
Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edition)
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780133594140
Author: James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
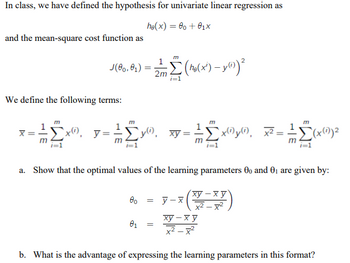
Transcribed Image Text:In class, we have defined the hypothesis for univariate linear regression as
he(x) = 00 + 0₁x
and the mean-square cost function as
2
J(00,01)
Σ (ho(x²) - y(i)) ²
2m
i=1
We define the following terms:
m
`x), y= 10.
;Σy"), xy = - ²
x(1) y(i) x²:
(x(1)) ²
m
a. Show that the optimal values of the learning parameters 00 and 0₁ are given by:
00 = y-x
xy−xy
x²-x²
01
=
ху-ху
x²-x²
b. What is the advantage of expressing the learning parameters in this format?
=
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Sum of Squared Errors: Remember from your statistics courses that if two random variables X and Y are related by a relation YaX+b and you had a set of observations {(1, 1), (2, 2)..... (z.)). then for every estimated values of a and b, the Sum of Squared Errors (SSE) was defined as in the following formula. SSE(-ar-b)². 1-1 The less SSE, the better a and b are estimated. Consider the following fixed list. In this list each sub-list of length two is standing for one pair (z.). Write a function that recieves two numbers a and b and returns the associated SSE. L- [[1, 2], [1.1, 2], [2, 7.1), (2.5, 7.21, (3, 11]]arrow_forward2. Use the rbinom() function to generate a random sample of size N = 50 from the bino- mial distribution Binomial(n, p), with n 6 and p = 0.3. Note that this distribution has mean u = np and standard deviation o = Vnp(1 – p). Record the obtained sample as a vector v. Repeat the tasks of Problem 1 for the sample v.arrow_forwardIn R, write a function that produces plots of statistical power versus sample size for simple linear regression. The function should be of the form LinRegPower(N,B,A,sd,nrep), where N is a vector/list of sample sizes, B is the true slope, A is the true intercept, sd is the true standard deviation of the residuals, and nrep is the number of simulation replicates. The function should conduct simulations and then produce a plot of statistical power versus the sample sizes in N for the hypothesis test of whether the slope is different than zero. B and A can be vectors/lists of equal length. In this case, the plot should have separate lines for each pair of A and B values (A[1] with B[1], A[2] with B[2], etc). The function should produce an informative error message if A and B are not the same length. It should also give an informative error message if N only has a single value. Demonstrate your function with some sample plots. Find some cases where power varies from close to zero to near…arrow_forward
- Please answer it asap. both questions.arrow_forwardLogistic regression aims to train the parameters from the training set D = {(x(i),y(i)), i 1,2,...,m, y ¤ {0,1}} so that the hypothesis function h(x) = g(0¹ x) 1 (here g(z) is the logistic or sigmod function g(z) can predict the probability of a 1+ e-z new instance x being labeled as 1. Please derive the following stochastic gradient ascent update rule for a logistic regression problem. 0j = 0j + a(y(¹) — hz(x)))x; ave. =arrow_forward2. An airline wants to evaluate the depth perception of its pilots over the age of fifty. A random sample of n = 14 airline pilots over the age of fifty are asked to judge the distance between two markers placed 20 feet apart at the opposite end of the laboratory. Assume we don't know the population standard deviation. The sample data listed here are the pilots' error (recorded in feet) in judging the distance. 2.9 2.6 2.9 2.6 2.4 2.0 2.3 2.2 2.5 2.3 2.8 2.5 2.7 2.6 Show a histogram of the data. Comment on any important features. How to create the histogram with python?arrow_forward
- 1(a). For an M/M/1 queuing system, write your own function in R to compute andoutput the:1. long-run probability po,p1,…,pn of there being 0,..,n people in the system.2. the values L, Lq, W, Wq, and Wse. The function should return elements with the names probs (vector of po,…,pn), L, Lq, W,Wq, and Wse (does not have to be in this order) The function should take as inputs, lambda (arrival rate), mu (service rate), and n (thenumber of people to compute probabilities for 0,…,n) Note: you are to code the computations for the above on your own, so none of the functionsin the queueing package are to be used. 1(b). Using your function from 1(a), find the values (b)-(f) in the Queuing Theory(M_M_1).arrow_forward8. Solve the following recurrence relations. (16 points) a. T(n) = 4T(n-1) + 1 for n > 1; T(1) = 1; b. T(n) = T(n/2) + 3; T(1) = 1; Here you can assume that n=2k for some integer k.arrow_forwardWe have that y*n+1=y*n=y*. Using the given model: yn+1 = byn(1-yn), we find that y* = 1-1/b and y* = 0 are fixed points. I have the function:def main(b,yInit,n): out=np.zeros((n,1)) y = yInit for i in range(n): out[i] = y y = b*(1-y)*y return out The graph model of this would depend both on the value of the initial population (y*) and choice of b. I need to graph this in python using interactive sliders widget [from matplotlib.widgets import slider], where one slider will control b value (x-axis) and another for y value (y-axis). I have the skeleton code for the sliders but have no idea how to graph this equation with it. (y* = between 0 to 1, b = 0 to 4)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780133594140Author:James Kurose, Keith RossPublisher:PEARSON
Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780133594140Author:James Kurose, Keith RossPublisher:PEARSON Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780124077263Author:David A. Patterson, John L. HennessyPublisher:Elsevier Science
Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780124077263Author:David A. Patterson, John L. HennessyPublisher:Elsevier Science Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)Computer EngineeringISBN:9781337569330Author:Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean AndrewsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)Computer EngineeringISBN:9781337569330Author:Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean AndrewsPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of Database ManagementComputer EngineeringISBN:9781337093422Author:Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. LastPublisher:Cengage Learning
Concepts of Database ManagementComputer EngineeringISBN:9781337093422Author:Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. LastPublisher:Cengage Learning Prelude to ProgrammingComputer EngineeringISBN:9780133750423Author:VENIT, StewartPublisher:Pearson Education
Prelude to ProgrammingComputer EngineeringISBN:9780133750423Author:VENIT, StewartPublisher:Pearson Education Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T...Computer EngineeringISBN:9781119368830Author:FITZGERALDPublisher:WILEY
Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T...Computer EngineeringISBN:9781119368830Author:FITZGERALDPublisher:WILEY

Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi...
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9780133594140
Author:James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher:PEARSON

Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi...
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9780124077263
Author:David A. Patterson, John L. Hennessy
Publisher:Elsevier Science

Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9781337569330
Author:Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean Andrews
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Concepts of Database Management
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9781337093422
Author:Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. Last
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Prelude to Programming
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9780133750423
Author:VENIT, Stewart
Publisher:Pearson Education

Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T...
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9781119368830
Author:FITZGERALD
Publisher:WILEY