
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
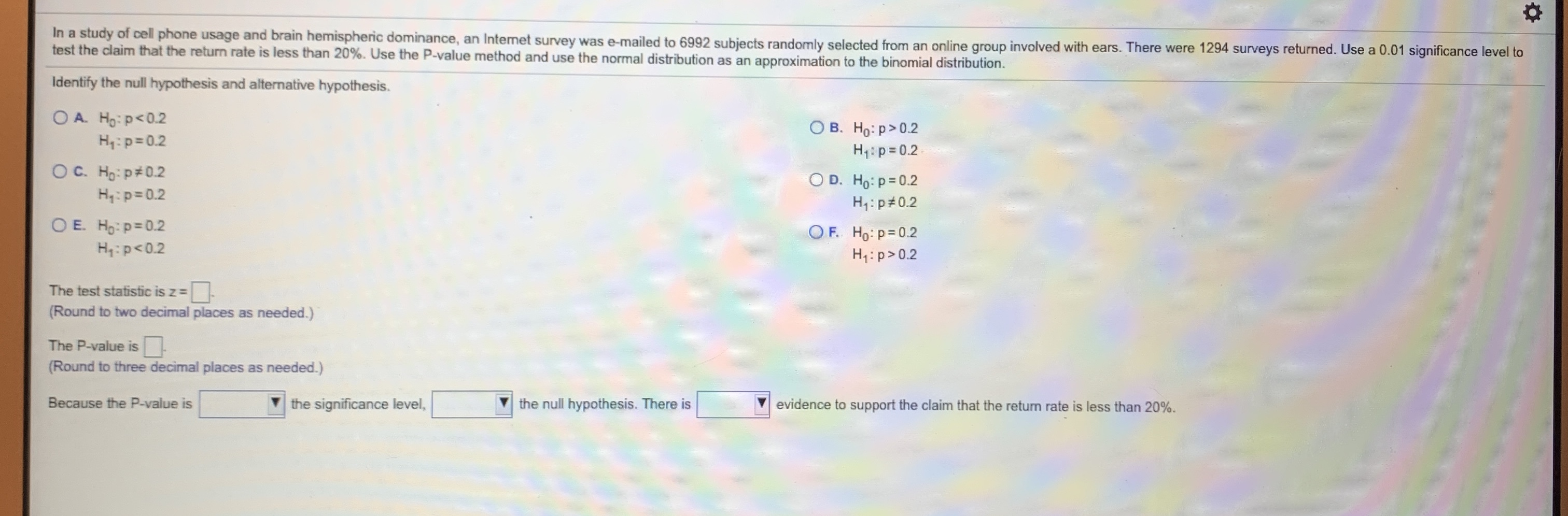
Transcribed Image Text:In a study of cell phone usage and brain hemispheric dominance, an Intemet survey was e-mailed to 6992 subjects randomly selected from an online group involved with ears. There were 1294 surveys returned. Use a 0.01 significance level to
test the claim that the return rate is less than 20%. Use the P-value method and use the normal distribution as an approximation to the binomial distribution.
Identify the null hypothesis and alternative hypothesis.
OA Ho p<0.2
Hy:p 0.2
O B. Ho: p>0.2
H1 p 0.2
O c. Ho p# 0.2
D. Ho: p 0.2
H p 0.2
H1 p 0.2
OE. Ho p 0.2
O F. Ho p 0.2
H1 p>0.2
Hy:p<0.2
The test statistic is z
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
The P-value is
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
the significance level,
Because the P-value is
the null hypothesis. There is
evidence to support the claim that the return rate is less than 20%
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A shoe company claims that running with their shoes improve people's speed. To evaluate that claim, we take a sample of 8 high-school level sprinters and have them run 100m with their own shoes, and then a week later, have them run again with the brand's shoes. Assume the time to run 100m follows a normal distribution, and run a test at a significance level 5% to determine if the new shoes make sprinters faster. Determine the hypothesis then run the test using either critical value OR p value approach. Do not forget to interpret your results. Below is the time they obtained with each pairs Runner Own shoes Brand Pair 1 12.25 10.25 10.75 9.50 3 14.00 14.50 4 11.00 10.00 13.00 11.75 6. 13.50 14.00 12.75 12.25 7 13.75 13.25 8.arrow_forwardA machine in a factory must be repaired if it produces more than 10% defectives in a day. A random sample of 100 produced items contains 15 defectives, and the supervisor says that the machine must be repaired. The P-value for the appropriate statistical test to evaluate the supervisor's decision is closest to:arrow_forwardThe Congressional Budget Office reports that 36% of federal civilian employees have a bachelor’s degree or higher (The Wall Street Journal). A random sample of 120 employees in the private sector showed that 33 have a bachelor’s degree or higher. Does this indicate that the percentage of employees holding bachelor’s degrees or higher in the private sector is less than in the federal civilian sector? Use alapha= .05 What is the null hypothesis? What is the alternative hypothesis? What distribution are you using? What test are you running? What is your conclusion?arrow_forward
- The president of a large free-standing laboratory claims that 80 percent of his 5,000 customers are satisfied with the service they receive. To test this claim, a MT research group surveyed 100 customers, using simple random sampling. Among the sampled customers, 73 percent say they are satisfied. Based on these findings, can we reject the president's hypothesis that 80% of the customers are very satisfied? Use a 0.05 level of significance.arrow_forwardConsider a sample of 50 football games, where 27 of them were won by the home team. Use a 0.05 significance level to test the claim that the probability that the home team wins is greater than one-half. What is the P-Value?arrow_forwardIn a study of cell phone usage and brain hemispheric dominance, an Internet survey was e-mailed to 6956subjects randomly selected from an online group involved with ears. There were 1290 surveys returned. Use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim that the return rate is less than 20%. Use the P-value method and use the normal distribution as an approximation to the binomial distribution. Identify the null hypothesis and alternative hypothesis. A. H0: p=0.2 H1: p≠0.2 B. H0: p=0.2 H1: p<0.2 C. H0: p>0.2 H1: p=0.2 D. H0: p≠0.2 H1: p=0.2 E. H0: p=0.2 H1: p>0.2 F. H0: p<0.2 H1: p=0.2 The test statistic is z= (Round to two decimal places as needed.) The P-value is (Round to three decimal places as needed.) Because the P-value is ▼ greater than less than the significance level, ▼ fail to reject reject the null hypothesis. There is ▼ insufficient…arrow_forward
