
Concept explainers
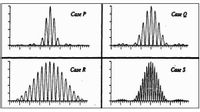
In the figure are shown graphs of the intensity pattern of light as a function of position on a screen produced by 4 sets of double slits labeled P, Q, R, and S. To produce the graphs, the laser beam and screen are held fixed while the slits are simply interchanged with one another. The graphs are plotted on the same scales for distance (horizontal axis) and intensity (vertical axis).
Rank the relative widths of the slits d and the separation of the slits a by selecting both the correct order and the correct ranking symbols (greater than or equal to). Note that if two or more of the scenarios are equal, you must list them from left to right in alphabetical order (P,Q,R,S) with the equal signs in-between. For example, P=R>S>Q would be correct but R=P>S>Q would not.
Ranking of slit widths:
Ranking of slit separations:
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

- A beam of unpolarized light of intensity Io is incident on a series of ideal polarizing filters as shown below. The polarization axis of the filters is indicated by the blue lines. If the polarization axis of the middle filter is 50° relative to the vertical, what is the intensity of the light at point C? lo 90° A Barrow_forwardThree polarizing plates whose planes are parallel are centered on a common axis. The directions of the transmission axes relative to the common vertical direction are shown in the figure below. A linearly polarized beam of light with plane of polarization parallel to the vertical reference direction is incident from the left onto the first disk with intensity Ii = 15.0 units (arbitrary). Calculate the transmitted intensity If when ?1 = 23.0°, ?2 = 43.0°, and ?3 = 61.0°. Hint: Make repeated use of Malus's law.arrow_forwardA beam of unpolarized light of intensity 6.45E3 W/m2 passes through a series of ideal polarizing filters with their polarizing directions turned to various angles as shown in the figure. What is the light intensity at point B (in W/m2)? Please use 3 sig figs and scientific notationarrow_forward
- Three polarizing filters are arranged in a sequence, as shown in the schematic diagram. Unpolarized light is incident on the first filter. The light that passes through the first filter is incident on the second, and the light that passes through the second filter is incident on the third. The direction of the polarization axis for each filter is indicated by lines drawn parallel to the axis. Indicate the polarization of the light that passes through each filter by dragging the appropriate image into each box. Polarizer 1 Polarizer 2 Polarizer 3 Answer Bank unpolarized light no lightarrow_forwardThree polarizing plates whose planes are parallel are centered on a common axis. The directions of the transmission axes relative to the common vertical direction are shown in the figure below. A linearly polarized beam of light with plane of polarization parallel to the vertical reference direction is incident from the left onto the first disk with intensity Ii = 14.5 units (arbitrary). Calculate the transmitted intensity If when ?1 = 18.0°, ?2 = 46.0°, and ?3 = 66.0°. Hint: Make repeated use of Malus's law. An arrow passes through three disks arranged in a row, with the faces of the disks perpendicular to the arrow. Before the arrow reaches the disks, it is labeled Ii. Each disk is labeled with an angle measured clockwise from the vertical. The first disk that the arrow passes through has angle ?1, the second disk has angle ?2, and the third disk has angle ?3. After the arrow exits the three disks, it is labeled If.arrow_forwardThe figure shows light of wavelength λ incident at angle φ on a reflection grating of spacing d. We want to find the angles θm at which constructive interference occurs. a. The figure shows paths 1 and 2 along which two waves travel and interfere. Find an expression for the path-length difference ∆r = r2 − r1. b. Show that the zeroth-order diffraction is simply a “reflection.” That is θo = φ. c. Light of wavelength 500 nm is incident at φ = 40o on a reflection grating having 700 reflection lines/mm. Find all angles θm at which light is diffracted. Negative values of θm are interpreted as an angle left of the vertical. d. Draw a picture showing a single 500 nm light ray incident at θm = 40o and showing all the diffracted waves at the correct angles.arrow_forward
- Three polarizing plates whose planes are parallel are centered on a common axis. The directions of the transmission axes relative to the common vertical direction are shown in the figure below. A linearly polarized beam of light with plane of polarization parallel to the vertical reference direction is incident from the left onto the first disk with intensity I; = 12.0 units (arbitrary). Calculate the transmitted intensity I, when 0₁ = 17.0°, 0₂ = 35.0°, and 03 = 55.0°. Hint: Make repeated use of Malus's law. If = units 0₁ 02 03arrow_forwardThree polarizing plates whose planes are parallel are centered on a common axis. The directions of the transmission axes relative to the common vertical direction are shown in the figure below. linearly polarized beam of light with plane of polarization parallel to the vertical reference direction is incident from the left onto the first disk with intensity I; = 13.0 units (arbitrary). Calculate the transmitted intensity If when 0₁ = 25.0°, 0₂ = 35.0°, and 03 = 59.0°. Hint: Make repeated use of Malus's law. If = 3.17 X Apply Malus' law to calculate the change in intensity at each polarizing plate, taking into account the direction of polarization of the light when it reaches each polarizer. units 0₁ I; 0₂ 0 ₂arrow_forwardA beam of light polarized along the y axis and moving along the +z axis passes through two polarized sheets with axes of polarization oriented 30◦ and 70◦ relatives to the y axis. The final intensity of the beam is measured to be 61 W/m2. What is the initial beam intensity? Express your answer to the nearest W/m2.arrow_forward
- A beam of unpolarized light of intensity 1.65E3 W/m² passes through a series of ideal polarizing filters with their polarizing directions turned to various angles as shown in the figure. What is the light intensity at point C (in W/m²)? % Unpolarized 60° 8 carrow_forwardConsider the geometry shown in the figure. The upper right quadrant is filled with a medium with a refractive index V3 and the rest of space is vacuum. A plane wave is n2 = incident on the xy plane from the left with an incident angle "1 = of 60 degrees. Its electric field is linearly polarized along the y direction. Find the power reflection and transmission coeffi- cients at the ryY plane and at the yz plane, respectively. What if the electric field is polarized in the xz plane? n2 = V3 y Oarrow_forwardProblem 2: Linearly polarized light is transmitted through two polarizers as shown in the figure. The light is polarized in the y direction. The axis of the first polarizer is at 8, -22° to the y direction. The axis of the second polarizer is at 8₂56 to the y direction. The intensity of the initial beam of polarized light is lo ly f Polarized Lightarrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





