
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
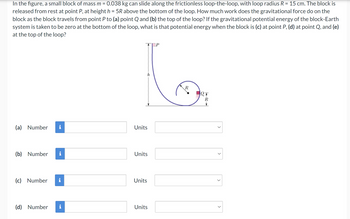
Transcribed Image Text:In the figure, a small block of mass m = 0.038 kg can slide along the frictionless loop-the-loop, with loop radius R = 15 cm. The block is
released from rest at point P, at height h = 5R above the bottom of the loop. How much work does the gravitational force do on the
block as the block travels from point P to (a) point Q and (b) the top of the loop? If the gravitational potential energy of the block-Earth
system is taken to be zero at the bottom of the loop, what is that potential energy when the block is (c) at point P, (d) at point Q, and (e)
at the top of the loop?
(a)
Number
Units
(b) Number
Units
(c) Number
Units
(d) Number i
Units
R
ет
>
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 8 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A 0.36-kg particle has a speed of 5.0 m/s at point A and kinetic energy of 8.0 J at point B. (a) What is its kinetic energy at A? (b) What is its speed at point B? m/s (c) What is the total work done on the particle as it moves from A to B?arrow_forwardA balky cow is leaving the barn as you try harder and harder to push her back in. In coordinates with the origin at the barn door, the cow walks from x = 0 to x = 6.9 m as you apply a force with x-component Fx=- [20.0 N + (3.0 N/m)x]. How much work does the force you apply do on the cow during this displacement?arrow_forwardA force of 12 Ib is required to hold a spring stretched 2 in. beyond its natural length. How much work W is done in stretching it from its natural length to 6 in. beyond its natural length?arrow_forward
- A rope pulls a 200 kg sleigh (which you may know) up a slope at incline angle θ = 30◦, through distance d = 20 m. The sleigh and its contents have a total mass of 200 kg. The snowy slope is so slippery that we take it to be frictionless. How much work is done by each force acting on the sleigh?arrow_forwardA 1100 kg roller coaster car starts at point A, then travels 155 ft at 40.0° below the horizontal to point B. (a)Taking point B to be the level where the gravitational potential energy of the car–Earth system is zero, what is the potential energy (in J) of the system when the car is at points A and B, and the change in potential energy (in J) as the coaster moves between these points? -at point A -at point B -change in potential energy J (b) Repeat part (a), setting the zero configuration with the car at point A. -at point A -at point B -change in potential energyarrow_forwardA typical muscle fiber is 2cm long and has a cross-section area of 3.1x10^-9m^2. When the muscle fiber is stimulated, it pulls with a force of 1.3mN. What is the work done by the muscle fiber as it contracts to a length of 1.4cm?arrow_forward
- A 0.41-kg particle has a speed of 3.0 m/s at point A and kinetic energy of 8.0 J at point B. (a) What is its kinetic energy at A? (b) What is its speed at point B? m/s (c) What is the total work done on the particle as it moves from A to B? Jarrow_forwardEarly one October, you go to a pumpkin patch to select your Halloween pumpkin. You lift the 3.0 kg pumpkin to a height of 1.3 m , then carry it 50.0 m (on level ground) to the check-out stand. Calculate the work you do on the pumpkin as you lift it from the ground. How much work do you do on the pumpkin as you carry it from the field?arrow_forwardA 2.0 kg bock of slippery cheese slides along a frictionless track from point a to point b. The cheese travels through a total distance of 20.0 m along the track and a net vertical distance of 8.4 m. Determine how much work is done on the cheese by gravitational force during the slide. Use g = 10 N/kg.arrow_forward
- Find approximate values for the work by dividing the area under the force curve into rectangles of width Δx=2m with height equal to the magnitude of the force in the center of the interval. With the interval being from x=0 to x=6m.arrow_forwardA constant force of 15 N in the negative y direction acts on a particle as it moves from the origin to the point (3i +3j -1k)m. How much work is done by the given force during this displacement?arrow_forwardA 25.0 kg child plays on a swing having support ropes that are 2.20 m long. Her brother pulls her back until the ropes are 42.0° from the vertical and releases her from rest. (a) What is her potential energy just as she is released, compared with the potential energy at the bottom of the swing’s motion? (b) How fast will she be moving at the bottom? (c) How much work does the tension in the ropes do as she swings from the initial position to the bottom of the motion?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON