn this problem, assume that the distribution of differences is approximately normal. Note: For degrees of freedom d.f. not in the Student's t table, use the closest d.f. that is smaller. In some situations, this choice of d.f. may increase the P-value by a small amount and therefore produce a slightly more "conservative" answer.Is fishing better from a boat or from the shore? Pyramid Lake is located on the Paiute Indian Reservation in Nevada. Presidents, movie stars, and people who just want to catch fish go to Pyramid Lake for really large cutthroat trout. Let row B represent hours per fish caught fishing from the shore, and let row A represent hours per fish caught using a boat. The following data are paired by month from October through April. Oct Nov Dec Jan Feb March April B: Shore 1.6 1.8 1.9 3.2 3.9 3.6 3.3 A: Boat 1.6 1.4 1.7 2.2 3.3 3.0 3.8 Use a 1% level of significance to test if there is a difference in the population mean hours per fish caught using a boat…arrow_forwardIn this problem, assume that the distribution of differences is approximately normal. Note: For degrees of freedom d.f. not in the Student's t table, use the closest d.f. that is smaller. In some situations, this choice of d.f. may increase the P-value by a small amount and therefore produce a slightly more "conservative" answer.Are America's top chief executive officers (CEOs) really worth all that money? One way to answer this question is to look at row B, the annual company percentage increase in revenue, versus row A, the CEO's annual percentage salary increase in that same company. Suppose a random sample of companies yielded the following data: B: Percent increasefor company26 21 27 18 6 4 21 37 A: Percent increasefor CEO23 23 22 14 -4 19 15 30 What is the value of the sample test statistic? (Round your answer to three decimal places.)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman