
Database System Concepts
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780078022159
Author: Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
In breadth-first and depth-first search, an undiscovered node is marked discovered when it is first encountered, and marked processed when it has been completely searched. At any given moment, several nodes might be simultaneously in the discovered state.
(a) Describe a graph on n vertices and a particular starting vertex v such that Θ(n) nodes are simultaneously in the discovered state during a breadth-first search starting from v.
(b) Describe a graph on n vertices and a particular starting vertex v such that Θ(n) nodes are simultaneously in the discovered state during a depth-first search starting from v.
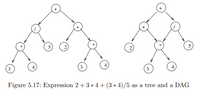
Transcribed Image Text:# Expression Tree and DAG Representation
The image illustrates two different representations of the mathematical expression \(2 + 3 \times 4 + (3 \times 4) / 5\): as a tree and as a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG).
## Tree Representation (Left Diagram)
- **Root Node (Top Level):** The root node is a plus sign (+), which indicates the main operation of addition.
- **Second Level:**
- The left child of the root node is a division sign (/), representing the operation \((3 \times 4) / 5\).
- The right child is another plus sign (+), representing the addition of \(2 + 3 \times 4\).
- **Third Level:**
- Under the division node (/), there are two children:
- The left child is a multiplication sign (*), representing \(3 \times 4\).
- The right child is the number 5.
- Under the second plus node (+):
- The left child is the number 2.
- The right child is a multiplication sign (*), denoting \(3 \times 4\).
- **Fourth Level:**
- Under each multiplication node (*), there are two numbers: 3 and 4. These represent the operands of the multiplication operation.
## DAG Representation (Right Diagram)
- **Root Node (Top Level):** The root node is a plus sign (+), representing the entire expression.
- **Second Level:**
- The left child of the root node is another plus sign (+), for \(2 + 3 \times 4\).
- The right child is a division sign (/), for \((3 \times 4) / 5\).
- **Third Level (Multiple Parents):**
- From the plus node on the left side:
- The left child is the number 2.
- The right child is a multiplication sign (*), which has two parent nodes (the plus node on the left and the division node on the right).
- From the division node on the right:
- The left child is the shared multiplication node (*).
- The right child is the number 5.
- **Fourth Level:**
- The shared multiplication node (*) has two children: the numbers 3 and 4, representing the operands for \(3 \times 4\).
By using a DAG,
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Take into consideration the limitations of a weighted graph representation by making use of an adjacency list representation.arrow_forwardGive an example of an application of a graph in computer science.Indicate whether the graph is directed or undirected. What significance, if any, does the presence of cycles have in this graph?Also indicate what significance, if any, there is to whether the graph is connected. Please provide reference at the end also and dont copy from other sitesarrow_forward3. Write an algorithm that uses an adjacency matrix, A[n][n], to determine if a graph is undirected (for every edge there is an edge in the reverse direction).arrow_forward
- What is the minimum number of 1’s in the adjacency matrix of a connected undirected graph of N vertices (without self–loops) ? How many 1’s are in the adjacency matrix of a complete graph of N vertices?arrow_forwardThe graph that has been traversed can be considered acyclic if and only if the Depth-first Search (DFS) algorithm does not identify any back edges?arrow_forwardRun a programme to calculate the average length of the paths identified and the empirical likelihood that BreadthFirstPaths will identify a path between two randomly picked vertices for various graph models.arrow_forward
- Please solve with the computer Question 2: Draw a simple undirected graph G that has 11 vertices, 7 edges.arrow_forwardWrite a function in a directed graph represented by adjacency lists that returns true (1) if an edge exists between two provided vertices u and v and false (0) otherwise.arrow_forward3. Kleinberg, Jon. Algorithm Design (p. 519, q. 28) Consider this version of the Independent Set Problem. You are given an undirected graph G and an integer k. We will call a set of nodes I "strongly independent" if, for any two nodes v, u € I, the edge (v, u) is not present in G, and neither is there a path of two edges from u to v. That is, there is no node w such that both (v, w) and (u, w) are present. The Strongly Independent Set problem is to decide whether G has a strongly independent set of size at least k. Show that the Strongly Independent Set Problem is NP-Complete.arrow_forward
- For the following undirected graph (unless otherwise indicated, always visit adjacent nodes in alphabetical order.), a. Give the adjacency matrix of the graph. b.Give the depth-first traversal of the graph. c.Give the breadth-first traversal of the graph.arrow_forwardplease send correct answer for part aarrow_forwardGiven N cities represented as vertices V₁, V2, un on an undirected graph (i.e., each edge can be traversed in both directions). The graph is fully-connected where the edge eij connecting any two vertices vį and vj is the straight-line distance between these two cities. We want to search for the shortest path from v₁ (the source) to VN (the destination). ... Assume that all edges have different values, and €₁,7 has the largest value among the edges. That is, the source and destination have the largest straight-line distance. Compare the lists of explored vertices when we run the uniform-cost search and the A* search for this problem. Hint: The straight-line distance is the shortest path between any two cities. If you do not know how to start, try to run the algorithms by hand on some small cases first; but remember to make sure your graphs satisfy the conditions in the question.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780134444321
Author:Tony Gaddis
Publisher:PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780132737968
Author:Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780133976892
Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337627900
Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education