- A certain drug is used to treat asthma. In a clinical trial of the drug, 18 of 282 treated subjects experienced headaches (based on data from the manufacturer). The accompanying calculator display shows results from a test of the claim that less than 11% of treated subjects experienced headaches. Use the normal distribution as an approximation to the binomial distribution and assume a 0.05 significance level. What is the final conclusion? A. There is sufficient evidence support the claim that less than 11% of treated subjects experienced headaches. B. There is not sufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that less than 11% of treated subjects experienced headaches. C. There is not sufficient evidence support the claim that less than 11% of treated subjects experienced headaches. D. There is sufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that less than 11% of treated subjects experienced headachesarrow_forwardA machine produces bolts with an average length of 16 inches. A manager selects a sample of 25 bolts. The average length in the sample was 15.95 inches with a variance of 0.4 inches.The acceptable variance for the length is 0.3 inches. (Note that 1 inch is equivalent to 2.54 cm). a. Construct a 95% confidence interval for the population variance. b. State the null and alternative hypotheses to test whether or not the population variance equals 0.3 inches. c. Compute the test statistic. d. The null hypothesis is to be tested at the 5% level of significance. State the decision rule for the test using the critical value approach. e. What do you conclude about the population variance?arrow_forwardIn a study of 809 randomly selected medical malpractice lawsuits, it was found that 509 of them were dropped or dismissed. Use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim that most medical malpractice lawsuits are dropped or dismissed. Identify the null and alternative hypotheses. The null hypothesis, Ho, is a statement that the value of a population parameter (such as proportion, p, mean, µ, or standard deviation, o) is equal to some claimed value. The alternative hypothesis, H,, is the statement that the parameter has a value that somehow differs from the null hypothesis and uses the inequalities , or #, corresponding to a left, right, or two-tailed test, respectively. 5arrow_forward
- Identify the statistic for this hypotheis test. Identify the p-value for this hypothesis test. Identify the conclusion for this hypothesis test.arrow_forwardIn a random sample of males, it was found that 25 write with their left hands and 217 do not. In a random sample of females, it was found that 58 write with their left hands and 450 do not. Use a .05 significance level to test the claim that the rate of left-handedness among males is less than that among females. Identify the test statistic.z=?arrow_forwardIn a study of cell phone usage and brain hemispheric dominance, an Internet survey was e-mailed to 6990 subjects randomly selected from an online group involved with ears. There were 1347 surveys returned. Use a 0 01 significance level to test the claim that the return rate is less than 20%. Use the P-value method and use the normal diştribution as an approximation to the binomial distribution. Identify the null hypothesis and alternative hypothesis. O A. Ho p>02 H p=02 О В. Но р302 H p0.2 The test statistic is z= (Round to two decimal places as needed.) The P-value is (Round to three decimal places as needed.) the null hypothesis. There is evidence to support the claim that the return rate is less than 20%. Because the P-value is the significance level,arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman