
Concept explainers
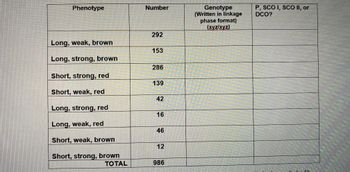
In a newly discovered species of Giant Pacific Octopus, long tentacles (L) are dominant to short tentacles (l), strong suction cups (S) are dominant to weak suction cups (s), and brown body color (B) is dominant to red body color (b). A trihybrid test cross was performed between male octopuses that were heterozygous for all three genes, and female octopuses that were homozygous recessive. (You may assume that the dominant alleles exhibit complete dominance.) The results of this cross are shown in the table attached
a) If the three genes are linked, draw a diagram that shows the correct orderof the three genes on the chromosome (with respect to which gene is in the middle) and also LABEL Region I and Region II on your diagram.
b) Calculate the map distances between each of the three genes. Please show the formula used for each calculation, and show ALL calculations. Define which region is your region I and which region is your region II. (For example, please state the region I is between genes x and y, and region II is between genes y and z.)
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

- In humans, free earlobes (E) are dominant to attached earlobes (e). An individual who is heterozygous for the earlobe trait mates with one who has attached earlobes. Write out the genotypes of both parents?arrow_forwardPink eye and albinism are two recessive traits found in the deer mouse, Peromyscus maniculatus. In mice with pink eye, the eye is devoid of color and appears pink from the blood vessels within it. Albino mice are completely lacking color both in their fur and in their eyes. F. H. Clark crossed pink‑eyed mice with albino mice; the resulting F1 had normal coloration in their fur and eyes. He then crossed these F1 mice with mice that were pink‑eyed and albino and obtained the mice shown in the table below. It is very hard to distinguish between mice that are albino and mice that are both pink‑eyed and albino, so he combined these two phenotypic classes (F. H. Clark, 1936, Journal of Heredity 27:259−260). Match the expected numbers of progeny with each phenotype if the genes for pink‑eye and albinism assort independently. Phenotype Observed Expected wild type, wild type 12 wild type, pink eyes 62 albino, wild type, or pink eyes 78 Total 152 152 Answer…arrow_forwardIn shorthorn cattle, the polled (hornless) condition (H) is dominant over the horned condition (h), also the heterozygous condition of red coat (W) and white coat (w) is roan. If a homozygous polled red animal is bred to a white horned one, what will the F1 and F2 be like?arrow_forward
- You have been working with a species of giant moths. You've found that Dark color (D) is dominant to Light color (d). You capture a moth in the wild (Moth X) bearing the dominant phenotype but want to don't know its genotype. Using 1 cross, how would you determine its genotype? You have been working with a species of giant moths. You've found that Dark color (D) is dominant to Light color (d). You capture a moth in the wild (Moth X) bearing the dominant phenotype but want to don't know its genotype. What would you expect the offspring to look like if moth x is heterozygous?arrow_forwardIn a newly discovered species of Giant Pacific Octopus, long tentacles (L) are dominant to short tentacles (l), strong suction cups (S) are dominant to weak suction cups (s), and brown body color (B) is dominant to red body color (b). A trihybrid test cross was performed between male octopuses that were heterozygous for all three genes, and female octopuses that were homozygous recessive. (You may assume that the dominant alleles exhibit complete dominance.) The results of this cross are shown in the table attached Please complete the table and answer the following questions: a) Are these genes linked? Explain why you think these genes are linked or unlinked? b) What is the genotype of each of the two parents that produced the offspring shown in the data table? Please indicate the linkage phase as you write the genotype of each parent. (Please write the genotypes in the format: xyz/xyz.) Genotype of male parent octopus: Genotype of female parent octopus:arrow_forwardfăctőrs suc 19) The genotype of a black snake is unknown. Black is a dominant allele, so the snake could be either BB or Bb. You cross this snake with a white snake (bb). Which of the following results of that cross would support the unknown genotype of the black snake being a homozygote? A) All F1 offspring are white B) All F1 offspring are black C) Half of the F1 offspring are white, the other half are black D) Three-quarters of the F1 offspring are black, the other quarter are white В x bb thearrow_forward
- Scale color in a lizard species is inherited via a single gene with 6 different alleles. (a) How many different types of gametes would be possible in this system? (b) What is the maximum number of different types of scale color gametes that could be produced from one individual lizard?arrow_forwarda) Based upon the results of these crosses, is the dwarfism trait in Andean condors autosomal or sex-linked? Once again, please explain the logic behind your conclusionarrow_forwardIf a heterozygous brown mouse is crossed with a homozygous white mouse, which of the following correctly describes their offspring? CHOOSE ALL THAT APPLY. A)50% are brown B)50% are white C)100% are white D)100% are brown E)100% are light brownarrow_forward
- In Labrador retrievers, two genes determine fur color: the E gene and the B gene. Black fur (B) is dominant to brown fur (b). However, the presence of (ee) will overshadow and create a puppy with yellow fur. Create a Punnett square crossing 2 Labs that are heterozygous for both genes. What are the resulting phenotypes? Don’t forget to take epistasis into account!arrow_forwardPhenotypically wild-type female Drosophila, whose mothers had spineless bristles (ss) and fathers had ebony bodies (e), produced the following offspring when crossed to homozygous males with ebony bodies and spineless bristles: 43 ebony bodies and spineless bristles 49 wild type 336 ebony bodies, wild type bristles 328 spineless bristles and wild type body color What is the map distance between the ebony body and spineless bristles loci? Group of answer choices 12.2 43.9 24.4 87.8 6.1arrow_forwardTwo organisms, AABBCCDDEE and aabbccddee, are mated to produce an F1 that is self-fertilized. If the capital letters represent dominant, independently assorting alleles: (a) how many different genotypes will occur in the F2? 3^5=243(AaBbCcDdEe) (b) what proportion of the F2 genotypes will be recessive for all five loci? (c) would you change your answers (a and/or b) if the initial cross occurred between AAbbCCddee X aaBBccDDEE parents? (d) would you change your answers (a and/or b) if the initial cross occurred between AABBCCDDEE X aabbccddEE parents?arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





