
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
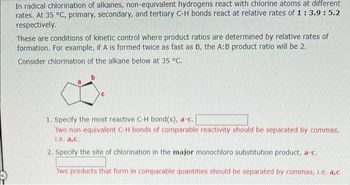
Transcribed Image Text:In radical chlorination of alkanes, non-equivalent hydrogens react with chlorine atoms at different
rates. At 35 °C, primary, secondary, and tertiary C-H bonds react at relative rates of 1 : 3.9: 5.2
respectively.
These are conditions of kinetic control where product ratios are determined by relative rates of
formation. For example, if A is formed twice as fast as B, the A:B product ratio will be 2.
Consider chlorination of the alkane below at 35 °C.
1. Specify the most reactive C-H bond(s), a-c.
Two non-equivalent C-H bonds of comparable reactivity should be separated by commas,
1.e. a,c.
2. Specify the site of chlorination in the major monochloro substitution product, a-c.
Two products that form in comparable quantities should be separated by commas, I.e. a,c
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Significance of GC analyses for hydrocarbons in the environmentarrow_forwardDraw structural formulas for the major organic product(s) of the reaction shown below. OCH 3 FeCl3 + Cl₂ • You do not have to consider stereochemistry. • If no reaction occurs, draw the organic starting material. • • Remember to include all of the formal charges on the atoms of any nitro groups. Draw one structure per sketcher. Add additional sketchers using the drop-down menu in the bottom right corner. • Separate multiple products using the + sign from the drop-down menu. ? ChemDoodleⓇarrow_forwardOrganic Reactions. You MUST write the complete reaction by chemical formulas eg. CH3-CH=CH2 + H2 O →................ 1./// 3,3-dimethyl pentene + H2 O → 2. /// 2-methy Propanol + IOI → 3. /// Cyclopentanone + IHI → 4. /// Ethy 2- bromo pentanoate + H2 O --------→ (Hydrolysis)arrow_forward
- 9,Which of the following is a combustion reaction? Group of answer choices A, H2SO4(aq) + Na2CO3(aq) =>Na2SO4(aq) + H2O(l)+ CO2(g) B, Ca(s) + 2HCl(aq) => CaCl2(aq) + H2(g) C, C2H4(g) + 3O2(g) => 2H2O(l)+ 2CO2(g) D, H2SO4(aq) + 2NaOH(aq) =>Na2SO4(aq) + 2H2O(l) E, Mg(s) +Cl2(aq) =>MgCl2(s) F, 2NaOH(aq) + MgCl2(aq)=> 2 NaCl(aq) + Mg(OH)2(s)arrow_forwardFf.142.arrow_forwardIdentify the missing organic reactants in the following reaction: H+ oom O OH H+ ya Note: This chemical equation only focuses on the important organic molecules in the reaction. Additional inorganic or small-molecule reactants or products (like H₂O) are not shown. In the drawing area below, draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic reactants X and Y. You may draw the structures in any arrangement that you like, so long as they aren't touching. Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forward
- List the requested biological classification or organic functional group(s) for the reactant, predict the reaction type, and predict the product(s) classification or functional group(s). Use the information to draw the major product(s)arrow_forwardCyclobutane decomposes rapidly at room temperature whereas cyclohexane is quite stable. Why is this the case? Please use rigorous organic chemistry terminology. arrow_forwardPredict products and draw structural formulas for the reactions below. All reactions must balance, but you do not have to show the structural formulas for the products of combustion reactions. cis-2-butene+ H2O --(H+)--->arrow_forward
- Chemistry the question numbers are in the top left corner of each picture. some questions have more than one picture. thanks!!!arrow_forwardShow all the structural formulas of the organic compounds, thank you!arrow_forwardFor the reaction shown below, 2.00 mL of a 2.00 M solution of bromine, 562 mg of alkene reactant, and excess acetic acid are used to obtain 322 mg of brominated product. What is the percent yield of brominated product? Bromine MW = 159.81 g/mol; Alkene reactant MW = 134.22 g/mol;Acetic acid MW = 60.05 g/mol; Brominated product MW = 328.04 g/molarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY