
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
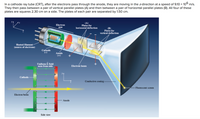
Transcribed Image Text:**Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) Explanation**
The illustration depicts the functioning of a Cathode Ray Tube (CRT), which is a fundamental component of older television sets and oscilloscopes. In this setup:
1. **Electron Gun**: Electrons are generated from a heated filament acting as the source. These electrons are then accelerated towards an anode.
2. **Motion of Electrons**: After passing through the anode, the electrons travel in the z-direction at a velocity of \(9.10 \times 10^6\) m/s.
3. **Deflection Mechanism**:
- **Vertical Deflection Plates (A)**: Electrons pass between a pair of vertical parallel plates. This arrangement allows for deflection in the horizontal direction.
- **Horizontal Deflection Plates (B)**: Electrons also traverse between horizontal parallel plates. This set enables deflection in the vertical direction.
4. **Dimensions of Plates**: Each of the four plates described is a square measuring 2.30 cm per side. The separation between plates of each pair is 1.50 cm.
5. **Diagram Details**:
- **Side View**: Shows the electron beam path from the cathode to the anode, affected by a uniform electric field (represented by arrows indicating direction).
- **Conductive Coating**: Covers the internal surface of the CRT to help focus and direct the electrons.
- **Fluorescent Screen**: At the end of the tube, where the electron beam strikes to create visible images or signals.
Overall, the CRT operates by manipulating the path of electron beams to create displays through controlled deflection and subsequent illumination of a fluorescent screen.

Transcribed Image Text:### Transcription for Educational Website
#### Diagram Explanation
The diagram shows an electron beam moving horizontally across a setup consisting of two sets of plates. In the side view of the setup:
- **Electron beam**: Represented by a yellow arrow moving from left to right, indicating the trajectory of the electrons.
- **Plates (A)**: The region where the electric field is zero, shown in green.
- **Plates (B)**: An area with a uniform electric field, depicted in red. The electric field deflects the electron beam downward as indicated by the green arrows pointing downwards.
- **Anode**: Labels the positive side at the end of the plates.
- **Fluorescent screen**: Positioned at the far right, where the deflected electron beam lands.
#### Educational Content
The electric field between plates (A) is zero. As the beam exits the space between plates (B), it has been deflected 1.90 mm downward (\(\Delta y = -1.90 \text{ mm}\)).
**Question**: What is the magnitude of the electric field between plates (B)?
**Given**:
- Deflection \(\Delta y = -1.90 \text{ mm}\)
- Mass of electron = \(9.109 \times 10^{-31} \text{ kg}\)
Calculate the electric field magnitude in \(\boxed{\phantom{N/C}} \text{N/C}\).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- If electrons have kinetic energy of 2000 eV, find (a) their speed, (b) the time needed to traverse a distance of 5 cm between plates that our horizontal, and (c) the vertical component of their velocity after passing between the plates if the electric field is 3.33 x 10^3 V/m.arrow_forwardchoose the letter of the correct answer.arrow_forwardOne form of nuclear radiation, beta decay, occurs when a neutron changes into a proton, an electron and a neutral particle called a neutrino. When this change happens to a neutron within the nucleus of an atom, the proton remains behind in the nucleus while the electron and neutrino are ejected from the nucleus. The ejected electron is called a beta particle. One nucleus that exhibits beta decay is the isotope of hydrogen 3H, called tritium, whose nucleus consists of one proton (making it hydrogen) and two neutrons (giving tritium an atomic mass m = 3u). Tritium is radioactive, and it decays to helium. Suppose an electron is ejected from a 3H atom, which has a radius of 1.000×10-14 m. The resulting 3He atom has the same radius as the 3H atom. What is the escape velocity of the electron ejected from the process? Note: Your answer may be larger than the speed of light which is okay in this scenario. To solve this problem correctly we would need to use special relativity.arrow_forward
- A hydrogen atom contains a single electron that moves in a circular orbit about a single proton. Assume the proton is stationary, and the electron has a speed of 7.6 105 m/s. Find the radius between the stationary proton and the electron orbit within the hydrogen atom.arrow_forwardAn evacuated tube uses an accelerating voltage of 55 kV to accelerate electrons to hit a copper plate and produce X-rays. Non-relativistically, what would be the maximum speed (in m/s) of these electrons?arrow_forwardUsing Kirchhoff's rules (and given E, = 71.0 V, E2 = 60.3 v, E3 = 79.5 V) calculate the following. 4.00 kf2 E, Ez R2E3.00 k2 2.00 k2 Figure P18.23arrow_forward
- A uniform, 2.00 × 106 -V/m electric field is used to accelerate an electron. (a) Calculate the energy the electron acquires once it has moved 40.0 cm across this field. (b) Find the distance it must move across the field to increase its energy by 50.0 GeV.arrow_forwardA proton's speed as it passes point A is 4.00×104 m/s. It follows the trajectory shown in the figure. What is the proton's speed at point B?arrow_forwardYour object has mass 34.4 kg, and you ve separated the boxes of protons and electrons by a distance of 77 m. If you were to release the clump of protons from their box, how much acceleration would the clump of protons undergo due to its attraction to the clump of electrons in the other box? 9.56E+23 m/s^2 1.20E+23 m/s^2 2.39E+23 m/s^2 4.78E+23 m/s^2arrow_forward
- this is tricky because x is attracting both Y and Zarrow_forwardIn the Bohr model of the hydrogen (H) atom, the electron moves on a circular path (orbit) around the nucleus,which consists of a single proton. In the ground state of H (the lowest energy level of H), the electron orbitsthe proton at a distance of 0.529 A (or 5.29 × 10^−11 m; 1 A˚ = 10^−10 m) with a linear speed of 2.19 × 10^6 m/s.(a) What is the angular speed of the electron?(b) How many orbits around the proton does the electron make each second?(c) What is the electron’s centripetal acceleration?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON